Abstract
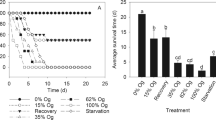
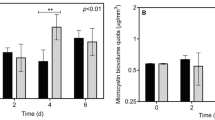
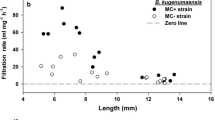
Many cyanobacterial species co-occur commonly in a freshwater ecosystem and can be consumed simultaneously by zooplankton. Both Microcystis aeruginosa and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii are the dominant species and coexist in eutrophic tropical waters, and they together are assumed to have exert a stronger effect on the life history traits of cladocerans than a single cyanobacterial species. In the present study, we tested the hypothesis with life-history experiments of Daphnia sienesis, a large cladoceran species in tropics. In the experiments, M. aeruginosa and C. raciborskii were used as a mixture of food with Chlorella pyrenoidosa for the experimental animals. D. sienesis showed excellent growth and survival on sole diets of C. pyrenoidosa (CP). By contrast, Daphnia’s growth decreased significantly and reproduction was completely inhibited when cyanobacteria comprised 100% of the food offered. The supplementation of C. pyrenoidosa into cyanobacterial diets significantly decreased their harmful effects on Daphnia, who improved the life history traits with the reduction of cyanobacterial percentage in mixed foods, irrespective of cyanobacterial species. Compared with the cultures of D. sienesis fed with a single cyanobacteria species, the animals in the treatments fed both M.aeruginosa-FACHB469 (F469) and C. raciborskii N8 (N8) had a lower growth rate in all the proportion of C. pyrenoidosa (25% CP, 50% CP or 75% CP). The strongest synergistic inhibition by the two cyanobacterial strains was found in the treatments with the 25% CP (i.e., 25% CP + 37.5% F469 + 37.5% N8), and no animal survived to maturity and reproduced. Thus, the simultaneous exposure to the two cyanobacterial species should be taken into account in assessing the ecological risks of cyanobacterial blooms, since multiple cyanobacterial coexistence can result in strong synergistic inhibition on growth and reproduction of zooplankton.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acs A, Kovács AW, Csepregi JZ, Törő N, Kiss G, Győri J, Vehovszky A, Kováts N, Farkas A (2013) The ecotoxicological evaluation of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii from Lake Balaton (Hungary) employing a battery of bioassays and chemical screening. Toxicon 70:98–106
Antunes JT, Leão PN, Vasconcelos VM (2015) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: review of the distribution, phylogeography, and ecophysiology of a global invasive species. Front Microbiol 6:473–485
Asselman J, Hochmuth JD, De Schamphelaere KAC (2014) A comparison of the sensitivities of Daphnia magna and Daphnia pulex to six different cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 39:1–7
Bednarska A, Joanna ŁOŚ, Dawidowicz P (2011) Temperature-dependent effect of filamentous cyanobacteria on Daphnia magna life history traits. J Limnol 70:353–358
Bednarska A, Pietrzak B, Pijanowska J (2014) Effect of poor manageability and low nutritional value of cyanobacteria on Daphnia magna life history performance. J Plankton Res 36:838–847
Bednarska A, Slusarczyk M (2013) Effect of non-toxic, filamentous cyanobacteria on egg abortion in Daphnia under various thermal conditions. Hydrobiologia 715:151–157
DeMott WR, Gulati RD, Van Donk E (2001) Daphnia food limitation in three hypereutrophic Dutch lakes: evidence for exclusion of large-bodied species by interfering filaments of cyanobacteria. Limnol Oceanogr 46:2054–2060
Demott WR, Muller-Navarra DC (1997) The importance of highly unsaturated fatty acids in zooplankton nutrition: evidence from experiments with Daphnia, a cyanobacterium and lipid emulsions. Freshw Biol 38:649–664
Demott WR, Zhang QX, Carmichael WW (1991) Effects of toxic cyanobacteria and purified toxins on the survival and feeding of a copepod and three species of Daphnia. Limnol Oceanogr 36:1346–1357
Freitas EC, Pinheiro C, Rocha O, Loureiro S (2014) Can mixtures of cyanotoxins represent a risk to the zooplankton? The case study of Daphnia magna Straus exposed to hepatotoxic and neurotoxic cyanobacterial extracts. Harmful Algae 31:143–152
Fulton RS, Paerl HW (1987) Effects of colonial morphology on zooplankton utilization of algal resources during blue-green-algal (Microcystis aeruginosa) blooms. Limnol Oceanogr 32:634–644
Ger KA, Hansson LA, Lürling M (2014) Understanding cyanobacteria-zooplankton interactions in a more eutrophic world. Freshw Biol 59:1783–1798
Ger KA, Urrutia-Cordero P, Frost PC, Hansson LA, Sarnelle O, Wilson AE, Lürling M (2016) The interaction between cyanobacteria and zooplankton in a more eutrophic world. Harmful Algae 54:128–144
Han BP, Lin X, Lei L, Gu J (2012) Survivals of D. galeata in sub-tropical reservoirs: harmful effects of toxic cyanobacteria in food source. Ecotoxicology 21:1692–1705
