Abstract
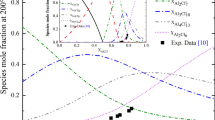
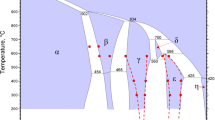
Thermodynamic modeling of the Pb-S and Cu-Pb-S systems is presented. All available experimental data in these systems are collected, assessed and used to optimize the model parameters. For the liquid phase, a solution (CuI, PbII, SII) is developed using the modified quasichemical model in pair approximation. Liquid copper, liquid lead metal, as well as matte phases are described using single solution with miscibility gaps. Earlier thermodynamic assessments available in the literature did not include all the data on the solubility of Cu and S in liquid Pb at low temperatures, < 750 °C (1023 K), which is important for lead fire refining. In the present study, these additional data points are used in the optimization. For the composition of lead in equilibrium with matte at temperatures > 900 °C (1123 K), a significant discrepancy among different sets of literature data and existing thermodynamic assessments is revealed. Preliminary experiments are performed with the goal to understand the nature of the problem and to develop the methodology based on high-temperature equilibration, rapid quenching and electron probe x-ray microanalysis. The results of this study help to select accurate literature results in the optimization of model parameters. The resulting database is applicable to calculate slag/matte/metal distribution of lead in copper smelting and converting, as well as for predictions in the lead smelting and fire refining.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Dessureault, Thermodynamic Modeling of Lead Smelting in the Blast Furnace, Université de Montréal, Montreal, 1994
S.A. Decterov and A.D. Pelton, Thermodynamic Modeling of Lead Distribution among Matte, Slag and Liquid Copper, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999, 30B(6), p 1033-1044
H. Johto and P. Taskinen, Phase Stabilities and Thermodynamic Assessment of the System Cu-Pb-S, Miner. Eng., 2013, 42, p 68-75
R.F. Blanks and G.M. Willis, Equilibria Between Lead, Lead Sulfide and Cuprous Sufide and the Decopperizing of Lead with Sulfur, Phys. Chem. Process Metall., 1961, 8, p 991-1028
T.R.A. Davey, Phase Systems Concerned with the Copper Drossing of Lead, Bull. Inst. Min. Metall., 1963, 678, p 553-620
R.J. Moffatt, G.M. Willis, Copper-Lead-Sulfur System at High Temperatures and Its Application to Continuous Copper Drossing, Aust. Inst. Min. Metall. Conference, June 1975, South Australia, p 167-185
R.J. Sinclair, The Extractive Metallurgy of Lead, AusIMM, Carlton, 2009
A.D. Pelton, S.A. Decterov, G. Eriksson, C. Robelin, and Y. Dessureault, The Modified Quasichemical Model. I—Binary Solutions, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, 31(4), p 651-659
A.D. Pelton and P. Chartrand, The Modified Quasichemical Model. II—Multicomponent Solutions, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, 32(6), p 1355-1360
T. Hidayat, D. Shishin, S. Decterov, and E. Jak, Critical Assessment and Thermodynamic Modeling of the Cu-Fe-O-Si System, CALPHAD, 2017, 58, p 101-114
E. Jak, P.C. Hayes, and H.-G. Lee, Improved methodologies for the determination of high temperature phase equilibria, Korean J. Miner. Mater. Inst. (Seoul), 1995, 1(1), p 1-8 (in English)
E. Jak, Integrated Experimental and Thermodynamic Modelling Research Methodology for Metallurgical Slags with Examples in the Copper Production field 9th International Conference on Molten Slags, Fluxes and Salts (MOLTEN12), 2012 of Conference (Beijing, China), The Chinese Society for Metals, 2012 Published
A. Fallah-Mehrjardi, T. Hidayat, P.C. Hayes, and E. Jak, Experimental Investigation of Gas/Slag/Matte/Tridymite Equilibria in the Cu-Fe-O-S-Si System in Controlled Gas Atmospheres: Development of Technique, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, 48(6), p 3002-3016
