Abstract
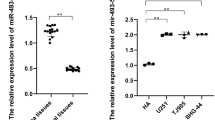
Glioma is the most common primary brain tumor and the most malignant type of glioma is glioblastoma with the character of high mortality, high recurrence rate and poor prognosis. MicroRNAs act as an important component in glioma development and thus may be a potential target for the treatment of glioma. There were some researches indicated that miR-210-3p played a role in glioma development, but if it can inhibit glioma growth, as well as the underlying mechanism, is still uncertain. In the present study, we investigated the effects of miR-210-3p and its potential target gene Iscu on glioma (C6) cells proliferation and migration in vitro as well as the influence of miR-210-3p on glioma growth in vivo. The results showed that miR-210-3p inhibited the proliferation and migration of C6 cells by regulating the expression of its target gene Iscu in vitro. We also demonstrated that glioma growth was suppressed in immunodeficient mice when they were implanted with C6 cells overexpressing miR-210-3p. Our data indicated that miR-210-3p played an important role in the prevention of glioma growth by targeting Iscu and so miR-210-3p/Iscu axis might be a potential target for the treatment of glioma.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ricard D, Idbaih A, Ducray F, Lahutte M, Hoang-Xuan K, Delattre JY (2012) Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 379:1984–1996
Zheng SQ, Qi Y, Wu J, Zhou FL, Yu H, Li L, Yu B, Chen XF, Zhang W (2019) CircPCMTD1 Acts as the sponge of miR-224-5p to promote glioma progression. Front Oncol 9:398
Jiang T, Mao Y, Ma W, Mao Q, You Y, Yang X, Jiang C, Kang C, Li X, Chen L, Qiu X, Wang W, Li W, Yao Y, Li S, Li S, Wu A, Sai K, Bai H, Li G, Chen B, Yao K, Wei X, Liu X, Zhang Z, Dai Y, Lv S, Wang L, Lin Z, Dong J, Xu G, Ma X, Cai J, Zhang W, Wang H, Chen L, Zhang C, Yang P, Yan W, Liu Z, Hu H, Chen J, Liu Y, Yang Y, Wang Z, Wang Z, Wang Y, You G, Han L, Bao Z, Liu Y, Wang Y, Fan X, Liu S, Liu X, Wang Y, Wang Q, Chinese Glioma Cooperative G (2016) CGCG clinical practice guidelines for the management of adult diffuse gliomas. Cancer Lett 375:263–273
Watkins S, Sontheimer H (2012) Unique biology of gliomas: challenges and opportunities. Trends Neurosci 35:546–556
Hanaei S, Afshari K, Hirbod-Mobarakeh A, Mohajer B, Amir Dastmalchi D, Rezaei N (2018) Therapeutic efficacy of specific immunotherapy for glioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Neurosci 29:443–461
Chen Y, Huang H, Yao C, Su F, Guan W, Yan S, Ni Z (2016) Antitumor activity of combined endostatin and thymidine kinase gene therapy in C6 glioma models. Cancer Med 5:2477–2486
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75:843–854
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR, Ruvkun G (2000) The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 403:901–906
Esteller M (2011) Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet 12:861–874
Iorio MV, Croce CM (2012) MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med 4:143–159
Liu CA, Chang CY, Hsueh KW, Su HL, Chiou TW, Lin SZ, Harn HJ (2018) Migration/invasion of malignant gliomas and implications for therapeutic treatment. Int J Mol Sci 19:E1115
Tumilson CA, Lea RW, Alder JE, Shaw L (2014) Circulating microRNA biomarkers for glioma and predicting response to therapy. Mol Neurobiol 50:545–558
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ (2017) MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16:203–222
Gomez Zubieta DM, Hamood MA, Beydoun R, Pall AE, Kondapalli KC (2017) MicroRNA-135a regulates NHE9 to inhibit proliferation and migration of glioblastoma cells. Cell Commun Signal 15:55
Shu M, Zheng X, Wu S, Lu H, Leng T, Zhu W, Zhou Y, Ou Y, Lin X, Lin Y, Xu D, Zhou Y, Yan G (2011) Targeting oncogenic miR-335 inhibits growth and invasion of malignant astrocytoma cells. Mol Cancer 10:59
Stojcheva N, Schechtmann G, Sass S, Roth P, Florea AM, Stefanski A, Stuhler K, Wolter M, Muller NS, Theis FJ, Weller M, Reifenberger G, Happold C (2016) MicroRNA-138 promotes acquired alkylator resistance in glioblastoma by targeting the Bcl-2-interacting mediator BIM. Oncotarget 7:12937–12950
