Abstract
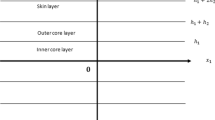
The present paper studies the anti-plane shear motion of an inhomogeneous elastic five-layered plate amidst the four contrasting material setups. The asymptotic analysis method in regard to the various material parameters is adopted for the study. The respective displacements, stresses and the Rayleigh-Lamb dispersion relation corresponding to the antisymmetric anti-plane motion with perfect interlayer and traction-free (on the outer faces) boundary conditions are determined. Furthermore, in order to analyze the said dispersion relation in the presence of these contrasts, a unification of parameters was proposed. The overall cutoff frequencies and the low-frequency estimates are determined for both the generalized and unified settings. A comparative analysis between the unified Rayleigh-Lamb dispersion relation and the optimal shortened polynomial dispersion relation is carried for each contrast. We also established some asymptotic formulae for the related unified displacements and stresses.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, J.D.: Wave Propagation in Elastic solids. Eight impression. Elsevier, The Netherland (1999)
Kaplunov, J.D., Kossovich, L.Y., Nolde, E.V.: Dynamics of Thin Walled Elastic Bodies. Academic Press, San Diego (1998)
Andrianov, I.V., Awrejcewicz, J., Danishevs’kyy, V.V., Ivankov, O.A.: Asymtotic Methods in the Theory of Plates with Mixed Boundary Conditions. Wiley, London (2014)
Gridin, D., Craster, R.V., Adamou, A.T.: Trapped modes in curved elastic plates. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser A 461(2056), 1181–1197 (2005)
Lee, P., Chang, N.: Harmonic waves in elastic sandwich plates. J. Elast. 9(1), 51–69 (1979)
Talebitooti, R., Johari, V., Zarastvand, M.: Wave transmission across laminated composite plate in the subsonic flow investigating two-variable refined plate theory. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 15, 5 (2018)
Talebitooti, R., Zarastvand, M., Gheibi, M.R.: Acoustic transmission through laminated composite cylindrical shell employing third order shear deformation theory in the presence of subsonic flow. Compos. Struct. 157(1), 95–110 (2016)
Talebitooti, R., Khameneh, A.M.C., Zarastvand, M.R., Kornokar, M.: Investigation of three-dimensional theory on sound transmission through compressed poroelastic sandwich cylindrical shell in various boundary configurations. J. Sandwich Struct Mater. 1, 10 (2018)
Talebitooti, R., Gohari, H.D., Zarastvand, M.R.: Multi objective optimization of sound transmission across laminated composite cylindrical shell lined with porous core investigating non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm. Aerospace Sci. Technol. 67, 269–280 (2017)
Talebitooti, R., Zarastvand, M.R., Gohari, H.D.: Investigation of power transmission across laminated composite doubly curved shell in the presence of external flow considering shear deformation shallow shell theory. J. Vib. Control 5 (2017)
Talebitooti, R., Zarastvand, M.R.: The effect of nature of porous material on diffuse field acoustic transmission of the sandwich aerospace composite doubly curved shell. Aerospace Sci. Technol. 78, 157–170 (2018)
Talebitooti, R., Zarastvand, M.R., Rouhani, A.H.S.: Investigating hyperbolic shear deformation theory on vibroacoustic behavior of the infinite functionally graded thick plate. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 16, 1 (2019)
Talebitooti, R., Zarastvand, M.R., Darvishgohari, H.: Multi-objective optimization approach on diffuse sound transmission through poroelastic composite sandwich structure. J. Sandwich Struct. Mater. 12, 10 (2019)
Ghassabi, M., Zarastvand, M.R., Talebitooti, R.: Investigation of state vector computational solution on modeling of wave propagation through functionally graded nanocomposite doubly curved thick structures. Eng. Comput. 59, 149 (2019)
Gohari, H.D., Zarastvand, M.R., Talebitooti, R.: Acoustic performance prediction of a multilayered finite cylinder equipped with porous foam media. J. Vib. Control 7 (2020)
Sahin, O., Erbas, B., Kaplunov, J., Savsek, T.: The lowest vibration modes of an elastic beam composed of alternating stiff and soft components. Appl. Mech, Arch (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-019-01612-2
Kaplunov, J., Prikazchikov, D.A., Prikazchikov, L.A., Sergushova, O.: The lowest vibration spectra of multi-component structures with contrast material properties. J. Sound Vib. 445, 132–147 (2019)
Erbas, B., Kaplunov, J., Nolde, E., Palsu, M.: Composite wave models for elastic plates. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phy. Eng. Sci. 474, 2214 (2018)
Kaplunov, J., Prikazchikov, D.A., Sergushova, O.: Multi-parametric analysis of the lowest natural frequencies of strongly inhomogeneous elastic rods. J. Sound Vib. 366, 264–276 (2016)
Søensen, R., Lund, E.: Thickness filters for discrete material and thickness optimization of laminated composite structures. Struc. Multidisc. Opt. (2015)
Talebitooti, R., Zarastvand, M.R., Gohari, H.D.: The influence of boundaries on sound insulation of the multilayered aerospace poroelastic composite structure. Aerospace Sci. Technol. 80, 452–471 (2018)
Talebitooti, R., Zarastvand, M.: Vibroacoustic behavior of orthotropic aerospace composite structure in the subsonic flow considering the third order Shear deformation theory. Aerospace Sci. Technol. 75, 227–236 (2018)
