Abstract
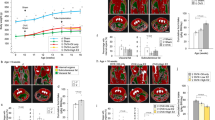
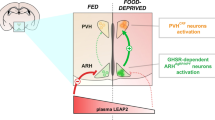
Ghrelin is an orexigenic agonist that acts directly on neurons in the hypothalamus, controlling appetite and energy balance. Although its role in appetite-associated neurons has been described, the relationship between peripheral ghrelin stimulation and oxytocin expression in the paraventricular nucleus is not fully understood. We evaluated the suppressive function of ghrelin in oxytocin-positive paraventricular nucleus neurons in ovariectomized C57BL/6 mice 2 h after ghrelin injection. The results showed that, in intact mice, peripheral ghrelin stimulation activated estrogen receptor alpha-expressing neurons during the estrous cycle and that agouti-related peptide mRNA expression was remarkably increased. Agouti-related peptide neuron axons co-localized with oxytocin neurons in the paraventricular nucleus. Moreover, the response of oxytocin-positive paraventricular nucleus neurons to ghrelin was suppressed in the proestrus period, while ghrelin decreased the serum concentration of estradiol in the proestrus phase. These data suggest that ghrelin may suppress oxytocin-positive neuron expression via the arcuate nucleus agouti-related peptide circuit, with the possible influence of estradiol in the murine estrous cycle. Unraveling the mechanism of ghrelin-induced oxytocin expression in the hypothalamus paraventricular nucleus broadens the horizon for ghrelin-related appetite research.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Aiceles V, Gombar FM, Cavalcante F, Ramos C (2019) Congenital hypothyroidism is associated with impairment of the leptin signaling pathway in the hypothalamus in male Wistar animals in adult life. Horm Metab Res. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0876-6007
Arnold M, Mura A, Langhans W, Geary N (2006) Gut vagal afferents are not necessary for the eating-stimulatory effect of intraperitoneally injected ghrelin in the rat. J Neurosci 26:11052–11060. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2606-06.2006
Asarian L, Geary N (2006) Modulation of appetite by gonadal steroid hormones. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 361:1251–1263. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2006.1860
Atasoy D, Betley JN, Su HH, Sternson SM (2012) Deconstruction of a neural circuit for hunger. Nature 488:172–177. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11270
Blouet C, Jo YH, Li X, Schwartz GJ (2009) Mediobasal hypothalamic leucine sensing regulates food intake through activation of a hypothalamus-brainstem circuit. J Neurosci 29:8302–8311. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1668-09.2009
Feng T, An S, Kinden R, Zhang X, Jia R, Tai F (2019) Alteration in oxytocin levels induced by early social environment affects maternal behavior and estrogen receptor alpha in mandarin voles (Microtus mandarinus). Behav Brain Res 365:36–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2019.02.038
Frazao R, Lemko HMD, Da Silva RP, Ratra DV, Lee CE, Williams KW, Zigman JM, Elias CF (2014) Estradiol modulates Kiss1 neuronal response to ghrelin. AJP Endocrinol Metab 306:E606–E614. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00211.2013
Gao Q, Mezei G, Nie Y, Rao Y, Choi CS, Bechmann I, Leranth C, Toran-Allerand D, Priest CA, Roberts JL, Gao XB, Mobbs C, Shulman GI, Diano S, Horvath TL (2007) Anorectic estrogen mimics leptin's effect on the rewiring of melanocortin cells and Stat3 signaling in obese animals. Nat Med 13:89–94. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1525
Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA (2012) AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:251–262. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3311
Hassouna R, Zizzari P, Viltart O, Yang SK, Gardette R, Videau C, Badoer E, Epelbaum J, Tolle V (2012) A natural variant of obestatin, Q90L, inhibits ghrelin's action on food intake and GH secretion and targets NPY and GHRH neurons in mice. PLoS ONE 7:e51135. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0051135
Hassouna R, Labarthe A, Zizzari P, Videau C, Culler M, Epelbaum J, Tolle V (2013) Actions of agonists and antagonists of the ghrelin/GHS-R Pathway on GH secretion, appetite, and cFos activity. Front Endocrinol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2013.00025
Heine PA, Taylor JA, Iwamoto GA, Lubahn DB, Cooke PS (2000) Increased adipose tissue in male and female estrogen receptor-alpha knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:12729–12734. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.23.12729
Ho JM, Blevins JE (2013) Coming full circle: contributions of central and peripheral oxytocin actions to energy balance. Endocrinology 154:589–596. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2012-1751