Hansson L-A, Gustafsson S, Rengefors K, Bomark L (2007) Cyanobacterial chemical warfare affects zooplankton community composition. Freshw Biol 52:1290–1301
Herrera NA, Echeverri LF, Ferrão-Filho AS (2015) Effects of phytoplankton extracts containing the toxin microcystin-LR on the survival and reproduction of cladocerans. Toxicon 95:38–45
Hochmuth JD, De Schamphelaere KAC (2014) The effect of temperature on the sensitivity of Daphnia magna to cyanobacteria is genus dependent. Environ Toxicol Chem 33:2333–2343
Jungmann D, Benndorf J (1994) Toxicity to Daphnia of a compound extracted from laboratory and natural Microcystis spp., and the role of microcystins. Freshw Biol 32:13–20
Lampert W (1987) Laboratory studies on zooplankton-cyanobacteria interactions. N Z J Mar Freshw Res 21:483–490
Leflaive J, Ten-Hage L (2007) Algal and cyanobacterial secondary metabolites in freshwaters: a comparison of allelopathic compounds and toxins. Freshw Biol 52:199–214
Lürling M (2003) Daphnia growth on microcystin-producing and microcystin-free Microcystis aeruginosa in different mixtures with the green alga Scenedesmus obliquus. Limnol Oceanogr 48:2214–2220
Miller TR, McMahon KD (2011) Genetic diversity of cyanobacteria in four eutrophic lakes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 78:336–348
Moustaka-Gouni M, Vardaka E, Tryfon E (2007) Phytoplankton species succession in a shallow Mediterranean lake (L. Kastoria, Greece): steady-state dominance of Limnothrix redekei, Microcystis aeruginosa and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Hydrobiologia 575:129–140
Nogueira IC, Saker ML, Pflugmacher S, Wiegand C, Vasconcelos VM (2004) Toxicity of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii to Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol 19:453–459
O’Neil JM, Davis TW, Burford MA, Gobler CJ (2012) The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: the potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 14:313–334
Panosso R, Lürling M (2010) Daphnia magna feeding on Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: the role of food composition, filament length and body size. J Plankton Res 32:1393–1404
Pianka ER (2000) Evolutionary ecology, 3rd edn. Harper & Row, New York, NY
Schmidt K, Jónasdóttir S (1997) Nutritional quality of two cyanobacteria: how rich is ‘poor’ food? Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 151:1–10
Semyalo R, Rohrlack T, Larsson P (2009) Growth and survival responses of a tropical Daphnia (Daphnia lumholtzi) to cell-bound microcystins. J Plankton Res 31:827–835
Smutná M, Babica P, Jarque S, Hilscherová KL, Maršálek B, Haeba M, Bláha L (2014) Acute, chronic and reproductive toxicity of complex cyanobacterial blooms in Daphnia magna and the role of microcystins. Toxicon 79:11–18
Soares MCS, Lürling M, Panosso R, Huszar VLM (2009a) Effects of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii on feeding and life-history characteristics of the grazer Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1183–1189
Soares MCS, de A, Rocha MI, Marinho MM, Azevedo SMFO, Branco CWC, Huszar VLM (2009b) Changes in species composition during annual cyanobacterial dominance in a tropical reservoir: physical factors, nutrients and grazing effects. Aquat Microb Ecol 57:137–149
Soares MCS, Lürling M, Huszar VLM (2010) Responses of the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus to two tropical toxic cyanobacteria (Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Microcystis aeruginosa) in pure and mixed diets with green algae. J Plankton Res 32:999–1008
Tillmanns AR, Wilson AE, Pick FR, Sarnelle O (2008) Meta-analysis of cyanobacterial effects on zooplankton population growth rate: species-specific responses. Fundam Appl Limnol 171:285–295
Weithoff G, Taube A, Bolius S (2017) The invasion success of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in experimental mesocosms: genetic identity, grazing loss, competition and biotic resistance. Aquat Invasions 12:333–341
Wilson AE, Sarnelle O, Tillmanns AR (2006) Effects of cyanobacterial toxicity and morphology on the population growth of freshwater zooplankton: Meta-analyses of laboratory experiments. Limnol Oceanogr 51:1915–1924
Urrutia-Cordero P, Ekvall MK, Hansson L-A (2015) Responses of cyanobacteria to herbivorous zooplankton across predator regimes: who mows the bloom? Freshw Biol 60:960–972
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 31770507), Water Resource Science and Technology Innovation Program of Guangdong Province (No. 2016-29), and Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province, China (No. 2015B020235007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, L., Huang, H., Peng, L. et al. Life-history responses of Daphnia sinensis simultaneously exposed to Microcystis aeruginosa and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Ecotoxicology 29, 771–779 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02220-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02220-5