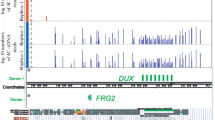
Abstract—rDNA genes play an important role in epigenetic regulation and in differentiation of eukaryotic cells. Using the 4C (circular chromosome conformation capture) approach and model HEK293T cells, we analyzed the rDNA-contacting gene FANK1, using anchor located inside rDNA genes. At the 5' end of the FANK1 gene we detected frequent contacts with rDNA clusters. The contact sites coincide with the border where chromatin state changes and nucleosome positioning. The adjacent genes DHX32, BCCIP and UROS are located in the active chromatin and are transcribed, but do not contact with rDNA genes, while FANK1 gene is silenced, and is located in repressed chromatin. Heat shock treatment dramatically changes the pattern of rDNA contacts in the region and induces about 4-fold increase in activation of the FANK1 gene. We conclude that rDNA contacts may be involved in repression of the FANK1 gene.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Dekker J., Rippe K., Dekker M. 2002. Capturing chromosome conformation. Science. 95, 1306–1311.https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1067799
Ulianov S.V., Khrameeva E.E., Gavrilov A.A., Flyamer I.M., Kos P., Mikhaleva E.A., Penin A.A., Logacheva M.D., Imakaev M.V., Chertovich A., Gelfand M.S., Shevelyov Y.Y., Razin S.V. 2016. Active chromatin and transcription play a key role in chromosome partitioning into topologically associating domains. Genome Res. 26, 70‒84. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.196006.115
Sidorenko D.S., Sidorenko I.A., Zykova T.Y., Goncharov F.P., Larsson J., Zhimulev I.F. 2019. Molecular and genetic organization of bands and interbands in the dot chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster.Chromosoma. 128, 97‒117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-019-00703-x
Sarnataro S., Chiariello A.M., Esposito A., Prisco A., Nicodemi M. 2017. Structure of the human chromosome interaction network. PLoS One. 12 (11), e0188201. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188201
Tchurikov N.A., Fedoseeva D.M., Sosin D.V., Snezhkina A.V., Melnikova N.V., Kudryavtseva A.V., Kravatsky Y.V., Kretova O.V. 2015. Hot spots of DNA double-strand breaks and genomic contacts of human rDNA units are involved in epigenetic regulation. J. Mol. Cell. Biol.7, 366‒382. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mju038
Savić N., Bär D., Leone S., Frommel S.C., Weber F.A., Vollenweider E., Ferrari E., Ziegler U., Kaech A., Shakhova O., Cinelli P., Santoro R. 2014. lncRNA maturation to initiate heterochromatin formation in the nucleolus is required for exit from pluripotency in ESCs. Cell Stem Cell.15, 720‒734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2014.10.005
Kretova O.V., Fedoseeva D.M., Kravatskii Yu.V., Alembekov I.R., Slovokhotov I.Yu., Churikov N.A. 2019. Homeotic DUX4 genes that control human embryonic development at the two-cell stage are surrounded by regions contacting with rDNA gene clusters. Mol. Biol. (Moscow). 53 (2), 237‒241. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026898419020083
Fullwood M.J., Ruan Y. 2009. ChIP-based methods for the identification of long-range chromatin interactions. J. Cell. Biochem. 107, 30–39. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.22116
Zhao Z., Sentürk N., Song C., Grummt I. 2018. lncRNA PAPAS tethered to the rDNA enhancer recruits hypophosphorylated CHD4/NuRD to repress rRNA synthesis at elevated temperatures. Genes Dev. 32, 836‒848. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.311688.118
Shaw G., Morse S., Ararat M., Graham F.L. 2002. Preferential transformation of human neuronal cells by human adenoviruses and the origin of HEK 293 cells. FASEB J.16, 869‒971.https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.01-0995fje
Graham F.L., Smiley J., Russell W.C., Nairn R. 1977. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J. Gen. Virol. 36, 59‒74.https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59
Wang H., Song W., Hu T., Zhang N., Miao S., Zong S., Wang L. 2011. Fank1 interacts with Jab1 and regulates cell apoptosis via the AP-1 pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci.68, 2129–2139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0559-4
Hnisz D., Abraham B.J., Lee T.I., Lau A., Saint-André V., Sigova A.A., Hoke H.A., Young R.A. 2013. Super-enhancers in the control of cell identity and disease. Cell.155, 934–947.
Kretova O.V., Fedoseeva D.M., Slovokhotov I.Yu., Klushevskaya E.S., Kravatskii Yu.V., Churikov N.A. 2020. Drosophila rRNA genes form stable contacts with the Tlk gene in the region of small RNA expression and have an effect on the organization of loop domains. Mol. Biol. (Moscow). 54, in press.
Funding
The study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant no. 18-14-00122). Mapping of true DNase-I-hypersensitive sites was supported by a grant from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 17-04-02152).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study does not contain any research involving humans or animals as research objects.
Conflict of interest. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Abbreviations: FANK1, gene of DNA-binding transcription factor (based on Gene Onthology data); DHX32, DEAH-Box Helicase gene 32; BCCIP, gene conservative protein in contact with proteins BRCA2 and p21; UROS, gene that controls heme synthesis; H3K27ac, mark of active chromatin; RNA-Seq, deep RNA sequencing.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kretova, O.V., Fedoseeva, D.M., Kravatsky, Y.V. et al. Contact Sites of rDNA Clusters with FANK1 Gene Correspond to Repressed Chromatin. Mol Biol 54, 229–232 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320020077
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320020077