Hou Y, Yang SP, Voogt JL (2003) Changes in estrogen receptor-alpha expression in hypothalamic dopaminergic neurons during proestrous prolactin surge. Endocrine 20:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:20:1-2:131
Howard AD, Feighner SD, Cully DF, Arena JP, Liberator PA, Rosenblum CI, Hamelin M, Hreniuk DL, Palyha OC, Anderson J, Paress PS, Diaz C, Chou M, Liu KK, McKee KK, Pong SS, Chaung LY, Elbrecht A, Dashkevicz M, Heavens R, Rigby M, Sirinathsinghji DJ, Dean DC, Melillo DG, Patchett AA, Nargund R, Griffin PR, DeMartino JA, Gupta SK, Schaeffer JM, Smith RG, Van der Ploeg LH (1996) A receptor in pituitary and hypothalamus that functions in growth hormone release. Science 273:974–977. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.273.5277.974
Kojima M (2005) Ghrelin: Structure and Function. Physiol Rev 85:495–522. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00012.2004
Krashes MJ, Shah BP, Koda S, Lowell BB (2013) Rapid versus delayed stimulation of feeding by the endogenously released AgRP neuron mediators GABA, NPY, and AgRP. Cell Metab 18:588–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.09.009
Krashes MJ, Shah BP, Madara JC, Olson DP, Strochlic DE, Garfield AS, Vong L, Pei H, Watabe-Uchida M, Uchida N, Liberles SD, Lowell BB (2014) An excitatory paraventricular nucleus to AgRP neuron circuit that drives hunger. Nature 507:238–242. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12956
Kublaoui BM, Gemelli T, Tolson KP, Wang Y, Zinn AR (2008) Oxytocin deficiency mediates hyperphagic obesity of Sim1 haploinsufficient mice. Mol Endocrinol 22:1723–1734. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2008-0067
Lesnikov VA, Tsvetkova IP (1985) Stereotaxic coordinates of the mouse hypothalamus. Fiziol Zh SSSR Im I M Sechenova 71:798–804
Li MM, Madara JC, Steger JS, Krashes MJ, Balthasar N, Campbell JN, Resch JM, Conley NJ, Garfield AS, Lowell BB (2019a) The paraventricular hypothalamus regulates satiety and prevents obesity via two genetically distinct circuits. Neuron. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.02.028
Li X, Fan K, Li Q, Pan D, Hai R, Du C (2019b) Melanocortin 4 receptor-mediated effects of amylin on thermogenesis and regulation of food intake. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 35:e3149. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3149
McLean AC, Valenzuela N, Fai S, Bennett SA (2012) Performing vaginal lavage, crystal violet staining, and vaginal cytological evaluation for mouse estrous cycle staging identification. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/4389
Musatov S, Chen W, Pfaff DW, Mobbs CV, Yang XJ, Clegg DJ, Kaplitt MG, Ogawa S (2007) Silencing of estrogen receptor alpha in the ventromedial nucleus of hypothalamus leads to metabolic syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:2501–2506. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0610787104
Newton AJ, Hess S, Paeger L, Vogt MC, Fleming LJ, Nillni EA, Bruning JC, Kloppenburg P, Xu AW (2013) AgRP innervation onto POMC neurons increases with age and is accelerated with chronic high-fat feeding in male mice. Endocrinology 154:172–183. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2012-1643
Olofsson LE, Pierce AA, Xu AW (2009) Functional requirement of AgRP and NPY neurons in ovarian cycle-dependent regulation of food intake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:15932–15937. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0904747106
Olszewski PK, Bomberg EM, Martell A, Grace MK, Levine AS (2007) Intraventricular ghrelin activates oxytocin neurons: implications in feeding behavior. NeuroReport 18:499–503. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0b013e328058684e
Park CJ, Zhao Z, Glidewell-Kenney C, Lazic M, Chambon P, Krust A, Weiss J, Clegg DJ, Dunaif A, Jameson JL, Levine JE (2011) Genetic rescue of nonclassical ERα signaling normalizes energy balance in obese Erα-null mutant mice. J Clin Investig 121:604–612. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI41702
Rak-Mardyla A (2013) Ghrelin role in hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian axis. J Physiol Pharmacol 64:695–704. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.6.553
Reichenbach A, Steyn FJ, Sleeman MW, Andrews ZB (2012) Ghrelin receptor expression and colocalization with anterior pituitary hormones using a GHSR-GFP mouse line. Endocrinology 153:5452–5466. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2012-1622
Rhea EM, Salameh TS, Gray S, Niu J, Banks WA, Tong J (2018) Ghrelin transport across the blood-brain barrier can occur independently of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Mol Metab 18:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2018.09.007
