Abstract
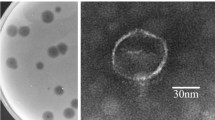
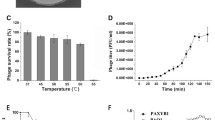
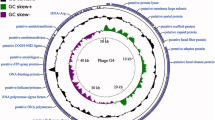
A lytic Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage vB_PaeP_LP14 belonging to the family Podoviridae was isolated from infected mink. The microbiological characterization revealed that LP14 was stable at 40 to 50 °C and stable over a broad range of pH (5 to 12). The latent period was 5 min, and the burst size was 785 pfu/infected cell. The whole-genome sequencing showed that LP14 was a dsDNA virus and has a genome of 73,080 bp. The genome contained 93 predicted open reading frames (ORFs), 17 of which have known functions including DNA replication and modification, transcriptional regulation, structural and packaging proteins, and host cell lysis. No tRNA genes were identified. BLASTn analysis revealed that phage LP14 had a high-sequence identity (96%) with P. aeruginosa phage YH6. Both morphological characterization and genome annotation indicate that phage LP14 is a memberof the family Podoviridae genus Litunavirus. The study of phage LP14 will provide basic information for further research on treatment of P. aeruginosa infections.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qi J, Li L, Du Y, Wang S, Wang J, Luo Y, Che J, Lu J, Liu H, Hu G, Li J, Gong Y, Wang G, Hu M, Shiganyan LY (2014) The identification, typing, and antimicrobial susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from mink with hemorrhagic pneumonia. Vet Microbiol 170(3–4):456–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.02.025
Traugott KA, Echevarria K, Maxwell P, Green K, Lewis JS 2nd (2011) Monotherapy or combination therapy? The Pseudomonas aeruginosa conundrum. Pharmacotherapy 31(6):598–608. https://doi.org/10.1592/phco.31.6.598
Shimizu T, Homma JY, Aoyama T, Onodera T, Noda H (1974) Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and spontaneous spread of pseudomonas pneumonia in a mink ranch. Infect Immun 10(1):16–20
Han MM, Mu LZ, Liu XP, Zhao J, Liu XF, Liu H (2014) ERIC-PCR genotyping of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from haemorrhagic pneumonia cases in mink. Vet Rec Open 1(1):e000043. https://doi.org/10.1136/vropen-2014-000043
Pedersen K, Hammer AS, Sorensen CM, Heuer OE (2009) Usage of antimicrobials and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance among bacteria from mink. Vet Microbiol 133(1–2):115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.06.005
McCallin S, Alam Sarker S, Barretto C, Sultana S, Berger B, Huq S, Krause L, Bibiloni R, Schmitt B, Reuteler G, Brussow H (2013) Safety analysis of a Russian phage cocktail: from metagenomic analysis to oral application in healthy human subjects. Virology 443(2):187–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2013.05.022
Hammer AS, Pedersen K, Andersen TH, Jorgensen JC, Dietz HH (2003) Comparison of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from mink by serotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Vet Microbiol 94(3):237–243
Yu X, Xu Y, Gu Y, Zhu Y, Liu X (2017) Characterization and genomic study of "phiKMV-Like" phage PAXYB1 infecting Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci Rep 7(1):13068. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13363-7
Vahdani M, Azimi L, Asghari B, Bazmi F, Rastegar Lari A (2012) Phenotypic screening of extended-spectrum ss-lactamase and metallo-ss-lactamase in multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa from infected burns. Ann Burns Fire Disasters 25(2):78–81
Ziha-Zarifi I, Llanes C, Kohler T, Pechere JC, Plesiat P (1999) In vivo emergence of multidrug-resistant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa overexpressing the active efflux system MexA-MexB-OprM. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43(2):287–291
Ballok AE, O'Toole GA (2013) Pouring salt on a wound: Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors alter Na+ and Cl- flux in the lung. J Bacteriol 195(18):4013–4019. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00339-13
Mulcahy LR, Isabella VM, Lewis K (2014) Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms in Disease. Microb Ecol 68(1):1–12
Pires DP, Vilas Boas D, Sillankorva S, Azeredo J (2015) Phage therapy: a step forward in the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Virol 89(15):7449–7456. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00385-15
Cao Z, Zhang J, Niu YD, Cui N, Ma Y, Cao F, Jin L, Li Z, Xu Y (2015) Isolation and characterization of a "phiKMV-like" bacteriophage and its therapeutic effect on mink hemorrhagic pneumonia. PLoS ONE 10(1):e0116571. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116571
Gong Z, Wang M, Yang Q, Li Z, Xia J, Gao Y, Jiang Y, Meng X, Liu Z, Yang D, Zhang F, Shao H, Wang D (2017) Isolation and complete genome sequence of a novel Pseudoalteromonas phage PH357 from the Yangtze River Estuary. Curr Microbiol 74(7):832–839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1244-8
Karumidze N, Thomas JA, Kvatadze N, Goderdzishvili M, Hakala KW, Weintraub ST, Alavidze Z, Hardies SC (2012) Characterization of lytic Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophages via biological properties and genomic sequences. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94(6):1609–1617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4119-8
Petsong K, Benjakul S, Chaturongakul S, Switt AIM, Vongkamjan K (2019) Lysis profiles of salmonella phages on salmonella isolates from various sources and efficiency of a phage cocktail against S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium. Microorganisms. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7040100
Debarbieux L, Leduc D, Maura D, Morello E, Criscuolo A, Grossi O, Balloy V, Touqui L (2010) Bacteriophages can treat and prevent Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections. J Infect Dis 201(7):1096–1104. https://doi.org/10.1086/651135
