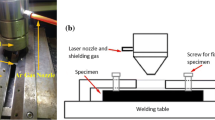
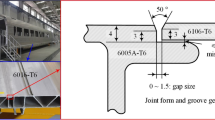
Abstract
Due to high hot crack susceptibility of Al-Mg-Si alloys, autogenous welding by rectangular pulsed laser beam has not been generally successful in the removal of cracks. In this research, the effect of pulsed Nd:YAG laser parameters and preheating on the creation of hot cracks in the 6061-T6 aluminum alloy was investigated. The sample that was fabricated by the laser parameters including 1 Hz, 0.12 mm/s, 10 ms, and without preheating exhibited the highest cooling rate and the smallest dendrite arm spacing but no hot crack was observed. The tensile test specimens of this sample fractured at a point far from the weld metal and a decrease in the precipitation of silicon and magnesium in the inter-dendritic space and the reduction of thermal stresses resulted in the elimination of hot cracks. However, according to macro-scale models for the creation of hot cracks, preheating decreased the tensile stresses in the BTR (brittle temperature range), but increasing the preheating temperature led to increasing rather than decreasing the hot crack length. In this case, the formation of hydrogen porosity, the segregation of silicon and magnesium, and the creation of low melting point compounds were the important parameters affecting the hot crack initiation and growth.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis JR (1993) ASM specialty handbook: aluminum and aluminum alloys. ASM International
Zhang YM, Pan C, Male AT (2000) Improved microstructure and properties of 6061 aluminum alloy weldments using a double-sided arc welding process. Metall Mater Trans A 31A
Ambriz RR, Mesmacque G, Ruiz A, Amrouche A, López VH (2010) Effect of the welding profile generated by the modified indirect electric arc technique on the fatigue behavior of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 527
Handbook AM (1992) Welding brazing and soldering. ASM International, Cleveland
Soysal T, Kou S (2018) A simple test for assessing solidification cracking susceptibility and checking validity of susceptibility prediction. Acta Mater 143:181–197
D’Urso G, Giardini C, Lorenzi S, Pastore T (2014) Fatigue crack growth in the welding nugget of FSW joints of a 6060 aluminum alloy. J Mater Process Technol
Abdulstaar MA, Al-Fadhalah KJ, Wagner L (2017) Microstructural variation through weld thickness and mechanical properties of peened friction stir welded 6061 aluminum alloy joints. Mater Charact 126:64–73
Society AW (1997) Structural welding code aluminum. AWS Structural Welding Comittee
Florea RS,Solanki KN,Bammann DJ, Baird JC, Jordon JB, Castanier MP (2012) Resistance spot welding of 6061-T6 aluminum: failure loads and deformation. Mater Des 34
Viveros KC, Ambriz RR, Amrouche A, Talha A, García C, Jaramillo D (2014) Cold hole expansion effect on the fatigue crack growth in welds of a 6061-T6 aluminum alloy. J Mater Process Technol
Mujibur Rahman ABM, Kumar S, Gerson AR (2007) Galvanic corrosion of laser weldments of AA6061 aluminium alloy. Corros Sci 49
Zhang DQ, Li J, Joo HG, Lee KY (2009) Corrosion properties of Nd:YAG laser–GMA hybrid welded AA6061 Al alloy and its microstructure. Corros Sci 51
Rahman ABMM, Kumar S, Gerson AR (2010) The role of silicon in the corrosion of AA6061 aluminium alloy laser weldments. Corros Sci 52
Vargas JA, Torres JE, Pacheco JA, Hernandez RJ (2013) Analysis of heat input effect on the mechanical properties of Al-6061-T6 alloy weld joints. Mater Des 52
Chu Q, Bai R, Jian H, Lei Z, Hu N, Yan C Microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of 6061 aluminum laser beam welded joints. Mater Charact
Kim DY, Park YW (2012) Weldability evaluation and tensile strength estimation model for aluminum alloy lap joint welding using hybrid system with laser and scanner head. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 22
Schneider A, Avilov V, Gumenyuk A, Rethmeier M (2013) Laser beam welding of aluminum alloys under the influence of an electromagnetic field. Phys Procedia 41
Bergmann JP, Bielenin M, Stambke M, Feustel T, Witzendorff PV, Hermsdorf J (2013) Effects of diode laser superposition on pulsed laser welding of aluminum. Phys Procedia 41
Zhang J, Weckman DC, Zhou Y (2008) Effects of temporal pulse shaping on cracking susceptibility of 6061-T6 aluminum NdYAG laser welds. Weld J 87:18–30