Rodriguez EM, Blazquez JL, Guerra M (2010) The design of barriers in the hypothalamus allows the median eminence and the arcuate nucleus to enjoy private milieus: the former opens to the portal blood and the latter to the cerebrospinal fluid. Peptides 31:757–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2010.01.003
Schmittgen TD, Zakrajsek BA (2000) Effect of experimental treatment on housekeeping gene expression: validation by real-time, quantitative RT-PCR. J Biochem Biophys Methods 46:69–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-022x(00)00129-9
Semple E, Shalabi F, Hill JW (2019) Oxytocin neurons enable melanocortin regulation of male sexual function in mice. Mol Neurobiol 9:6310–6323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1514-5
Shaw AM, Irani BG, Moore MC, Haskell-Luevano C, Millard WJ (2005) Ghrelin-induced food intake and growth hormone secretion are altered in melanocortin 3 and 4 receptor knockout mice. Peptides 26:1720–1727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2004.12.026
Smith JT, Reichenbach A, Lemus M, Mani BK, Zigman JM, Andrews ZB (2013) An eGFP-expressing subpopulation of growth hormone secretagogue receptor cells are distinct from kisspeptin, tyrosine hydroxylase, and RFamide-related peptide neurons in mice. Peptides 47:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2013.06.012
Stark R, Ashley SE, Andrews ZB (2013) AMPK and the neuroendocrine regulation of appetite and energy expenditure. Mol Cell Endocrinol 366:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2012.06.012
Szabo R, Menesi R, Ma H, Szalai Z, Daruka L, Toth G, Gardi J, Galfi M, Borzsei D, Kupai K, Juhasz A, Radacs M, Laszlo FA, Varga C, Posa A (2019) New metabolic influencer on oxytocin release: the ghrelin. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040735
Tao YX (2010) The melanocortin-4 receptor: physiology, pharmacology, and pathophysiology. Endocr Rev 31:506–543. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2009-0037
Tolson KP, Gemelli T, Gautron L, Elmquist JK, Zinn AR, Kublaoui BM (2010) Postnatal Sim1 deficiency causes hyperphagic obesity and reduced Mc4r and oxytocin expression. J Neurosci 30:3803–3812. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.5444-09.2010
Vercruysse P, Vieau D, Blum D, Petersen A, Dupuis L (2018) Hypothalamic alterations in neurodegenerative diseases and their relation to abnormal energy metabolism. Front Mol Neurosci 11:2. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00002
Wang Q, Liu C, Uchida A, Chuang J, Walker A, Liu T, Osborne-Lawrence S, Mason BL, Mosher C, Berglund ED, Elmquist JK, Zigman JM (2014) Arcuate AgRP neurons mediate orexigenic and glucoregulatory actions of ghrelin. Mol Metab 3:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2013.10.001
Wren AM, Small CJ, Abbott CR, Dhillo WS, Seal LJ, Cohen MA, Batterham RL, Taheri S, Stanley SA, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (2001) Ghrelin causes hyperphagia and obesity in rats. Diabetes 50:2540–2547. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.50.11.2540
Wu Q, Whiddon BB, Palmiter RD (2012) Ablation of neurons expressing agouti-related protein, but not melanin concentrating hormone, in leptin-deficient mice restores metabolic functions and fertility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:3155–3160. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1120501109
Yu Z, Geary N, Corwin RL (2011) Individual effects of estradiol and progesterone on food intake and body weight in ovariectomized binge rats. Physiol Behav 104:687–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.07.017
Zhang G, Cai D (2011) Circadian intervention of obesity development via resting-stage feeding manipulation or oxytocin treatment. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 301:E1004–E1012. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00196.2011
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31660701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DP, KF, and QL performed the research and designed the experiments, and DP wrote the manuscript. HL, PL, and RH contributed to the study design and data analysis. GC is the guarantor of this work and, as such, had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Inner Mongolia University Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (approval no. SYCK2014-002).
Additional information
Communicated by Sreedharan Sajikumar.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, D., Fan, K., Li, Q. et al. Response of the expression of oxytocin neurons to ghrelin in female mice. Exp Brain Res 238, 1085–1095 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05793-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05793-z