Abstract
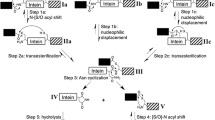
Protein trans-splicing is a naturally occurring process in which two protein fragments are ligated by a reaction between two intein domains, called split inteins. Despite their usefulness in research, the reactivity and structure of only a few split inteins have been studied. We used cell-based kanamycin selection and next-generation sequencing (NGS) to simultaneously measure the splicing reactivity of 298 N-intein–C-intein combinations derived from the DnaE gene of cyanobacteria. Additionally, we confirmed the splicing activities by measuring the growth of cells individually harboring each split intein under kanamycin selection. Overall, the N-intein–C-intein combinations were promiscuous in their trans-splicing activities, although certain combinations did not splice actively. These results and the NGS-based analysis in this research would be helpful for the development of novel split inteins and further understanding of the trans-splicing mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shah, N. H. and T. W. Muir (2014) Inteins: nature’s gift to protein chemists. Chem. Sci. 5: 446–461.
Noren, C. J. J. Wang, and F. B. Perler (2000) Dissecting the chemistry of protein splicing and its applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 39: 450–466.
Saleh, L. and F. B. Perler (2006) Protein splicing in cis and in trans. Chem. Rec. 6: 183–193.
Lopez-Igual, R., J. Bernal-Bayard, A. Rodriguez-Paton, J. M. Ghigo, and D. Mazel (2019) Engineered toxin-intein antimicrobials can selectively target and kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria in mixed populations. Nat. Biotechnol. 37: 755–760.
Shah, N. H., M. Vila-Perelló, and T. W. Muir (2011) Kinetic control of one-pot trans-splicing reactions by using a wild-type and designed split intein. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 50: 6511–6515.
Lienert, F., J. P. Torella, J. H. Chen, M. Norsworthy, R. R. Richardson, and P. A. Silver (2013) Two- and three-input TALEbased AND logic computation in embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 41: 9967–9975.
Shah, N. H. E. Eryilmaz, D. Cowburn, and T. W. Muir (2013) Naturally split inteins assemble through a “capture and collapse” mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135: 18673–18681.
Ramirez, M., N. Valdes, D. Guan, and Z. Chen (2013) Engineering split intein DnaE from Nostoc punctiforme for rapid protein purification. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 26: 215–223.
Aranko, A. S. A. Wlodawer, and H. Iwai (2014) Nature’s recipe for splitting inteins. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 27: 263–271.
Busche, A. E. A. S. Aranko, M. Talebzadeh-Farooji, F. Bernhard, V. Dotsch, and H. Iwai (2009) Segmental isotopic labeling of a central domain in a multidomain protein by protein trans-splicing using only one robust DnaE intein. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 48: 6128–6131.
Appleby-Tagoe, J. H. I. V. Thiel, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, H. D. Mootz, and X. Q. Liu (2011) Highly efficient and more general cis- and trans-splicing inteins through sequential directed evolution. J. Biol. Chem. 286: 34440–34447.
Stevens, A. J. Z. Z. Brown, N. H. Shah, G. Sekar, D. Cowburn, and T. W. Muir (2016) Design of a split intein with exceptional protein splicing activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138: 2162–2165.
Iwai, H., S. Zuger, J. Jin, and P. H. Tam (2006) Highly efficient protein trans-splicing by a naturally split DnaE intein from Nostoc punctiforme. FEBS Lett. 580: 1853–1858.
Dassa, B., G. Amitai, J. Caspi, O. Schueler-Furman, and S. Pietrokovski (2007) Trans protein splicing of cyanobacterial split inteins in endogenous and exogenous combinations. Biochemistry. 46: 322–330.
Cheriyan, M., S. H. Chan, and F. Perler (2014) Traceless splicing enabled by substrate-induced activation of the Nostoc punctiforme Npu DnaE intein after mutation of a catalytic cysteine to serine. J. Mol. Biol. 426: 4018–4029.
Cheriyan, M., C. S. Pedamallu, K. Tori, and F. Perler (2013) Faster protein splicing with the Nostoc punctiforme DnaE intein using non-native extein residues. J. Biol. Chem. 288: 6202–6211.
Lockless, S. W. and T. W. Muir (2009) Traceless protein splicing utilizing evolved split inteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 106: 10999–11004.
