Abstract
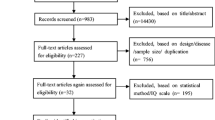
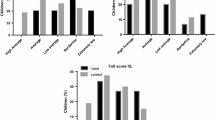
To explore the relationship between total intelligence quotient (IQ), verbal intelligence quotient (VIQ), performance intelligence quotient (PIQ), and fluoride exposure in children aged 8–12 years in coal-burning fluorosis area of Dafang County, Guizhou Province, China. The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children Revised in China (WISC-CR) was used to test the total IQ, VIQ, and PIQ in 99 children aged 8–12 years (55 in dental fluorosis group and 44 in control group). The differences in the intellectual levels between the two groups were compared, and the correlation between the intellectual level of children exposed to fluoride and the exposure dose of fluoride was analyzed. The VIQ, PIQ, and total IQ in the dental fluorosis group were 85.64 ± 16.53, 94.87 ± 12.73, and 88.51 ± 12.77, respectively, and these were lower than those in the control group (94.34 ± 16.04, 99.23 ± 12.44, and 96.64 ± 11.70, respectively). Significant difference was observed in VIQ and total IQ between the two groups (P = 0.002, P = 0.01), but not in the PIQ (P > 0.05). Each item of VIQ impairment (common sense, similar, arithmetic, vocabulary, and understanding) was significantly lower than those without VIQ impairment in the dental fluorosis group (P < 0.05). There was a significant difference in two items of building blocks and decoding between PIQ impairment and normal group (P < 0.05). Children with fluorosis in coal-burning areas had impaired IQ and obviously had impaired VIQ. Thus, the language learning ability should be strengthened in children exposed to fluorosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Strunecka A, Patocka J (1999) Pharmacological and toxicological effects of aluminofluoride complexes. Fluoride 32(4):230–242
Strunecka A, Strunecky O, Patocka J (2002) Fluoride plus aluminum: useful tools in laboratory investigations, but messengers of false information. Physiol Res 51(6):557–564
Anna Strunecka JP, Russell L. Blaylock, Niloufer J. Chinoy Fluoride interactions: from molecules to disease. Curr Signal Transduction Ther 2 (3):p.190–213
Sternweis PC, Gilman AG (1982) Aluminum: a requirement for activation of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by fluoride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 79(16):4888–4891
Chabre M (1990) Aluminofluoride and beryllofluoride complexes: a new phosphate analogs in enzymology. Trends Biochem Sci 15(1):6–10
Moimaz SA, Saliba O, Marques LB, Garbin CA, Saliba NA (2015) Dental fluorosis and its influence on children's life. Braz Oral Res 29:1–7
Pramanik S, Saha D (2017) The genetic influence in fluorosis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 56:157–162
Guo H, Kuang P, Luo Q, Cui H, Deng H, Liu H, Lu Y, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Li Y, Wang X, Zhao L (2017) Effects of sodium fluoride on blood cellular and humoral immunity in mice. Oncotarget 8(49):85504–85515
Jothiramajayam M, Sinha S, Ghosh M, Nag A, Jana A, Mukherjee A (2014) Sodium fluoride promotes apoptosis by generation of reactive oxygen species in human lymphocytes. J Toxicol Environ Health A 77(21):1269–1280
Narsimha A (2018) Elevated fluoride concentration levels in rural villages of Siddipet, Telangana State, South India. Data Brief 16:693–699
Waugh DT, Potter W, Limeback H, Godfrey M (2016) Risk assessment of fluoride intake from tea in the Republic of Ireland and its implications for public health and water fluoridation. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13(3)
Aggeborn L, Öhman M (2017) The effects of fluoride in the drinking water. Working Paper
Qin X, Wang S, Yu M, Zhang L, Li X, Zuo Z, Zhang X, Wang L (2009) Child skeletal fluorosis from indoor burning of coal in southwestern China. J Environ Public Health 2009:969764