Harper DR, Enright MC (2011) Bacteriophages for the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Appl Microbiol 111(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05003.x
Spilker T, Coenye T, Vandamme P, LiPuma JJ (2004) PCR-based assay for differentiation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from other Pseudomonas species recovered from cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol 42(5):2074–2079. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.42.5.2074-2079.2004
Forozsh FM, Irajian G, Moslehi TZ, Fazeli H, Salehi M, Rezania S (2012) Drug resistance pattern of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from cystic fibrosis patients at Isfahan AL Zahra hospital, Iran (2009–2010). Iran J Microbiol 4(2):94–97
Lu L, Cai L, Jiao N, Zhang R (2017) Isolation and characterization of the first phage infecting ecologically important marine bacteria Erythrobacter. Virol J 14(1):104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-017-0773-x
Ackermann HW (2009) Basic phage electron microscopy. Methods Mol Biol 501:113–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-164-6_12
Zhou W, Feng Y, Zong Z (2018) Two new lytic bacteriophages of the myoviridae family against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Front Microbiol 9:850. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00850
Han Y, Wang M, Liu Q, Liu Y, Wang Q, Duan X, Liu L, Jiang Y, Shao H, Guo C (2019) Genome analysis of two novel lytic vibrio maritimus phages isolated from the Coastal Surface Seawater of Qingdao China. Curr Microbiol 76(10):1225–1233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01736-2
Liu Z, Wang M, Meng X, Li Y, Wang D, Jiang Y, Shao H, Zhang Y (2017) Isolation and genome sequencing of a novel pseudoalteromonas phage PH1. Curr Microbiol 74(2):212–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-016-1175-9
Yang Z, Liu X, Shi Y, Yin S, Shen W, Chen J, Chen Y, Chen Y, You B, Gong Y, Luo X, Zhang C, Yuan Z, Peng Y (2019) Characterization and genome annotation of a newly detected bacteriophage infecting multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Adv Virol 164(6):1527–1533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04213-0
Besemer J, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M (2001) GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucleic Acids Res 29(12):2607–2618
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M, Meyer F, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Osterman AL, Overbeek RA, McNeil LK, Paarmann D, Paczian T, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Reich C, Stevens R, Vassieva O, Vonstein V, Wilke A, Zagnitko O (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom 9:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305(3):567–580. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evolut 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Alikhan NF, Petty NK, Ben Zakour NL, Beatson SA (2011) BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom 12:402. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-402
Sullivan MJ, Petty NK, Beatson SA (2011) Easyfig: a genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 27(7):1009–1010. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr039
Zhao Y, Wang K, Jiao N, Chen F (2009) Genome sequences of two novel phages infecting marine roseobacters. Environ Microbiol 11(8):2055–2064. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01927.x
Yang M, Du C, Gong P, Xia F, Sun C, Feng X, Lei L, Song J, Zhang L, Wang B, Xiao F, Yan X, Cui Z, Li X, Gu J, Han W (2015) Therapeutic effect of the YH6 phage in a murine hemorrhagic pneumonia model. Res Microbiol 166(8):633–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2015.07.008
Nechaev S, Severinov K (2003) Bacteriophage-induced modifications of host RNA polymerase. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:301–322. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090942
Morozova V, Babkin I, Kozlova Y, Baykov I, Bokovaya O, Tikunov A, Ushakova T, Bardasheva A, Ryabchikova E, Zelentsova E, Tikunova N (2019) Isolation and characterization of a novel Klebsiella pneumoniae N4-like bacteriophage KP8. Viruses. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11121115
Lenneman BR, Rothman-Denes LB (2015) Structural and biochemical investigation of bacteriophage N4-encoded RNA polymerases. Biomolecules 5(2):647–667. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5020647
Dyson ZA, Tucci J, Seviour RJ, Petrovski S (2016) Isolation and characterization of bacteriophage SPI1, which infects the activated-sludge-foaming bacterium Skermania piniformis. Adv Virol 161(1):149–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2631-8
Daniel A, Bonnen PE, Fischetti VA (2007) First complete genome sequence of two Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteriophages. J Bacteriol 189(5):2086–2100. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01637-06
Delisle AL, Barcak GJ, Guo M (2006) Isolation and expression of the lysis genes of Actinomyces naeslundii phage Av-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(2):1110–1117. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.72.2.1110-1117.2006
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by a grant from the Donkey Industry Innovation Team Program of Modern Agricultural Technology System from Shandong Province, China (SDAIT-27). The authors would like to thank Jia Wang, Peng Song, and Wenshi Zhong for their help during this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, X., Zhao, F., Sun, H. et al. Characterization and Complete Genome Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Bacteriophage vB_PaeP_LP14 Belonging to Genus Litunavirus. Curr Microbiol 77, 2465–2474 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02011-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02011-5