Picelli, S., A. K. Bjorklund, B. Reinius, S. Sagasser, G. Winberg, and R. Sandberg (2014) Tn5 transposase and tagmentation procedures for massively scaled sequencing projects. Genome Res. 24: 2033–2040.
Hwang, B., S. Heo, N. Cho, H. Seo, and D. Bang (2019) Facilitated large-scale sequence validation platform using Tn5-tagmented cell lysates. ACS Synth. Biol. 8: 596–600.
Bolger, A. M. M. Lohse, and B. Usadel (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 30: 2114–2120.
Li, H. and R. Durbin (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 25: 1754–1760.
Perler, F. B. (2002) InBase: the intein database. Nucleic Acids Res. 30: 383–384.
Hasenbrink, G., S. Schwarzer, L. Kolacna, J. Ludwig, H. Sychrova, and H. Lichtenberg-Frate (2005) Analysis of the mKir2.1 channel activity in potassium influx defective Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains determined as changes in growth characteristics. FEBS Lett. 579: 1723–1731.
Shah, N. H. G. P. Dann, M. Vila-Perello, Z. Liu, and T. W. Muir (2012) Ultrafast protein splicing is common among cyanobacterial split inteins: implications for protein engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134: 11338–11341.
Wang, B., B. J. DeKosky, M. R. Timm, J. Lee, E. Normandin, J. Misasi, R. Kong, J. R. McDaniel, G. Delidakis, K. E. Leigh, T. Niezold, C. W. Choi, E. G. Viox, A. Fahad, A. Cagigi, A. Ploquin, K. Leung, E. S. Yang, W. P. Kong, W. N. Voss, A. G. Schmidt, M. A. Moody, D. R. Ambrozak, A. R. Henry, F. Laboune, J. E. Ledgerwood, B. S. Graham, M. Connors, D. C. Douek, N. J. Sullivan, A. D. Ellington, J. R. Mascola, and G. Georgiou (2018) Functional interrogation and mining of natively paired human VH:VL antibody repertoires. Nat. Biotechnol. 36: 152–155.
Hu, J. H. S. M. Miller, M. H. Geurts, W. Tang, L. Chen, N. Sun, C. M. Zeina, X. Gao, H. A. Rees, Z. Lin, and D. R. Liu (2018) Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity. Nature. 556: 57–63.
Choi, G. C. G. P. Zhou, C. T. L. Yuen, B. K. C. Chan, F. Xu, S. Bao, H. Y. Chu, D. Thean, K. Tan, K. H. Wong, Z. Zheng, and A. S. L. Wong (2019) Combinatorial mutagenesis en masse optimizes the genome editing activities of SpCas9. Nat. Methods. 16: 722–730.
Villiger, L., H. M. Grisch-Chan, H. Lindsay, F. Ringnalda, C. B. Pogliano, G. Allegri, R. Fingerhut, J. Häberle, J. Matos, M. D. Robinson, B. Thöny, and G. Schwank (2018) Treatment of a metabolic liver disease by in vivo genome base editing in adult mice. Nat. Med. 24: 1519–1525.
Schaerli, Y., M. Gili, and M. Isalan (2014) A split intein T7 RNA polymerase for transcriptional AND-logic. Nucleic Acids Res. 42: 12322–12328.
Wang, T., A. H. Badran, T. P. Huang, and D. R. Liu (2018) Continuous directed evolution of proteins with improved soluble expression. Nat. Chem. Biol. 14: 972–980.
Acknowledgments
We thank the members of the Bang Lab for their critical comments during this work. This work was supported by: (i) the Mid-career Researcher Program (NRF-2018R1A2A 1A05079172) from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Planning; (ii) the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the NRF, funded by the Korean government (MSIT; NRF-2016M3A9B6948494); (iii) the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the NRF, funded by the Korean government (MSIT; NRF-2018M3A9H3024850) and (iV) the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI18C2282).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
12257_2019_394_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Aptamer-based Fluorescent Assay for Simple and Sensitive Detection of Fipronil in Liquid EggsPromiscuous Trans-splicing Activities Revealed by Next Generation Sequencing-based Analysis of 298 Split Inteins
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, H.N., Bang, D. Promiscuous Trans-splicing Activities Revealed by Next Generation Sequencing-based Analysis of 298 Split Inteins. Biotechnol Bioproc E 25, 293–301 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0394-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0394-x