Luo KL, Li L, Zhang SX (2011) Coal-burning roasted corn and chili as the cause of dental fluorosis for children in southwestern China. J Hazard Mater 185(2–3):1340–1347
Spittle B (2008) Fluoride poisoning: is fluoride in your drinking water-and from other sources-making you sick? Paua Press Limited, Dunedin
McClure FJ (1933) A review of fluorine and its physiological effects. Physiol Rev 13(3):277–300
Carlsson A (1978) Current problems of the pharmacology and toxicology of fluorides. Lakartidningen 75(14):1388–1392
Strunecka A, Strunecky O, Guan ZZ (2019) The resemblance of fluorosis pathology to that of autism spectrum disorder: a mini-review. Fluoride 52(2):105–115
Rocha-Amador D, Navarro ME, Carrizales L, Morales R, Calderon J (2007) Decreased intelligence in children and exposure to fluoride and arsenic in drinking water. Cad Saude Publica 23(Suppl 4):S579–S587
Seraj B, Shahrabi M, Shadfar M, Ahmadi R, Fallahzadeh M, Eslamlu HF, Kharazifard MJ (2012) Effect of high water fluoride concentration on the intellectual development of children in makoo/Iran. J Dent (Tehran) 9(3):221–229
Aravind A, Dhanya RS, Narayan A, Sam G, Adarsh VJ, Kiran M (2016) Effect of fluoridated water on intelligence in 10-12-year-old school children. J Int Soc Prev Commun Dent 6(Suppl 3):S237–s242
Yu X, Chen J, Li Y, Liu H, Hou C, Zeng Q, Cui Y, Zhao L, Li P, Zhou Z, Pang S, Tang S, Tian K, Zhao Q, Dong L, Xu C, Zhang X, Zhang S, Liu L, Wang A (2018) Threshold effects of moderately excessive fluoride exposure on children's health: a potential association between dental fluorosis and loss of excellent intelligence. Environ Int 118:116–124
Razdan P, Patthi B, Kumar JK, Agnihotri N, Chaudhari P, Prasad M (2017) Effect of fluoride concentration in drinking water on intelligence quotient of 12-14-year-old children in Mathura District: a cross-sectional study. J Int Soc Prev Commun Dent 7(5):252–258
Liang F, Li P (2019) Characteristics of cognitive in children with learning difficulties. Transl Neurosci 10:141–146
Demsky YI, Gass CS, Golden CJ (1998) Interpretation of VIQ-PIQ and intersubtest differences on the Spanish version of the WAIS. Assessment 5(1):25–30
Dean HT (1942) The investigation of physiological effects by the epidemiological method. In: Moulton FR, ed. Paper presented at the American Association for the Advancement of Science, Washington, DC,
Wang SQ, Zhang XY (1998) Theory and application of Wechsler intelligence scale for children (in chinese). Beijing People's publishing Press
Li D, Jin Y, Vandenberg SG, Zhu YM, Tang CH (1990) Report on Shanghai norms for the Chinese translation of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Revised. Psychol Rep 67(2):531–541
Sun DJ, Gao YH Epidemic and control of endemic fluorosis in China. In: XXXIVth conference of the International Society for Fluoride Research, Guiyang, China, 18–20 October 2018
Gao J, Li DS, An D, Liang Y, Zhang RZ, Ye HB, Yao DC, Zhang BY, Zhang NH (2015) Analysis of control and treatment effect on coal-burning endemic fluorosis in Guizhou Province from 2010 to 2014.(in Chinese). J Guiyang Med Coll 40(11):1179–1184
Wei N, Li Y, Deng J, Xu SQ, Guan ZZ (2014) The effects of comprehensive control measures on intelligence of school-age children in coal-burning-borne endemic fluorosis areas. (in Chinese). Chin J Local Med 033(3):320–322
Dec K, Lukomska A, Maciejewska D, Jakubczyk K, Baranowska-Bosiacka I, Chlubek D, Wasik A, Gutowska I (2017) The influence of fluorine on the disturbances of homeostasis in the central nervous system. Biol Trace Elem Res 177(2):224–234
Hu YH, Wu SS (1988) Fluoride in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with fluorosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51(12):1591–1593
Khan SA, Singh RK, Navit S, Chadha D, Johri N, Navit P, Sharma A, Bahuguna R (2015) Relationship between dental fluorosis and intelligence quotient of school going children in and around Lucknow District: a cross-sectional study. J Clin Diagn Res 9(11):Zc10–Zc15