Sheikhi M, Malek Ghaini F, Assadi H (2015) Prediction of solidification cracking in pulsed laser welding of 2024 aluminum alloy. Acta Mater 82:12
Witzendorff PV, Kaierle S, Suttmann O, Overmeyer L (2015) In situ observation of solidification conditions in pulsed laser welding of AL6082 aluminum alloys to evaluate their impact on hot cracking susceptibility. Metall Mater Trans A 46A:11
von Witzendorff P,Kaierle S, Suttmann O,Overmeyer L (2016) Monitoring of solidification crack propagation mechanism in pulsed laser welding of 6082 aluminum. In: SPIE LASE. International Society for Optics and Photonics, pp 97410H–97410H-14
Rappaz M, Drezet JM, Gremaud M (1999) A new hot-tearing criterion. Metall Mater Trans A 30A(2):449–455
Liu J, Kou S (2016) Crack susceptibility of binary aluminum alloys during solidification. Acta Mater 110:84–94
Kou S (2015) A criterion for cracking during solidification. Acta Mater 88:366–374
Liu J, Kou S (2015) Effect of diffusion on susceptibility to cracking during solidification. Acta Mater 100:359–368
Danis Y, Lacoste E, Arvieu C (2010) Numerical modeling of inconel 738LC deposition welding: prediction of residual stress induced cracking. J Mater Process Technol 210(14):2053–2061
Ebrahimzadeh H, Mousavi SAAA (2012) Investigation on pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding of 49Ni–Fe soft magnetic alloy. Mater Des 38:115–123
Hossain Ebrahimzadeh HF, Mousavi SAAA, Ghahramani A (2020) Microstructural analyses of aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloys welded by pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding. Int J Miner Metall Mater
Zain-ul-Abdein M, Nelias D, Jullien J-F, Deloison D (2009) Prediction of laser beam welding-induced distortions and residual stresses by numerical simulation for aeronautic application. J Mater Process Technol 209(6):2907–2917
Masubuchi K (1980) Chapter 3 - Fundamental information on residual stresses. In: Analysis of welded structures, Pergamon, pp 88–111
Sheikhi M, Malek Ghaini F, Assadi H (2014) Solidification crack initiation and propagation in pulsed laser welding of wrought heat treatable aluminium alloy. Sci Technol Weld Join 19(3):250–255
Kou S (2003) Welding metallurgy, 2nd edn. Wiley, New Jersey
Al-Akel AS, Abdelatif AK, Gharbia FA (2002) Effect of preheating on hot cracking susceptibility of welded austenitic stainless steel. 5
Hekmatjou H, Naffakh-Moosavy H (2018) Hot cracking in pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding of AA5456. Opt Laser Technol 103:22–32
He X, Fuerschbach P, DebRoy T (2003) Heat transfer and fluid flow during laser spot welding of 304 stainless steel. J Phys D Appl Phys 36(12):1388
He X, Elmer J, DebRoy T (2005) Heat transfer and fluid flow in laser microwelding. J Appl Phys 97(8):084909
Nie F et al (2018) Microstructure and mechanical properties of pulse MIG welded 6061/A356 aluminum alloy dissimilar butt joints. J Mater Sci Technol 34(3):551–560
Zhang J, Weckman DC, Zhou Y (2008) Effects of temporal pulse shaping on cracking susceptibility of 6061-T6 aluminum Nd:YAG laser welds. Weld J 87:18s–30s
Mai TA, Spowage AC (2004) Characterisation of dissimilar joints in laser welding of steel–kovar, copper–steel and copper–aluminium. Mater Sci Eng A 374(1):224–233
Ye X, Zhang P, Zhao J, Ma P (2018) Effect of macro- and micro-segregation on hot cracking of Inconel 718 superalloy argon-arc multilayer cladding. J Mater Process Technol 258:251–258
Arivarasu M et al (2014) Micro-segregation studies on the continuous Nd: YAG laser beam welded AISI 316L. Procedia Engineering 97:892–901
Praveen P, Yarlagadda P (2005) Meeting challenges in welding of aluminum alloys through pulse gas metal arc welding. J Mater Process Technol 164:1106–1112
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the metallography lab of the School of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, University of Tehran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Recommended for publication by Commission IX - Behaviour of Metals Subjected to Welding
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebrahimzadeh, H., Farhangi, H. & Mousavi, S.A.A.A. Hot cracking in autogenous welding of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy by rectangular pulsed Nd:YAG laser beam. Weld World 64, 1077–1088 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-020-00899-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-020-00899-y