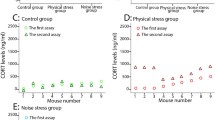
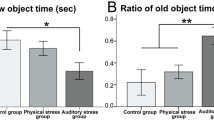
We studied the possibility of developing an autism model based on chronic prenatal psychological stress caused by variable frequency ultrasound 20-45 kHz. The offspring of female rats stressed during pregnancy demonstrated reduced time of social contacts in the social interaction test, increased anxiety in the open-field test, and memory impairment in the Morris water maze test in comparison with the control (intact) rat offspring. We also found a reducing trend in the BDNF gene expression in the amygdala in males of the experimental group. The results showed the possibility of developing the animal autism model based on prenatal stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belzung C, Lemoine M. Criteria of validity for animal models of psychiatric disorders: focus on anxiety disorders and depression. Biol. Mood Anxiety Disord. 2011;1(1). ID 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-5380-1-9
Boersma GJ, Lee RS, Cordner ZA, Ewald ER, Purcell RH, Moghadam AA, Tamashiro KL. Prenatal stress decreases Bdnf expression and increases methylation of Bdnf exon IV in rats. Epigenetics. 2014;9(3):437-447.
Chadman KK. Animal models for autism in 2017 and the consequential implications to drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017;12(12):1187-1194.
Chadman KK, Yang M, Crawley JN. Criteria for validating mouse models of psychiatric diseases. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2009;150B(1):1-11.
Ehrlich DE, Josselyn SA. Plasticity-related genes in brain development and amygdala-dependent learning. Genes Brain Behav. 2016;15(1):125-143.
Kazdoba TM, Leach PT, Yang M, Silverman JL, Solomon M, Crawley JN. Translational mouse models of autism: advancing toward pharmacological therapeutics. Curr. Top Behav. Neurosci. 2016;28):1-52.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402-408.
Morgan JT, Nordahl CW, Schumann CM. The Amygdala in Autism Spectrum Disorders. The Neuroscience of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Buxbaum JD, Hof PR, eds. Waltham, 2013. P. 297-312.
Morozova AY, Zubkov EA, Koshkin FA, Storozheva ZI, Chekhonin VP. Expression of genes encoding serotonin receptors and SERT in various brain structures of stressed rats after chronic exposure to ultrasound. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014;156(3):317-319.
Morozova AY, Zubkov EA, Storozheva ZI, Kekelidze ZI, Chekhonin VP. Effect of ultrasonic irradiation on the development of symptoms of depression and anxiety in rats. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013;154(6):740-743.
Servadio M, Vanderschuren LJ, Trezza V. Modeling autismrelevant behavioral phenotypes in rats and mice: do ‘autistic’ rodents exist?. Behav. Pharmacol. 2015;26(6):522-540.
Varcin KJ, Alvares GA, Uljarević M, Whitehouse A.J.O. Prenatal maternal stress events and phenotypic outcomes in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2017;10(11):1866-1877.
Varghese M, Keshav N, Jacot-Descombes S, Warda T, Wicinski B, Dickstein DL, Harony-Nicolas H, De Rubeis S, Drapeau E, Buxbaum JD, Hof PR. Autism spectrum disorder: Neuropathology and animal models. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;134(4):537-566.
Zhang H, Shang Y, Xiao X, Yu M, Zhang T. Prenatal stressinduced impairments of cognitive flexibility and bidirectional synaptic plasticity are possibly associated with autophagy in adolescent male-offspring. Exp. Neurol. 2017;298(Pt A):68-78.
Zorkina YA, Zubkov EA, Morozova AY, Ushakova VM, Chekhonin VP. The comparison of a new ultrasound-induced depression model to the chronic mild stress paradigm. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019;13. ID 146. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00146
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 168, No. 12, pp. 687-691, December, 2019
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abramova, O.V., Zubkov, E.A., Zorkina, Y.A. et al. Social and Cognitive Impairments in Rat Offspring after Ultrasound-Induced Prenatal Stress. Bull Exp Biol Med 168, 730–733 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04790-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04790-0