Saxena S, Sahay A, Goel P (2012) Effect of fluoride exposure on the intelligence of school children in Madhya Pradesh, India. J Neurosci Rural Pract 3(2):144–149
Gui CZ, Ran LY, Li JP, Guan ZZ (2010) Changes of learning and memory ability and brain nicotinic receptors of rat offspring with coal burning fluorosis. Neurotoxicol Teratol 32(5):536–541
Ballantyne AO, Scarvie KM, Trauner DA Verbal and performance IQ patterns in children after perinatal stroke. Dev Neuropsychol 10 (1):39–50
Xiang Q, Liang Y, Chen L, Wang C, Chen B, Chen X, Zhou M (2003) Effect of fluoride in drinking water on children's intelligence. Fluoride 36(2):84–94
Tang QQ, Du J, Ma HH, Jiang SJ, Zhou XJ (2008) Fluoride and children's intelligence: a meta-analysis. Biol Trace Elem Res 126(1–3):115–120
Kogan MD, Vladutiu CJ, Schieve LA, Ghandour RM, Blumberg SJ, Zablotsky B, Perrin JM, Shattuck P, Kuhlthau KA, Harwood RL, Lu MC (2018) The prevalence of parent-reported autism spectrum disorder among US children. Pediatrics 142(6):e20174161
Liu YJ, Gao Q, Wu CX, Guan ZZ (2010) Alterations of nAChRs and ERK1/2 in the brains of rats with chronic fluorosis and their connections with the decreased capacity of learning and memory. Toxicol Lett 192(3):324–329
Mullenix PJ, Denbesten PK, Schunior A, Kernan WJ (1995) Neurotoxicity of sodium fluoride in rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 17(2):169–177
Yu Y, Yang W, Dong Z, Wan C, Zhang J, Liu J, Xiao K, Huang Y, Lu B (2008) Neurotransmitter and receptor changes in the brains of fetuses from areas of endemic fluorosis. Fluoride 41(2):134–138
Ge Y, Ning H, Feng C, Wang H, Yan X, Wang S, Wang J (2006) Apoptosis in brain cells of offspring rats exposed to high fluoride and low iodine. Fluoride 39(3):173–178
Li W, Jiang B, Cao X, Xie Y, Huang T (2017) Protective effect of lycopene on fluoride-induced ameloblasts apoptosis and dental fluorosis through oxidative stress-mediated Caspase pathways. Chem Biol Interact 261:27–34
Suzuki M, Bandoski C, Bartlett JD (2015) Fluoride induces oxidative damage and SIRT1/autophagy through ROS-mediated JNK signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 89:369–378
Lou DD, Guan ZZ, Liu YJ, Liu YF, Zhang KL, Pan JG, Pei JJ (2013) The influence of chronic fluorosis on mitochondrial dynamics morphology and distribution in cortical neurons of the rat brain. Arch Toxicol 87(3):449–457
D-d L, Zheng D, Ma R-r, K-l Z, Pan J-g, Y-j L, Yu Y-n, Z-z G (2019) Altered fission1 and mitofusion 1 in mitochondira induced by exposure to fluoried causes apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. Fluoride 52(2):116–134
Acknowledgements
We thank the Guizhou Medical University and Department of Child Healthcare in Guiyang Maternal and Child Health Hospital for their help and support. We also thank the children and their parents who participated in this study for their contribution and time.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was financed by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (81460483).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Didong Lou, Yan Luo, and Jing Liu contributed equally to this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethic Approval
The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the Guizhou Medical University and Guiyang Maternal and Child Health Hospital.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from parents and respective school authorities.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, D., Luo, Y., Liu, J. et al. Refinement Impairments of Verbal-Performance Intelligent Quotient in Children Exposed to Fluoride Produced by Coal Burning. Biol Trace Elem Res 199, 482–489 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02174-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02174-z