Abstract
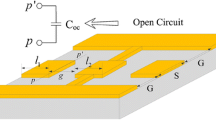
In this communication, we have designed, simulated, performance improved, fabricated and characterized a shunt capacitive RF MEMS switch with perforated serpentine membrane (Au). Fabrication is done using surface micromachining with four masks. AlN dielectric material of 50 nm thickness is offering high isolation of − 58.5 dB at 31.5 GHz, and incorporation of perforation to the membrane the switch insertion loss is very low i.e., − 0.4 dB. The perforated serpentine membrane with non-uniform meanders of 500 nm thickness using Au material is helped to reduce the actuation voltage, the fabricated switch is requiring 4.5 V actuation voltage. DC sputtering PVD is used to deposit metal (Au) and dielectric (AlN) thin Films. S1813 photoresist is used as a sacrificial layer and the membrane structure is released using piranha, IPA and critical point drying (Pressure 1260 Psi, Temperature 31 °C).

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal S, Kashyap R, Guha K, Baishya S (2016a) Modeling and analysis of capacitance in consideration of the deformation in RF MEMS shunt switch. Super Lattices Microstruct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2016.10.022
Agarwal S, Kashyap R, Guha K, Baishya S (2016b) Modeling and analysis of capacitance in consideration of the deformation in RF MEMS shunt switch. Super Lattices Microstruct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2016.10.022
Alastalo AT, Mattila T, Seppä H (2003) Analysis of a MEMS transmission line. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 51(8):1977–1981
Badía MF-B, Buitrago E, Ionescu AM (2012) RF MEMS shunt capacitive switches using AlN compared to Si3N4 dielectric. J Micro Electro Mech Syst 21(5):1229–1240
Chawla P, Khanna R (2014) Design, analysis and comparison of various MEMS switches for reconfigurable planar antenna. Acta Polytech Hung 11:21–40
Demirel K, Yazgan E, Demir S, Akın T (2016) A new temperature-tolerant RF MEMS switch structure design and fabrication for Ka-band. J Microelectromech Syst 25(1):60–68
Dragoman M, Aldrigo M, Adam G (2017) Phased antenna arrays based on non-volatile resistive switches. IET Microw Antennas Propag 11(8):1169–1173. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-map.2016.0974
Dussopt L, Rebeiz GM (2003) Intermodulation distortion and power handling in RF mems switches, varactors, and tunable filters. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 51(4):1247–1256
Fouladi S, Mansour RR (2010) Capacitive RF MEMS switches fabricated in standard 0.35-μm CMOS technology. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 58(2):478–486
Guha K, Kumar M, Parmar A, Baishya S (2016) Performance analysis of RF MEMS capacitive switch with non-uniform meandering technique. Microsyst Technol 22:2633–2640
Guha K, Laskar NM, Gogoi HJ, Borah AK, Baishnab KL, Baishya S (2017) Novel analytical model for optimizing the pull-in voltage in a flexured MEMS switch incorporating beam perforation effect. Solid State Electron 137:85–94
Hijazi YS, Vlasov YA, Larkins GL Jr (2003a) Design of a superconducting MEM shunt switch for RF applications. IEEE Trans Appl Supercond 13(2):696–699
Hijazi YS, Hanna D, Fairweather D, Vlasov YA, Larkins GL Jr (2003b) Fabrication of a superconducting mem shunt switch for RF applications. IEEE Trans Appl Supercond 13(2):700–703
Jensen BD, Saitou K, Volakis JL, Kurabayashi K (2003) Fully integrated electrothermal multidomain modeling of RF MEMS switches. IEEE Microw Wirel Compon Lett 13(9):364–366
Kolis P, Bajaj AK, Koslowski M (2017) Quantification of uncertainty in creep failure of RF-MEMS Switches. J Microelectromech Syst 26(1):1–12
Koutsoureli M, Michalas L, Papandreou E, Papaioannou G (2017) Dielectric charging asymmetry in SiN films used in RF MEMS capacitive switches. IEEE Trans Device Mater Reliab 17(1):1
Li M, Zhao J, You Z, Zhao G (2016a) Design and fabrication of a low insertion loss capacitive RF MEMS switch with novel micro-structures for actuation. Solid State Electron. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sse.2016.10.004
Li M, Zhao J, You Z, Zhao G (2016b) Design and fabrication of a low insertion loss capacitive RF MEMS switch with novel micro-structures for actuation. Solid State Electron. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sse.2016.10.004
Liu Y, Bey Y, Liu X (2016) Extension of the hot-switching reliability of RF-MEMS switches using a series contact protection technique. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 64(10):3151–3162
Liu Y, Bey Y, Liu X (2017) High-power high-isolation RF-MEMS switches with enhanced hot-switching reliability using a shunt protection technique. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 65(9):1–12
Mardivirin D, Pothier A, Crunteanu A, Vialle B, Blondy P (2009) Charging in dielectricless capacitive RF-MEMS switches. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 57(1):231–236
Mercado LL, Lee T-YT, Kuo S-M, Hause V, Amrine C (2003) Thermal solutions for discrete and wafer-level RF MEMS switch. IEEE Trans Adv Packag 26(3):318–326