Ghassabi, M., Talebitooti, R., Zarastvand, M.R.: State vector computational technique for three-dimensional acoustic sound propagation through doubly curved thick structure. Comp. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 352(1), 324–344 (2019)
Zarastvand, M.R., Ghassabi, M., Talebitooti, R.: Acoustic insulation characteristics of shell structures: a review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 10, 129 (2019)
Sayyad, A.S., Ghugal, Y.M.: Bending, buckling and free vibration of laminated composite and sandwich beams: a critical review of literature. Compos. Struct. 171, 486–504 (2017)
Belarbi, M.O., Tati, A., Ounis, H., Khechai, A.: On the free vibration analysis of laminated composite and sandwich plates: a layerwise finite element formulation. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 10, 456 (2017)
Naumenko, K., Eremeyev, V.A.: A layer-wise theory for laminated glass and photovoltaic panels. Compos. Struct. 112, 283–291 (2014)
Altenbach, H., Eremeyev, V.A., Naumenko, K.: On the use of the first order shear deformation plate theory for the analysis of three-layer plates with thin soft core layer. ZAMM 95(10), 1004–1011 (2015)
Kaplunov, J., Prikazchikov, D., Prikazchikova, L.: Dispersion of elastic waves in a strongly inhomogeneous three-layered plate. Int. J. Solids Struct. 113, 169–179 (2017)
Prikazchikov, L.A., Aydın, Y.E., Erbas, B., Kaplunov, J.: Asymptotic analysis of anti-plane dynamic problem for a three-layered strongly inhomogeneous laminate. Math. Mech. Solids 56, 189 (2018)
Erbas, B.: Low frequency antiplane shear vibrations of a three-layered elastic plate. Eskişehir Techn. Uni. J. Sci. Techno. A: Appl. Sci. Eng. 19(4), 867–879 (2018)
Wang, X., Shi, G.: A simple and accurate sandwich plate theory accounting for transverse normal strain and interfacial stress continuity. Compos. Struct. 107, 620–628 (2014)
Ryazantseva, M.Y., Antonov, F.K.: Harmonic running waves in sandwich plates. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 59, 184–192 (2012)
Rogerson, G.A., Prikazchikova, L.A.: Generalisations of long wave theories for pre-stressed compressible elastic plates. Int. J. NonLinear Mech. 44(5), 520–529 (2009)
Zhai, Y., Li, Y., Liang, S.: Free vibration analysis of five-layered composite sandwich plates with two-layered viscoelastic cores. Solids Struct. 200(15), 346–357 (2018)
Lopez-Aenlle, M., Pelayo, F.: Static and dynamic effective thickness in five-layered glass plates. Solids Struct. 212(15), 259–270 (2019)
Conlan, N., Casey, J.: Comparing predicted and on site performance of CLT partitions and flanking elements. Proc. Inst. Acoust. 37, 2 (2015)
Shishehsaz, M., Raissi, H., Moradi, S.: Stress distribution in a five-layer circular sandwich composite plate based on the third and hyperbolic shear deformation theories. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 86, 469 (2019)
Khalil, H.K.C., Hadi, N.H.: Non-destructive damage assessment of five layers fiber glass/polyester composite materials laminated plate by using lamb waves simulation. J. Eng. 5, 25 (2019)
Baltazar, M.F, M. Almas: Lamination parameter optimization of flat fibre reinforced plates for vibration frequency criteria. Semantic Scholar, ID 125335818 (2013)
Assadi, A., Najaf, H.: Nonlinear static bending of single-crystalline circular nanoplates with cubic material anisotropy. Arch. Appl. Mech. 90, 847–868 (2020)
Demirkus, D.: Antisymmetric bright solitary SH waves in a nonlinear heterogeneous plate. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 69(128) (2018)
Demirkus, D.: Non-linear bright solitary SH waves in a hyperbolically heterogeneous layer. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 102, 53–61 (2018)
Nawaz, R., Ayub, M.: Closed form solution of electromagnetic wave diffraction problem in a homogeneous bi-isotropic medium. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 20, 189 (2015)
Lotfy, K., El-Bary, A.A.: Wave propagation of generalized magneto-thermoelastic interactions in an elastic medium under influence of initial stress. Iranian J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Mech. Eng. 56, 869 (2019)
Kaplunov, J., Nobili, A.: Multi-parametric analysis of strongly inhomogeneous periodic waveguides with internal cut-off frequencies. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 40(9), 3381–3392 (2017)
Craster, R., Joseph, L., Kaplunov, J.: Long-wave asymptotic theories: the connection between functionally graded waveguides and periodic media. Wave Motion 51(4), 581–588 (2014)
Maghsoodi, A., Ohadi, A., Sadighi, M.: Calculation of Wave Dispersion Curves in Multilayered Composite-Metal Plates. Shock Vib. ID 410514 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The first author, Rahmatullah Ibrahim Nuruddeen, sincerely acknowledges the 2017 CIIT-TWAS Full-time Postgraduate Fellowship Award (FR Number: 3240299480).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix A
The dispersion matrix posed by the problem in Sect. 4 is as follows:
with the following shortend terms in the matrix above
where
Note that the dimensionless form of the above formulae is used in the main text via Eqs. (9)–(11).
Appendix B
Some of the polynomial coefficients of Eq. (15) of Sect. 4 are as follows:
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nuruddeen, R.I., Nawaz, R. & Zia, Q.M.Z. Asymptotic analysis of an anti-plane shear dispersion of an elastic five-layered structure amidst contrasting properties. Arch Appl Mech 90, 1875–1892 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-020-01702-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-020-01702-6