Camps C, Buffa FM, Colella S, Moore J, Sotiriou C, Sheldon H, Harris AL, Gleadle JM, Ragoussis J (2008) hsa-miR-210 Is induced by hypoxia and is an independent prognostic factor in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:1340–1348
Ho AS, Huang X, Cao H, Christman-Skieller C, Bennewith K, Le QT, Koong AC (2010) Circulating miR-210 as a novel hypoxia marker in pancreatic cancer. Transl Oncol 3:109–113
Malzkorn B, Wolter M, Liesenberg F, Grzendowski M, Stuhler K, Meyer HE, Reifenberger G (2010) Identification and functional characterization of microRNAs involved in the malignant progression of gliomas. Brain Pathol 20:539–550
Huang X, Ding L, Bennewith KL, Tong RT, Welford SM, Ang KK, Story M, Le QT, Giaccia AJ (2009) Hypoxia-inducible mir-210 regulates normoxic gene expression involved in tumor initiation. Mol Cell 35:856–867
Zong WX, Rabinowitz JD, White E (2016) Mitochondria and Cancer. Mol Cell 61:667–676
Rouault TA, Tong WH (2008) Iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis and human disease. Trends Genet 24:398–407
McCormick RI, Blick C, Ragoussis J, Schoedel J, Mole DR, Young AC, Selby PJ, Banks RE, Harris AL (2013) miR-210 is a target of hypoxia-inducible factors 1 and 2 in renal cancer, regulates ISCU and correlates with good prognosis. Br J Cancer 108:1133–1142
Bush NA, Chang SM, Berger MS (2017) Current and future strategies for treatment of glioma. Neurosurg Rev 40:1–14
Ahir BK, Ozer H, Engelhard HH, Lakka SS (2017) MicroRNAs in glioblastoma pathogenesis and therapy: a comprehensive review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 120:22–33
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M, Rajewsky N (2005) Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 37:495–500
Shenouda SK, Alahari SK (2009) MicroRNA function in cancer: oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer Metastasis Rev 28:369–378
Lee D, Sun S, Zhang XQ, Zhang PD, Ho AS, Kiang KM, Fung CF, Lui WM, Leung GK (2015) MicroRNA-210 and endoplasmic reticulum chaperones in the regulation of chemoresistance in glioblastoma. J Cancer 6:227–232
Chen Z, Li Y, Zhang H, Huang P, Luthra R (2010) Hypoxia-regulated microRNA-210 modulates mitochondrial function and decreases ISCU and COX10 expression. Oncogene 29:4362–4368
Liu S, Jiang T, Zhong Y, Yu Y (2019) miR-210 inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting the brain-derived neurotrophic factor in glioblastoma. J Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28414
Zhang S, Lai N, Liao K, Sun J, Lin Y (2015) MicroRNA-210 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting regulator of differentiation 1 in glioblastoma cells. Folia Neuropathol 53:236–244
Shang C, Hong Y, Guo Y, Liu YH, Xue YX (2014) MiR-210 up-regulation inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in glioma cells by targeting SIN3A. Med Sci Monit 20:2571–2577
Lavon I, Zrihan D, Granit A, Einstein O, Fainstein N, Cohen MA, Cohen MA, Zelikovitch B, Shoshan Y, Spektor S, Reubinoff BE, Felig Y, Gerlitz O, Ben-Hur T, Smith Y, Siegal T (2010) Gliomas display a microRNA expression profile reminiscent of neural precursor cells. Neuro-oncology 12:422–433
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province and Nantong University for the research grants. We also acknowledge the editor and reviewers for their helpful comments on this paper.
Funding
This study was supported by the following grants: Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20170447), Undergraduate Innovation Training Program of Nantong University (2019141).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
We have no conflicts of interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Liu, J., Li, W. et al. MiR-210-3p Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of C6 Cells by Targeting Iscu. Neurochem Res 45, 1813–1824 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03043-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03043-w