Abstract
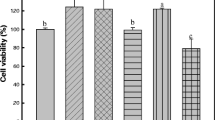
Melanin provides photoprotection against UV irradiation, but excessive melanin accumulation can cause several problems such as darkened skin, melasma, and freckles. Although many anti-melanogenic agents have been developed for skin-whitening cosmetics, safety issues have been raised regarding these products. As natural substances are often non-toxic and are considered by some to be safer than synthetic compounds, various attempts have been made to synthesize active derivatives from natural substances. In this study, we evaluated the anti-melanogenic effects of four synthesized derivatives (compound 2a, 2b, 2c, and 2d) of kojic and hydroxycinnamic acids which are natural anti-melanogenic substances. Three of these derivatives (2a, 2b, and 2c) inhibited tyrosinase, which catalyzes a rate-limiting step of melanogenesis. Additionally, cell viability and melanin formation were investigated using B16F10 melanoma cells. Compounds 2b and 2c exhibited cytotoxicity towards B16F10 melanoma cells, while compound 2a caused a significant decrease in melanin formation without cytotoxicity. Thus, compound 2a may be viable as a potent skin-whitening agent derived from natural compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brenner, M. and V. J. Hearing (2008) The protective role of melanin against UV damage in human skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 84: 539–549.
Liu, J. J. and D. E. Fisher (2010) Lighting a path to pigmentation: mechanisms of MITF induction by UV. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 23: 741–745.
Videira, I. F., D. F. Moura, and S. Magina (2013) Mechanisms regulating melanogenesis. An Bras Dermatol. 88: 76–83.
Korner, A. and J. Pawelek (1982) Mammalian tyrosinase catalyzes three reactions in the biosynthesis of melanin. Science. 217: 1163–1165.
Li, J., L. Y. Tang, W. W. Fu, J. Yuan, Y. Y. Sheng, and Q. P. Yang (2016) Low-concentration hydrogen peroxide can upregulate keratinocyte intracellular calcium and PAR-2 expression in a human keratinocyte-melanocyte co-culture system. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 308: 723–731.
Singh Arora, D. and R. Kumar Sharma (2010) Ligninolytic fungal laccases and their biotechnological applications. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 160: 1760–1788.
Jung, E., J. A. Lee, S. Shin, K. B. Roh, J. H. Kim, and D. Park (2013) Madecassoside inhibits melanin synthesis by blocking ultraviolet-induced inflammation. Molecules. 18: 15724–15736.
Kim, B., S. H. Lee, K. Y. Choi, and H. S. Kim (2015) NNicotinoyl tyramine, a novel niacinamide derivative, inhibits melanogenesis by suppressing MITF gene expression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 764: 1–8.
Abe, Y., K. Okamura, M. Kawaguchi, Y. Hozumi, H. Aoki, T. Kunisada, S. Ito, K. Wakamatsu, K. Matsunaga, and T. Suzuki (2016) Rhododenol-induced leukoderma in a mouse model mimicking Japanese skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 81: 35–43.
Saruno, R., F. Kato, and T. Ikeno (1979) Kojic Acid, a Tyrosinase Inhibitor from Aspergillus albus. Agric. Biol. Chem. 43: 1337–1338.
Wang, X. R., H. M. Cheng, X. W. Gao, W. Zhou, S. J. Li, X. L. Cao, and D. Yan (2019) Intercalation assembly of kojic acid into Zn-Ti layered double hydroxide with antibacterial and whitening performances. Chin Chem Lett. 30: 919–923.
Lim, J. Y., K. Ishiguro, and I. Kubo (1999) Tyrosinase inhibitory p-coumaric acid from ginseng leaves. Phytother Res. 13: 371–375.
An, S. M., S. I. Lee, S. W. Choi, S. W. Moon, and Y. C. Boo (2008) p-Coumaric acid, a constituent of Sasa quelpaertensis Nakai, inhibits cellular melanogenesis stimulated by alphamelanocyte stimulating hormone. Br. J. Dermatol. 159: 292–299.
Cho, U. M., D. H. Choi, D. S. Yoo, S. J. Park, and H. S. Hwang (2019) Inhibitory effect of ficin derived from fig latex on inflammation and melanin production in skin cells. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 24: 288–297.
Hong, S. J., J. H. Lee, E. J. Kim, H. J. Yang, Y. K. Chang, J. S. Park, and S. K. Hong (2017) In vitro and in vivo investigation for biological activities of neoagarooligosaccharides prepared by hydrolyzing agar with β-agarase. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 22: 489–496.
An, S. M., J. S. Koh, and Y. C. Boo (2010) p-coumaric acid not only inhibits human tyrosinase activity in vitro but also melanogenesis in cells exposed to UVB. Phytother Res. 24: 1175–1180.
Noh, J. M., S. Y. Kwak, H. S. Seo, J. H. Seo, B. G. Kim, and Y. S. Lee (2009) Kojic acid-amino acid conjugates as tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19: 5586–5589.
Seo, Y. K., S. J. Kim, Y. C. Boo, J. H. Baek, S. H. Lee, and J. S. Koh (2011) Effects of p-coumaric acid on erythema and pigmentation of human skin exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 36: 260–266.
Hashemi, S. M. and S. Emami (2015) Kojic acid-derived tyrosinase inhibitors: synthesis and bioactivity. Pharm. Biomed. Res. 1: 1–17.
Sasaki, M., M. Kondo, K. Sato, M. Umeda, K. Kawabata, Y. Takahashi, T. Suzuki, K. Matsunaga, and S. Inoue (2014) Rhododendrol, a depigmentation-inducing phenolic compound, exerts melanocyte cytotoxicity via a tyrosinase-dependent mechanism. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 27: 754–763.
Le, H. T., B. N. Hong, Y. R. Lee, J. H. Cheon, T. H. Kang, and T. W. Kim (2016) Regulatory effect of hydroquinone-tetraethylene glycol conjugates on zebrafish pigmentation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 26: 699–705.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a research grant of The University of Suwon in 2018.
The authors claim no conflict of interest to declare. Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M., Park, H.Y., Jung, K.H. et al. Anti-melanogenic Effects of Kojic Acid and Hydroxycinnamic Acid Derivatives. Biotechnol Bioproc E 25, 190–196 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0421-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0421-y