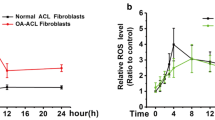
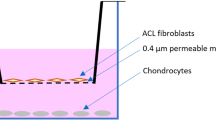
Abstract
Objective
Interleukin (IL)-1β in the joint cavity increases to promote healing after anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury. Synovial tissue is a major joint microenvironmental regulator after ACL injury. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of synovial cells (SCs) on lysyl oxidase (LOX) and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) production by ACL fibroblasts (ACLfs) in the presence of IL-1β.
Results
This study sheds light on the regulation of LOX and MMP-1, -2, -3 expression by ACLfs co-cultured with SCs and treated with IL-1β. LOX and MMP-1, 2, 3 gene/protein expression in IL-1β/stretch-stimulated ACLfs co-cultured with SCs were measured by real-time quantitative PCR and Western blot. Meanwhile, MMP-2 activity was analyzed by zymogram. The results showed that co-culture with SCs increased LOX and MMP-1, -2, -3 gene and protein expression in the presence of IL-1β. Next, ACLfs were subjected to 12% mechanical stretch to simulate pathological injury. Under these conditions, SCs inhibited IL-1β-mediated upregulation of LOXs. However, IL-1β enhanced the expression of MMP-1, -2, -3 in injured ACLfs.
Conclusions
SCs can either inhibit or increase LOX production in the presence of IL-1β, while promoting the accumulation of MMP in injured ACLfs. These results may provide crucial insights into the mechanisms underlying ACL poor healing capacity after injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
All data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Akkiraju H, Nohe A (2015) Role of chondrocytes in cartilage formation, progression of osteoarthritis and cartilage regeneration. J Dev Biol 3:177–192. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb3040177
Andrea PM, Ewald AJ, Zena W (2007) Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:221–233. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2125
Barker HE, Cox TR, Erler JT (2012) The rationale for targeting the LOX family in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 12:540. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3319
Bicer EK, Lustig S, Servien E, Selmi TAS, Neyret P (2010) Current knowledge in the anatomy of the human anterior cruciate ligament. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18:1075–1084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-009-0993-8
Bloemen V, Schoenmaker T, de Vries TJ, Everts V (2010) Direct cell-cell contact between periodontal ligament fibroblasts and osteoclast precursors synergistically increases the expression of genes related to osteoclastogenesis. J Cell Physiol 222:565–573. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.21971
Cooper JA, Sahota JS, Jay WG, Janell C, Doty SB, Laurencin CT (2007) Biomimetic tissue-engineered anterior cruciate ligament replacement. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3049–3054. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0608837104
Duquin TR, Wind WM, Fineberg MS, Smolinski RJ, Buyea CM (2009) Current trends in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Knee Surg 22:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1247719
Haller JM, Swearingen CA, Partridge D, Mcfadden M, Thirunavukkarasu K, Higgins TF (2015) Intraarticular matrix metalloproteinases and aggrecan degradation are elevated after articular fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res 473:3280–3288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-015-4441-4
Irie K, Uchiyama E, Iwaso H (2003) Intraarticular inflammatory cytokines in acute anterior cruciate ligament injured knee. Knee 10:93–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0968-0160(02)00083-2
Kamath GV, Murphy T, Creighton RA, Viradia N, Taft TN, Spang JT (2014) Anterior cruciate ligament injury, return to play, and reinjury in the Elite Collegiate Athlete: analysis of an NCAA dvision I cohort. Am J Sport Med 42:1638–1643. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546514524164
Kang YM, Choi YR, Yun CO, Park O, Suk KS, Kim HS, Park MS, Lee BH, Lee HM, Moon SH (2014) Down-regulation of collagen synthesis and matrix metalloproteinase expression in myofibroblasts from Dupuytren nodule using adenovirus-mediated relaxin gene therapy. J Orthop Res 32:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.22535
Khosravi R, Sodek KL, Xu WP, Bais MV, Saxena D, Faibish M, Trackman PC (2014) A novel function for lysyl oxidase in pluripotent mesenchymal cell proliferation and relevance to inflammation-associated osteopenia. PLoS ONE 9:e100669. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0100669
Lucero HA, Kagan HM (2006) Lysyl oxidase: an oxidative enzyme and effector of cell function. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:2304–2316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-006-6149-9
Mäki JM, Räsänen J, Tikkanen H, Sormunen R, Mäkikallio K, Kivirikko KI, Soininen R (2002) Inactivation of the lysyl oxidase gene lox leads to aortic aneurysms, cardiovascular dysfunction, and perinatal death in mice. Circulation 106:2503–2509. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000038109.84500.1e
Mäki JM, Sormunen R, Lippo S, Kaarteenahowiik R, Soininen R, Myllyharju J (2005) Lysyl oxidase is essential for normal development and function of the respiratory system and for the integrity of elastic and collagen fibers in various tissues. Am J Pathol 167:927–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9440(10)61183-2
McLean GW, Carragher NO, Avizienyte E, Evans J, Brunton VG, Frame MC (2005) The role of focal-adhesion kinase in cancer—a new therapeutic opportunity. Nat Rev Cancer 5:505. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1647
