Abstract
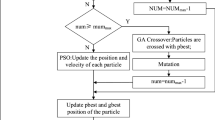
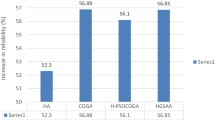
Redundancy allocation problem (RAP) is a non-linear programming problem which is very difficult to solve through existing heuristic and non-heuristic methods. In this research paper, three algorithms namely heuristic algorithm (HA), constraint optimization genetic algorithm (COGA) and hybrid genetic algorithm combined with particle swarm optimization (HGAPSO) are applied to solve RAP. Results obtained from individual use of genetic algorithm (GA) and particle swarm optimization (PSO) encompass some shortcomings. To overcome the shortcomings with their individual use, HGAPSO is introduced which combines fascinating properties of GA and PSO. Iterative process of GA is used by this hybrid approach after fixing initial best population from PSO. The results obtained from HA, COGA and HGAPSO with respect to increase in reliability are 50.76, 47.30 and 62.31 respectively and results with respect to CPU time obtained are 0.15, 0.209 and 3.07 respectively as shown in Table 3 of this paper. COGA and HGAPSO are programmed by Matlab.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arif SM, Hussain A, Shin DR (2016) A survey on particle swarm optimization for use in distributed generation placement and sizing. In: MATEC web conferences 70
Banks A, Vincent J, Anyakoha C (2008) A review of particle swarm optimization, part II: hybridisation, combinatorial, multicriteria and constrained optimization, and indicative applications. Nat Comput 7:109–124
Billionnet A (2008) Redundancy allocation for series-parallel systems using integer linear programming. IEEE Trans Reliab 57(3):507–516
Busacca PG, Marseguerra M, Zio E (2001) Multiobjective optimization by genetic algorithms: application to safety systems. Reliab Eng Saf Syst 72:59–74
Chang WD (2009) PID control for chaotic synchronization using particle swarm optimization chaos. Solitons Fractals 39(2):910–917
Coello CAC, Pulido GT, Lechuga MS (2004) Handling multiple objectives with particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Evolut Comput 8(3):256–279
David WC, Alice ES (1996) Solving the redundancy allocation problem using a combined neural network/genetic algorithm approach
Devi S, Garg D (2017) Redundancy-allocation in neel metal products limited. Indian J Sci Technol 10(30):1–5
Devi S, Sahu A, Garg D (2017) Redundancy optimization problem via comparative analysis of H-PSOCOGA. In: IEEE Xplore, pp 18–23
Gandelli Grimaccia F, Mussetta M, Pirinoli P, Zich RE (2006) Genetical swarm optimization: an evolutionary algorithm for antenna design. J Autom 47(3–4):105–112
Garg H (2014) Solving structural engineering design optimization problems using an artificial bee colony algorithm. J Ind Manag Optim 10(3):777–794
Garg D, Kumar K (2009) Reliability analysis of pharmaceutical plant using Matlab-tool. Int J Electron Eng Res 1(2):127–133
Garg D, Kumar K (2010) Meenu, availability optimization for screw plant based on genetic algorithm. Int J Eng Sci Technol 2(4):658–668
Garg H, Sharma SP (2013) Reliability-redundancy allocation problem of pharmaceutical plant. J Eng Sci Technol 8(2):190–198
Ghodrati A, Lotfi S (2012) A hybrid CS/GA algorithm for global optimization. In: Proceedings of the international conference on soft computing for problem solving, Roorkee, pp 397–404
Ghorabaeea MK, Amiria M, Azimib P (2015) Genetic algorithm for solving bi-objective redundancy allocation problem with k-out-of-n subsystems. Appl Math Model 39(20):6396–6409
Grimaccia Mussetta M, Pirinoli P, Zich RE (2007) Genetical swarm optimization: self-adaptive hybrid evolutionary algorithm for electromagnetic. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 55(3):781–785
Grimaldi EA, Grimacia F, Mussetta M, Pirinoli P, Zich RE (2004) A new hybrid genetical swarm algorithm for electromagnetic optimization. In: Proceedings of international conference on computational electromagnetics and its applications, Beijing, China, pp 157–160
Gupta R, Agarwal M (2006) Penalty guided genetic search for redundancy optimization in multi-state series-parallel power system. J Comb Optim 12:257–277
Habib M, Chehade H, Yalaoui F, Chebbo N, Jarkass I (2016) Availability optimization of a redundant dependent system using genetic algorithm. IFAC-Papers Online 49(12):733–738
Holland JH (1975a) Adoption in neural and artificial systems. The University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor
Holland JH (1975b) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. The University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor
Kanagaraj G, Ponnambalam SG, Jawahar N (2013) A hybrid cuckoo search and genetic algorithm for reliability-redundancy allocation problems. Comput Ind Eng 66:1115–1124
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1998) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on neural networks, Piscataway, NJ, USA
Kong X, Gao L, Ouyang H, Li S (2014) Solving the redundancy allocation problem with multiple strategy choices using a new simplified particle swarm optimization. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 144:147–158
Krink T, Lvbjerg M (2002) The lifecycle model: combining particle swarm optimization, genetic algorithms and hill climbers. In: Proceedings of the parallel problem solving from nature, pp 621–630
Ouyang Z, Liu Y, Ruan SJ, Jiang T (2019) An improved particle swarm optimization algorithm for reliability-redundancy allocation problem with mixed redundancy strategy and heterogeneous components. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 181:62–74
Puzzi S, Carpinteri A (2008) A double-multiplicative dynamic penalty approach for constrained evolutionary optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 35:431–445
Robinson J, Sinton S, Samii YR (2002) Particle swarm, genetic algorithm, and their hybrids: optimization of a profiled corrugated horn antenna. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international symposium in antennas and propagation society, pp 314–317
Saleem EAA, Dao TM, Liu ZH (2018) Multiple-objective optimization and design of series-parallel systems using novel hybrid genetic algorithm meta-heuristic approach. World J Eng Technol 6:532–555
Zhang JD, Jia DL, Li K (2008) FIR digital filters design based on chaotic mutation particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on audio, language and image processing, pp 418–422
Zhao JQ, Wang L, Zeng P, Fan WH (2012) An effective hybrid genetic algorithm with flexible allowance technique for constrained engineering design optimization. Expert Syst Appl 39:6041–6051
Zielinski K, Weitkemper P, Laur R (2009) Optimization of power allocation for interference cancellation with particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 13(1):128–150
Zou D, Wu L, Gao L, Wang X (2010) A modi¯ed particle swarm optimization algorithm for reliability problems. In: IEEE fifth int. conf.: bio-inspired computing: theories and applications (BIC-TA), pp 1098–1105
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devi, S., Garg, D. Hybrid genetic and particle swarm algorithm: redundancy allocation problem. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 11, 313–319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-019-00858-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-019-00858-x