Abstract
Objective
Vagal nerve stimulator (VNS) implantation at an early age seems to lead to improved quality of life and cognitive outcome. The aim of this analysis is to evaluate whether specific patient or seizure characteristics might lead to better seizure control, cognitive outcome, and higher quality of life in children undergoing VNS implantation.
Methods
Primary outcome measure was reduction in seizure frequency. Secondary outcome measures were epilepsy outcome assessed by McHugh and Engel classifications, reduction in antiepileptic drugs (AED), developmental and cognitive outcome, as well as quality of life assessed through the pediatric quality of life (PEDSQL™) questionnaire and care giver impression (CGI) scale. Forty-five consecutive children undergoing VNS implantation were analyzed for the following subgroups: age (categorized to 1–2 years old, 3–5 years old, 6–12 years old, and 13–18 years old), sex, underlying cause (categorized to idiopathic, encephalitis, stroke, syndromic), duration of preoperative seizures (dichotomized to under or above 89 months, corresponding to the median of the whole cohort), and preoperative seizure frequency (dichotomized to under and above 360 seizures per month).
Results
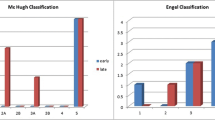
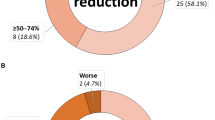
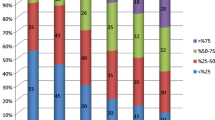
Encephalitis as the underlying cause for seizures was the only variable significantly associated with higher reduction rate of seizure frequency. Patients with VNS implantation at the age of ≤ 2 years showed a strong association with better developmental and cognitive outcome, as well as quality of life. Shorter duration of preoperative seizures and higher preoperative seizure frequency showed a strong association with better developmental outcome, as well as quality of life. Engel outcome scores were significantly better in patients with epilepsy due to encephalitis (100% Engel I–III). However, patients with epilepsy due to encephalitis showed significantly higher complication rates (71.4%, p = 0.045).
Conclusions
Children suffering from epilepsy due to encephalitis show higher seizure reduction rates after VNS implantation when compared with children suffering from epilepsy due to other causes. Developmental and cognitive outcomes as well as quality of life of children undergoing VNS implantation is strongly associated with shorter duration of preoperative seizures and implantation at a young age.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eriksson KJ, Koivikko MJ (1997) Prevalence, classification, and severity of epilepsy and epileptic syndromes in children. Epilepsia 38:1275–1282. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1997.tb00064.x
Ramos-Lizana J, Aguilera-López P, Aguirre-Rodríguez J, Cassinello-García E (2009) Response to sequential treatment schedules in childhood epilepsy. Seizure 18:620–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2009.07.001
Mohanraj R, Brodie MJ (2006) Diagnosing refractory epilepsy: response to sequential treatment schedules. Eur J Neurol 13:277–282. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01215.x
Berg AT, Shinnar S, Levy SR, Testa FM, Smith-Rapaport S, Beckerman B (2001) Early development of intractable epilepsy in children: a prospective study. Neurology 56:1445–1452. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.56.11.1445
Berg AT, Wusthoff C, Shellhaas RA, Loddenkemper T, Grinspan ZM, Saneto RP, Knupp KG, Patel A, Sullivan JE, Kossoff EH, Chu CJ, Massey S, Valencia I, Keator C, Wirrell EC, Coryell J, Millichap JJ, Gaillard WD (2019) Immediate outcomes in early life epilepsy: a contemporary account. Epilepsy Behav 97:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.05.011
Soleman J, Knorr C, Datta AN, Strozzi S, Ramelli GP, Mariani L, Guzman R (2018) Early vagal nerve stimulator implantation in children: personal experience and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 34:893–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3694-5
Soleman J, Stein M, Knorr C, Datta AN, Constantini S, Fried I, Guzman R, Kramer U (2018) Improved quality of life and cognition after early vagal nerve stimulator implantation in children. Epilepsy Behav 88:139–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.09.014
Healy S, Lang J, Te Water Naude J et al (2013) Vagal nerve stimulation in children under 12 years old with medically intractable epilepsy. Childs Nerv Syst 29:2095–2099. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2143-3
Elliott RE, Rodgers SD, Bassani L, Morsi A, Geller EB, Carlson C, Devinsky O, Doyle WK (2011) Vagus nerve stimulation for children with treatment-resistant epilepsy: a consecutive series of 141 cases. J Neurosurg Pediatr 7:491–500. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.2.PEDS10505
Alexopoulos AV, Kotagal P, Loddenkemper T, Hammel J, Bingaman WE (2006) Long-term results with vagus nerve stimulation in children with pharmacoresistant epilepsy. Seizure 15:491–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2006.06.002
Thompson EM, Wozniak SE, Roberts CM, Kao A, Anderson VC, Selden NR (2012) Vagus nerve stimulation for partial and generalized epilepsy from infancy to adolescence. J Neurosurg Pediatr 10:200–205. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.5.PEDS11489
