Abstract
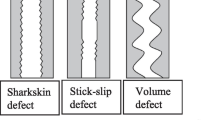
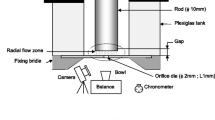
The present work aimed to investigate the influence of flow geometry on volume instability associated to a linear polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). To do so, a convergent radial flow was created at the die entrance. The performed particle image velocimetry (PIV) recordings under unstable flow regime, in capillary rheometer, characterized by the new entrance zone, show a new pattern of streamlines above the die and a disappearance of the vortex developed in the corner of the reservoir. Photographs of the extrudate strands obtained at the die exit depict a new morphology of defect which appears with a well-established radial flow. These results led to the correlation agreement between the gross melt fracture and the flow instability at the entrance zone. It also proved the importance of elongational and shear components linked to the upstream flow in the appearance and development of volume distortion.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allal A, Lavernhe A, Vergnes B, Marin G (2006) Relationships between molecular structure and sharkskin defect for linear polymers. J Non Newtonian Fluid Mech 134:127–135
Ansari M, Hatzikiriakos SG, Sukhadia AM, Rohlfing DC (2011) Rheology of Ziegler Natta and metallocene high-density polyethylenes: broad molecular weight distribution effects. Rheol Acta 50(1):17–27
Ayadi A, Elgasri S, Mezghani A, Castro M, Elhaouani F (2011) Effect of radial flow in the die entrance region on gross melt fracture of PDMS extrudate. J. Non Newtonian Fluid Mech. 166:661–666
Bagley EB, Schreiber HP (1961) Effect of die entry geometry on polymer melts fracture and extrudate distortion. Trans Soc Rheol 5:341–353
Ballenger TF, White JL (1971) The development of the velocity field in polymer melts in a reservoir approaching a capillary die. J Appl Polym Sci 15:1949–1962
Barnes HA (2003) A review of the rheology of filled viscoelastic systems. Rheol Rev 2003:1–36
Bergem N (1976) Visualization studies of polymer melt flow anomalies in extrusion. In: Proceedings of the VIIth International Congress on Rheology. Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, pp 50–54
Carrot C, Guillet J (2000) Viscoélasticité non linéaire des polymères fondus, Techniques de l’Ingénieur, traité Plastiques et Composites, AM 3630
Combeaud C (2004) Study of volume instabilies in extrusion of polypropylene and polystyrene, PHD, University of Mines
Den Otter JL (1970) Mechanisms of melt fracture. Plast Polym:155–168
Doerpinghaus PJ, Baird DG (2003) Comparison of the melt fracture behavior of metallocene and conventional polyethylenes. Rheol Acta 42(6):544–556
Done DS, Baird DG, Average AE (1983) The influence of porous media on the flow of polymer melts in capillaries. Chem Eng Commun 21:293–309
Elgasri S, Ayadi A, Elhaouani F (2011) Effect of die geometry on helical defect during extrusion of PDMS across a radial flow upstream the contraction. J Non Newtonian Fluid Mech 166:1415–1420
Elkissi N, Piau JM (1996) Stability phenomena during polymer melt extrusion. In: Piau JM, Agassant JF (eds) Rheology for polymer melts processing. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Elkissi N, Piau JM, Attane P, Turrel G (1993) Shear rheometry of polydimethysiloxanes. Master curves and testing of Gleissle and Yamamoto relations. Rheol Acta 32:293–310
Elkissi N, Piau JM, Toussaint F (1997) Sharkskin and cracking of polymer melt extrudates. J Non Newtonian Fluid Mech 68(2–3):271–290
Goutille Y, Guillet J (2002) Influence of filters in the die entrance region on gross melt fracture: extrudate and flow visualization. J Non Newtonian Fluid Mech 102:19–36
Goutille Y, Majesté JC, Tassin JF, Guillet J (2003) Molecular structure and gross melt fracture triggering. J Non Newtonian Fluid Mech 111:175–198
Ketata M, Ayadi A, Elkissi N, Bradai C (2017) Effect of rheological and physical properties on mitigation of melt fracture instability during extrusion of polymer melts through a radial flow die. Rheol Acta 56:341–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-017-0995-2
Koopmans R (2002) Engineering techniques, processed plastics and composites, AM3657
Legrand F, Piau JM (1998) Spatially resolved stress birefringence and flow visualization in the flow instabilities of a polydimethylsyloxane extruded through a slit die. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 77:123–150
Meh M (1997) Private communication
Miller E, Rothstein JP (2004) Control of sharkskin instability in the extrusion of polymer melts using induced temperature gradients. Rheol Acta 44(2):160–173
Miller E, Lee SJ, Rothstein JP (2006) The effect of temperature gradients on the sharkskin surface instability in polymer extrusion through a slit die. Rheol Acta 45(6):943–950
Muller R, Vergnes B (1996) Validity of the stress optical law and application of birefringence to polymer complex flows. In: Piau JM, Agassant JF (eds) Rheology for Polymer Processing. Elsevier 5:257–284
Oyanagi Y (1973) A study of irregular flow behavior of high density polyethylene. Appl Polymer Symp 20:123–136
Piau JM, ElKissi N, Tremblay B (1988) Low Reynolds number flow visualization of linear and branched silicones upstream of orifice dies. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 30:197–232
Piau JM, ElKissi N, Tremblay B (1990) Influence of upstream instabilities and wall slip on melt fracture and sharkskin phenomena during silicones extrusion through orifice dies. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 34:145–180
Piau JM, Nigen S, ElKissi N (2000) Effect of die entrance filtering on mitigation of upstream instability during extrusion of polymer melts. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 91:37–57
Rothstein JR, McKinley GH (2001) The axisymmetric contraction expansion: the role of extensional rheology on vortex growth dynamics and the enhanced pressure drop. J Non Newtonian Fluid Mech 98:33–63
Sentmanat M, Hatzikiriakos SG (2004) Mechanism of gross melt fracture elimination in the extrusion of polyethylenes in the presence of boron nitride. Rheol Acta 43:624–633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00379-004-0359-6
Tordella JP (1969) In: Eirich FR (ed) Unstable flow of molten polymers in rheology, vol V. Academic Press, New York
Wang SQ, Drda PA (1996) Superfluid-like stick-slip transition in capillary flow of linear polyethylene: 1. General features. Macromolecules 29:4115–4119
Wang S, Drda PA (1997) Stick-slip transition in capillary flow of linear polyethylene: 3. Surface conditions. Rheol Acta 36:128–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00366818
Wassner E, Schmidt M, Münstedt H (1999) Entry flow of a low-density polyethylene melt into a slit die: an experimental study by laser-Doppler velocimetry. J Rheol 43(6):1339–1353
Weill A (1980) About the origin of sharkskin. Rheol Acta 19(5):623–632
White JL (1973) Critique on flow patterns in polymer fluids at the entrance of a die and instabilities leading to extrudate distortion. Appl Polym Symp 20:155–174
Yang X, Wang SQ, Halasa A, Ishida H (1998) Fast flow behavior of highly entangled monodisperse polymers. 1. Interfacial stick-slip transition of polybutadiene melts. Rheol Acta 37:415–423
Zhu X, Yang W, Wang S (2013) Exploring shear yielding and strain localization at the die entry during extrusion of entangled melts. J Rheol 57(1):349–364. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.4769898
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ketata, M., Ayadi, A., Bradai, C. et al. Effect of a radial flow foregoing a capillary die on the behavior of extruded PDMS: velocity field–distorted strand correlation. Rheol Acta 59, 425–434 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-020-01207-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-020-01207-7