Murphy G, Nagase H (2008) Progress in matrix metalloproteinase research. Mol Aspects Med 29:290–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2008.05.002
Øiestad B, Engebretsen L, Storheim K, Risberg M (2009) Winner of the 2008 systematic review competition: knee osteoarthritis after anterior cruciate ligament injury: a systematic review. Am J Sports Med. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546509338827
Roerink ME, Schaaf ME, Dinarello CA, Knoop H, Meer JWM (2017) Interleukin-1 as a mediator of fatigue in disease: a narrative review. J Neuroinflamm 14:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0796-7
Sung K, Yang L, Whittemore DE, Shi Y, Jin G, Hsieh AH, Akeson WH, Sung LA (1996) The differential adhesion forces of anterior cruciate and medial collateral ligament fibroblasts: effects of tropomodulin, talin, vinculin, and alpha-actinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9182–9187. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.17.9182
Tang Z, Yang L, Zhang J, Xue R, Wang Y, Chen P, Sung K-LP (2009) Coordinated expression of MMPs and TIMPs in rat knee intra-articular tissues after ACL injury. Connect Tissue Res 50:315–322
Wang Y, Yang L, Zhang J, Xue R, Tang Z, Huang W, Jiang D, Tang X, Chen P, Sung KL (2010) Differential MMP-2 activity induced by mechanical compression and inflammatory factors in human synoviocytes. Mol Cell Biomech 7:105–114
Wang C, Xie J, Jiang J, Huang W, Chen R, Xu C, Zhang Y, Fu C, Yang L, Chen PC (2015) Differential expressions of the lysyl oxidase family and matrix metalloproteinases-1, 2, 3 in posterior cruciate ligament fibroblasts after being co-cultured with synovial cells. Int Orthop 39:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-014-2573-x
Wang C, Xu C, Chen R, Yang L, Sung KL (2018) Different expression profiles of the lysyl oxidases and matrix metalloproteinases in human ACL fibroblasts after co-culture with synovial cells. Connect Tissue Res 59:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/03008207.2017.1401615
Xie J, Huang W, Jiang J, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Xu C, Yang L, Chen P, Sung KL (2013a) Differential expressions of lysyl oxidase family in ACL and MCL fibroblasts after mechanical injury. Injury 44:893–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2012.08.046
Xie J, Wang C, Yin L, Xu CM, Zhang Y, Sung KL (2013b) Interleukin-1 beta influences on lysyl oxidases and matrix metalloproteinases profile of injured anterior cruciate ligament and medial collateral ligament fibroblasts. Int Orthop 37:495–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1549-y
Xie J, Wang CL, Yang W, Wang J, Chen C, Zheng L, Sung KLP, Zhou X (2018) Modulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 through connected pathways and growth factors is critical for extracellular matrix balance of intra-articular ligaments. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 12(1):e550–e565. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.2325
Xu K, Sha Y, Wang S, Chi Q, Liu Y, Wang C, Yang L (2019) Effects of Bakuchiol on chondrocyte proliferation via the PI3K-Akt and ERK1/2 pathways mediated by the estrogen receptor for promotion of the regeneration of knee articular cartilage defects. Cell Prolif 52:e12666. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12666
Zhang J, Yang L, Tang Z, Xue R, Wang Y, Luo Z, Huang W, Sung KL (2009) Expression of MMPs and TIMPs family in human ACL and MCL fibroblasts. Connect Tissue Res 50:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/03008200802376139
Zhang Y, Huang W, Jiang J, Xie J, Xu C (2014) Influence of TNF-α and biomechanical stress on matrix metalloproteinases and lysyl oxidases expressions in human knee synovial fibroblasts. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22:1997–2006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2425-z
Zhang Y, Jiang J, Jing X, Xu C, Wang C, Lin Y, Li Y, Sung KL (2017) Combined effects of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β on lysyl oxidase and matrix metalloproteinase expression in human knee synovial fibroblastsin vitro. Exp Ther Med 14:5258–5266. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.5264
Zhong J, Guo B, Xie J, Deng S, Fu N, Lin S, Li G (2015) Crosstalk between adipose-derived stem cells and chondrocytes: when growth factors matter. Bone Res 4:15036. https://doi.org/10.1038/boneres.2015.36
Zhou D, Lee HS, Villarreal F, Teng A, Lu E, Reynolds S, Qin C, Smith J, Sung KLP (2005) Differential MMP-2 activity of ligament cells under mechanical stretch injury: An in vitro study on human ACL and MCL fibroblasts. J Orthop Res 23:949–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orthres.2005.01.022
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11532004, 11832008, 11602181, 11802096), Innovation and Attracting Talents Program for College and University (‘‘111’’ Project) (B06023), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Number: 2018M630867), the Visiting Scholar Foundation of Key Laboratory of Biorheological Science and Technology (Chongqing University), Ministry of Education (Grant Number: CQKLBST-2018-009) and (Grant Number: CQKLBST-2018-006), Sharing fund of Chongqing university’s large-scale equipment (2009063038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Chi, Q., Sha, Y. et al. Mechanical injury and IL-1β regulated LOXs and MMP-1, 2, 3 expression in ACL fibroblasts co-cultured with synoviocytes. Biotechnol Lett 42, 1567–1579 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02870-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-02870-9