D. Shishin, T. Hidayat, U. Sultana, M. Shevchenko, and E. Jak, Experimental Measurement and Thermodynamic Model Predictions of the Distributions of Cu, As, Sb and Sn Between Liquid Lead and PbO-FeO-Fe2O3-SiO2, Submitted to Slag. Int. J. Mater. Res., 2020
D. Shishin, T. Hidayat, U. Sultana, M. Shevchenko, and E. Jak, Experimental Study and Thermodynamic Calculations of the Distribution of Ag, Au, Bi and Zn Between Pb Metal and Pb-Fe-O-Si Slag. J. Sustain. Metall., 2020, 6, p. 68-77
D. Shishin, J. Chen, T. Hidayat, and E. Jak, Thermodynamic Modelling of the Pb-As and Cu-Pb-As Systems Supported by Experimental Study, J. Phase Equilib. Differ., 2019, 40, p 758-767
C.W. Bale, E. Belisle, P. Chartrand, S.A. Decterov, G. Eriksson, A.E. Gheribi, K. Hack, I.H. Jung, Y.B. Kang, J. Melancon, A.D. Pelton, S. Petersen, C. Robelin, J. Sangster, P. Spencer, and M.A. Van Ende, FactSage Thermochemical Software and Databases, 2010–2016, CALPHAD, 2016, 54, p 35-53 (in English)
S. Petersen and K. Hack, The Thermochemistry Library ChemApp and Its Applications, Int. J. Mater. Res., 2007, 98(10), p 935-945 (in English)
P. Koukkari, K. Penttila, K. Hack, and S. Petersen, ChemSheet: An Efficient Worksheet Tool for Thermodynamic Process Simulation, EUROMAT 99 Biannu. Meet. Fed. Eur. Mater. Soc. (FEMS), 2000, 3, p 323-330 (in English)
S. Petersen, K. Hack, P. Monheim, and U. Pickartz, SimuSage: The Component Library for Rapid Process Modeling and Its Applications, Int. J. Mater. Res., 2007, 98(10), p 946-953 (in English)
T. Jantzen and P.J. Spencer, Thermodynamic Assessments of the Cu-Pb-Zn and Cu-Sn-Zn Systems, CALPHAD: Comput. Coupling Phase Diagr. Thermochem., 1998, 22(3), p 417-434 (in English)
D. Shishin and S.A. Decterov, Critical Assessment and Thermodynamic Modeling of Cu-O and Cu-O-S systeMs, CALPHAD, 2012, 38, p 59-70
P. Waldner, Thermodynamic modeling of the Cu-S system, Ecole Polytechnioque de Montreal, Montreal, QC, Canada, FTmisc in C. W. Bale, et al., FactSage Thermochemical Software and Databases: Recent Developments. CALPHAD, vol. 33, pp. 295–311 (2009)
P. Waldner, Gibbs Energy Modeling of the Cu-S Liquid Phase: Completion of the Thermodynamic Calculation of the Cu-S System, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, 51(2), p 805-817
A.D. Pelton, A General “Geometric” Thermodynamic Model for Multicomponent Solutions, CALPHAD, 2001, 25(2), p 319-328
F.H. Hayes, H.L. Lukas, G. Effenberg, and G. Petzow, A Thermodynamic Optimization of the Copper-Silver-Lead system, Z. Metallkd., 1986, 77(11), p 749-754 (in English)
J.C. Lin, R.C. Sharma, and Y.A. Chang, The Pb-S (Lead-Sulfur) System, Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr., 1986, 7(4), p 374-381
K. Friedrich and A. Leroux, Lead and Sulphur, Metallurgie, 1905, 2, p 536-539
E. Miller and K.L. Komarek, Retrograde Solubility in Semiconducting Intermetallic Compounds, Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME, 1966, 236(6), p 832-840
G. Kullerud, The Lead Sulfur System, Am. J. Sci., 1969, 267, p 233-256
R.H. Eric and M. Timucin, Phase Equilibria and Thermodynamics in the Lead-Lead Sulphide System, J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall., 1988, 88, p 353-361
K. Itagaki and A. Yazawa, Thermodynamic investigation of the liquid Pb-S system by using a drop calorimeter, Thermochim. Acta, 1985, 88(1), p 261-266 (in English)
J. Bloem and F.A. Kroger, The P-T-X Phase Diagram of the Lead-Sulfur System, Z. Phys. Chem., 1956, 7, p 1-14
A.V. Novoselova, V.P. Zlomanov, S.G. Karbanov, O.V. Matveyev, and A.M. Gas’kov, Physico-Chemical Study of the Germanium, Tin and Lead Chalcogenides, Progr. Solid State Chem., 1972, 7, p 85-91
L.S. Kovalenko, V.A. Snurnikova, and A.V. Vanyukov, Phase Equilibriums in the Lead-Sulfur System, Tsvetn. Met., 1976, 10, p 21-22
N. Fukatsu and Z. Kozuka, Phase Equilibria in the System Pb-SO, Metall. Rev. MMIJ, 1984, 1, p 27-46
T. Rytkonen, M. Pelto, and A. Taskinen, Thermodynamics of Pb-S Solutions, Scand. J. Metall., 1986, 15, p 73-76
