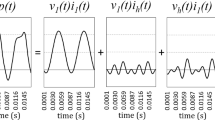
Abstract
The different reactive power and energy metering methods used by electric energy meters on medium and high voltage consumers present different results between themselves, notably in the presence of distorted voltage and current signals. Over recent decades, many discussions and various propositions have been put into action, all of which aimed at a worldwide unification of power and reactive energy metering methods. However, the problem still persists and the objective of this study therefore lies in performing of a quantitative update, concerning the impacts of these different methods on the reactive energy metering for billing purposes. In this context, each of the methods frequently used by the electric energy meter manufacturers will be covered in an analytical manner, seeking the mathematical understanding of the divergences that exist between them. In concurrent fashion, calibration tests will be performed in the laboratory aimed at the correct quantification of measurement deviations found under specific distortion conditions in voltage and current waveforms, when comparing meters from different manufacturers and models. A new electric energy meter, that contemplates all known metering methods, was developed with the aim of performing a measurement campaign allowing for the comparison of the performance of each one of these methods under real load conditions, considering many different types of consumer. The obtained results, in addition to providing a quantitative update of the magnitude of existing deviations, also demonstrate a great concern regarding the lack of isonomy currently found around the world in the metering of reactive power and energy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cataliotti A, Cosentino V, Nuccio S (2008) The measurement of reactive energy in polluted distribution power systems: an analysis of the performance of commercial static meters. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 23:1296–1301. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRD.2008.919239
Djokić B, Bosnjaković P (1998) A high accuracy reactive power and reactive energy meter. Electr Eng 81:41. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01233055
Bošnjakovié P, Djokié B (1992) Reactive energy measurement using frequency controlled analog-to-pulse-rate converter. Archiv f Elektrotechnik 75:131. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01577631
Toral SL, Quero JM, Franquelo LG (2001) Reactive power and energy measurement in the frequency domain using random pulse arithmetic. IEEE Proc Sci Meas Technol 148:63–67. https://doi.org/10.1049/ip-smt:20010305
Emanuel AE (1990) Powers in nonsinusoidal situations—a review of definitions and physical meaning. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 5:1377–1389. https://doi.org/10.1109/61.57980
Emanuel AE (2010) Power definitions and the physical mechanism of power flow. Wiley, New York
IEEE (2000) IEEE. Std. 1459–2000: IEEE trial-use standard definitions for the measurement of electric power quantities under sinusoidal, nonsinusoidal, balanced or unbalanced conditions. https://doi.org/10.1109/ieeestd.2000.93398
Filipski PS, Baghzouz Y, Cox MD (1994) Discussion of power definitions contained in the IEEE Dictionary. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 9:1237–1244. https://doi.org/10.1109/61.311149
Shepherd W, Zakikhani P (1972) Suggested definition of reactive power for nonsinusoidal systems. In: Proceedings of the Institution of Electrical Engineers. https://doi.org/10.1049/piee.1972.0268
Shepherd W, Zakikhani P, Sharon D (1974) Reactive power definition and power factor improvement in non-linear systems. In: Proceedings of the Institution of Electrical Engineers. https://doi.org/10.1049/piee.1974.0087
Kusters NL, Moore WJM (1980) On the definition of reactive power under nonsinusoidal conditions. IEEE Trans Power Appar Syst 5:1845–1854. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAS.1980.319833
Czarnecki LS (1985) Considerations on the reactive power in nonsinusoidal situations. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.1985.4315358
Fryze S (1932) Active, reactive and apparent power in circuits with nonsinusoidal voltages and currents. Elektrotechnische Z 53:596–599
Budeanu CI (1927) Reactive and fictitious powers. Romanian National Institute, Bucharest
Filipski P (1980) A new approach to reactive current and reactive power measurement in nonsinusoidal systems. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 29:423–426. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.1980.4314972
Fazio Jr A, Sampaio LP et al (2011) Comparative analysis for reactive energy measurement methodologies, under non-sinusoidal conditions in three phase four-wire circuits. In: XI Brazilian power electronics conference. https://doi.org/10.1109/cobep.2011.6085277
Guo S, Qiang F, Xianzhuang M (2012) A compensation method of phase-shift error on reactive power measurement. In: Proceedings of 2012 international conference on measurement, information and control. https://doi.org/10.1109/mic.2012.6273371
Souza WA, Marafão FP et al (2015) Power quality, smart meters and additional information from different power terms. IEEE Lat Am Trans 13:158–165. https://doi.org/10.1109/TLA.2015.7040643
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The authors thank the Energisa Group for the financial support as part of the Program for Research and Technological Development of the Electricity Energy Sector established by the Brazilian Electricity Regulatory Agency (ANEEL). Additionally this study was financed in part by the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel—Brazil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001 and by the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xavier, G.L., Miyasaka, G., Silvério, E.T. et al. An update on the performance of reactive energy meters under non-sinusoidal conditions. Electr Eng 102, 1881–1891 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-020-00970-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-020-00970-3