Molaei S, Ganji BA (2016) Design and simulation of a novel RF MEMS shunt capacitive switch with low actuation voltage and high isolation. Microsyst Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-2923-2
Mulloni V, Margesin B, Farinelli P, Marcelli R, Lucibello A, De Angelis G (2015) Cycling reliability of RF-MEMS switches with Gold-Platinum multilayers as contact material. Microsyst Technol 23:3843–3850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2782-2
Nejad AG, Hasani JY (2016) Effects of contact roughness and trapped free space on characteristics of RF-MEMS capacitive shunt switches. Can J Electr Comput Eng 39(2):132–140
Ok SJ, Kim C, Baldwin DF (2003) High density, high aspect ratio through-wafer electrical interconnect vias for mems packaging. IEEE Trans Adv Packag 26(3):302–309
Pal J, Zhu Y, Lu J, Dao D, Khan F (2016) High power and reliable SPST/SP3T RF MEMS switches for wireless applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett 37(9):1
Park J, Shim ES, Choi W, Kim Y, Kwon Y, Cho D (2009) A non-contact-type RF MEMS switch for 24-GHz radar applications. J Micro Electro Mech Syst 18(1):163–173
Peroulis D, Pacheco SP, Sarabandi K, Katehi LPB (2003) Electromechanical considerations in developing low-voltage RF MEMS. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 51(1):259–270
Persano A, Cola A, De Angelis G, Taurino A, Siciliano P, Quaranta F (2011) Capacitive RF MEMS switches with tantalum-based materials. J Microelectromech Syst 20(2):365–370
Philippine MA, Zareie H, Sigmund O, Rebeiz GM, Kenny TW (2013) Experimental validation of topology optimization for RF MEMS capacitive switch design. J Microelectromech Syst 22(6):1296–1309
Puyal V, Dragomirescu D, Villeneuve C, Ruan J, Pons P, Plana R (2009) Frequency scalable model for MEMS capacitive shunt switches at millimeter-wave frequencies. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 57(11):2824–2833
Ramadoss R, Lee S, Lee YC, Bright VM, Gupta KC (2003) Fabrication, assembly, and testing of RF MEMS capacitive switches using flexible printed circuit technology. IEEE Trans Adv Packag 26(3):248–254
Rebeiz GM, Muldavin JB (2001) RF MEMS switches and switch circuits. IEEE Microw Mag 2:59–71
Rizk JB, Rebeiz GM (2003) W-Band CPW RF MEMS circuits on quartz substrates. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 51(7):1857–1862
Saias D, Robert P, Boret S, Billard C, Bouche G, Belot D, Ancey P (2003) An above IC MEMS RF Switch. IEEE J Solid State Circuits 38(12):2318–2324
Sharma P, Perruisseau-Carrier J, Moldovan C, Ionescu AM (2014) Electromagnetic performance of RF NEMS graphene capacitive switches. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2013.2290945
Sharma U, Kumar M, Sharma R, Saha T, Jain KK, Dutta S, Sharma EK (2017) Fabrication process induced changes in scattering parameters of meander type RFMEMS shunt switch. Microsyst Technol 12:5561–5570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3314-z
Shekhar S, Vinoy KJ, Suresh GKA (2017) Surface-micromachined capacitive RF switches with low actuation voltage and steady contact. J Micro Electro Mech Syst 26:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1109/jmems.2017.2688519
Stefanini R, Chatras M, Blondy P, Rebeiz GM (2011) Miniature MEMS switches for RF applications. J Microelectromech Syst 20(6):1324–1335
Wang J, Bielen J, Salm C, Krijnen G, Schmitz J (2016) On the small-signal capacitance of RF MEMS switches at very low frequencies. J Electron Devices Soc 4(6):1
Yang H-H, Han C-H, Choi S-J, Choi D-H, Yoon J-B (2015a) Signal power-insensitive analog MEMS tunable capacitor by immobilizing the movable plates. J Microelectromech Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/JMEMS.2015.2420121
Yang H-H, Han C-H, Choi S-J, Choi D-H, Yoon J-B (2015b) Signal power-insensitive analog MEMS tunable capacitor by immobilizing the movable plates. J Microelectromech Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/JMEMS.2015.2420121
Zhang S, Su W, Zaghloul M, Thibeault B (2008) Wideband CMOS compatible capacitive MEMS switch for RF applications. IEEE Microw Wirel Compon Lett 18(9):599–601
Zhang N, Mei L, Wang C, Deng Z, Yang J, Guo Q (2017) A switchable band pass filter employing RF MEMS switches and open-ring resonators. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 64(8):1–7
Zohur A, Mopidevi H, RodrigoM D, Unlu L, Jofre L, Cetiner BA (2013) RF MEMS reconfigurable two-band antenna. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett 12:72–75
Acknowledgements
This Research was performed using the facilities at CeNSE, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, Funded by Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thalluri, L.N., Guha, K., Srinivasa Rao, K. et al. Perforated serpentine membrane with AlN as dielectric material shunt capacitive RF MEMS switch fabrication and characterization. Microsyst Technol 26, 2029–2041 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-04755-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-04755-3