R.M. Grant and B. Russell, Thermodynamic Study of Dilute Sulfur and Copper-Sulfur Solutions in Lead (Activity (of Sulfur, in Lead Solns., Copper Effect on)), Met. Trans., 1970, 1, p 75-83 (in English)
L.G. Twidwell, A.H. Larson, Influence of Additive Elements on the Activity Coefficient of Sulfur in Liquid Lead At 600 deg (Antimony Alloys; Bismuth Alloys; Copper Alloys; Gold Alloys; Silver Alloys; Tin Alloys (Lead-, Sulfur Activity Coeff. in); Activity (of Sulfur in Liquid Lead, Addn. Element Effect on); Lead Alloys (Sulfur Activity Coeff. in liquid)). Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME, 236(10), 1414–1420 (1966) (in English)
L.L. Cheng and C.B. Alcock, Thermodynamic Study of Dilute Solutions of Sulfur in Liquid Tin and Lead, Metall. Soc. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Petrol. Eng. Trans., 1961, 221, p 295-300
T.R. Cho and M.G. Jung, Ternary Misicibility Gap (Phase Diagram) of the Lead-Copper-Sulfur System at 1000 Degree C, Nonmunjip - Ch’ungnam Taehakkyo Kongop Koyuk Yon’guso, 1983, 6, p 52-55
S. Goto, O. Ogawa, and K. Kuriyama, Isothermal Sections of the Ternary Copper-Lead-Sulfur System in the Temperature Range 600–1200 °C, Nippon Kogyo Kaishi, 1983, 99, p 921-924
K. Azuma, S. Goto, and N. Takebe, Thermodynamic Studies of PbS in Copper Mattes, I, Nippon Kogyo Kaishi, 1970, 86, p 35-40
R.H. Eric and M. Timucin, Phase Relations and Thermodynamics in the Copper-Lead-Sulfur System, J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall., 1989, 89(5), p 141-146 (in English)
W. Guertler and G. Landau, Crystallization Diagrams of the System Copper-Lead-Sulfur, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 1934, 218, p 321-345
H. Eric and M. Timucin, Activities in Cu2S-FeS-PbS Melts at 1200 °C, Metall. Trans. B, 1981, 12B(3), p 493-500
V.N. Nesterov, R.A. Isakova, and A.S. Shendyapin, Activity of Lead in Sulfide Melts, Zh. Fiz. Khim., 1969, 43(12), p 3181-3183
J. Botor, R. Zebik, and J. Konieczny, Thermodynamic Properties of Molten Sulfides; Dicopper Sulfide-Lead Monosulfide, Thermochim. Acta, 1990, 164, p 65-77
N.I. Kopylov, M.Z. Toguzov, V.I. Yarygin, An investigation of the system PbS-Cu1.8S-ZnS. Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR, Metally., 1976, 6, p 80-83
G.C. Kaushal and M.L. Kapoor, Thermodynamics of Dilute Solutions of Sulfur in Binary Lead-Copper Alloy Solvents, Met. Forum, 1982, 5, p 130-136
S.N. Sinha, Distribution of Iron, Lead, Cobalt, Tin, Silver, and Gold Between Copper and Matte, University of Utah, Utah, 1984
T. Michimoto, T. Ohdan, N. Suzuki, K. Ichii, and T. Oishi, Solubilities of Copper and Sulfur in Molten Lead, Resour. Process., 2007, 54, p 139-144
D. Shishin, M. Shevchenko, V. Prostakova, P.C. Hayes, E. Jak, Thermodynamic Modelling of Molten Slag, Matte, Metal and Speiss Phases for the Pyrometallurgy of Lead (Pb) Processing Systems, 11th Molten Slags, Fluxes and Salts [MOLTEN 2020], 2020 of Conference (Seoul, Korea), 2020 Published
D. Shishin, S.A. Decterov, and E. Jak, Thermodynamic Assessment of Slag-Matte-Metal Equilibria in the Cu-Fe-O-S-Si System, J. Phase Equilib. Diff., 2018, 39(5), p 456-475
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Australian Research Council Linkage Program LP140100480, and industry partners, Atlantic Copper, Aurubis, BHP Billiton Olympic Dam Operation, Kazzinc Glencore, PASAR Glencore, Outotec Oy (Espoo), Anglo American Platinum, Umicore, Rio Tinto Kennecott, Peñoles and Boliden for the financial and technical support for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shishin, D., Chen, J. & Jak, E. Thermodynamic Modeling of the Pb-S and Cu-Pb-S Systems with Focus on Lead Refining Conditions. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 41, 218–233 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-020-00811-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-020-00811-7