Coykendall DS, Gauderer MWL, Blouin RR, Morales A (2010) Vagus nerve stimulation for the management of seizures in children: an 8-year experience. J Pediatr Surg 45:1479–1483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2010.02.066
Cersósimo RO, Bartuluchi M, Fortini S, Soraru A, Pomata H, Caraballo RH (2011) Vagus nerve stimulation: effectiveness and tolerability in 64 paediatric patients with refractory epilepsies. Epileptic Disord 13:382–388. https://doi.org/10.1684/epd.2011.0479
Colicchio G, Policicchio D, Barbati G, Cesaroni E, Fuggetta F, Meglio M, Papacci F, Rychlicki F, Scerrati M, Zamponi N (2010) Vagal nerve stimulation for drug-resistant epilepsies in different age, aetiology and duration. Childs Nerv Syst 26:811–819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-009-1069-2
Orosz I, McCormick D, Zamponi N, Varadkar S, Feucht M, Parain D, Griens R, Vallée L, Boon P, Rittey C, Jayewardene AK, Bunker M, Arzimanoglou A, Lagae L (2014) Vagus nerve stimulation for drug-resistant epilepsy: a European long-term study up to 24 months in 347 children. Epilepsia 55:1576–1584. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.12762
Bodin E, Le Moing A-G, Bourel-Ponchel E et al (2016) Vagus nerve stimulation in the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy in 29 children. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 20:346–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2016.01.011
Zamponi N, Rychlicki F, Corpaci L, Cesaroni E, Trignani R (2008) Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is effective in treating catastrophic 1 epilepsy in very young children. Neurosurg Rev 31:291–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-008-0134-8
Yu C, Ramgopal S, Libenson M, Abdelmoumen I, Powell C, Remy K, Madsen JR, Rotenberg A, Loddenkemper T (2014) Outcomes of vagal nerve stimulation in a pediatric population: a single center experience. Seizure 23:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2013.10.002
Varni JW, Seid M, Rode CA (1999) The PedsQL: measurement model for the pediatric quality of life inventory. Med Care 37:126–139. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005650-199902000-00003
Tsai J-D, Chang Y-C, Lin L-C, Hung K-L (2016) The neuropsychological outcome of pediatric patients with refractory epilepsy treated with VNS — a 24-month follow-up in Taiwan. Epilepsy Behav 56:95–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.12.030
Menascu S, Kremer U, Schiller Y, Blatt I, Watemberg N, Boxer M, Goldberg H, Korn-Lubetzki I, Steinberg M, Ben-Zeev B (2013) The Israeli retrospective multicenter open-label study evaluating vagus nerve stimulation efficacy in children and adults. Isr Med Assoc J 15:673–677
Hallböök T, Lundgren J, Stjernqvist K, Blennow G, Strömblad LG, Rosén I (2005) Vagus nerve stimulation in 15 children with therapy resistant epilepsy; its impact on cognition, quality of life, behaviour and mood. Seizure 14:504–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2005.08.007
Thompson PJ, Duncan JS (2005) Cognitive decline in severe intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia 46:1780–1787. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2005.00279.x
Vendrame M, Alexopoulos AV, Boyer K, Gregas M, Haut J, Lineweaver T, Wyllie E, Loddenkemper T (2009) Longer duration of epilepsy and earlier age at epilepsy onset correlate with impaired cognitive development in infancy. Epilepsy Behav 16:431–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2009.08.008
Livanova MRI Guidelines for VNS Therapy®. http://omamedical.fi/en/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2018/09/MRI-Guidelines-for-VNS-Therapy-2018.pdf. Accessed 22 Feb 2020
Englot DJ, Chang EF, Auguste KI (2011) Vagus nerve stimulation for epilepsy: a meta-analysis of efficacy and predictors of response. J Neurosurg 115:1248–1255. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.7.JNS11977
Elliott RE, Morsi A, Kalhorn SP, Marcus J, Sellin J, Kang M, Silverberg A, Rivera E, Geller E, Carlson C, Devinsky O, Doyle WK (2011) Vagus nerve stimulation in 436 consecutive patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy: long-term outcomes and predictors of response. Epilepsy Behav 20:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2010.10.017
Ji T, Yang Z, Liu Q, Liao J, Yin F, Chen Y, Zou L, Li B, Gao Y, Shu X, Huang S, Gao F, Liang J, Lin SF, Peng J, Song S, Wang J, Che C, Sun W, Tian M, Yang L, Hua Y, Hao Y, Cai L, Li L, Jiang Y (2019) Vagus nerve stimulation for pediatric patients with intractable epilepsy between 3 and 6 years of age: study protocol for a double-blind, randomized control trial. Trials 20:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-018-3087-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knorr, C., Greuter, L., Constantini, S. et al. Subgroup analysis of seizure and cognitive outcome after vagal nerve stimulator implantation in children. Childs Nerv Syst 37, 243–252 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04628-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-020-04628-0