Abstract
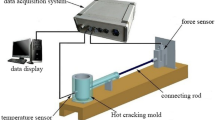
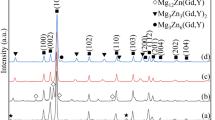
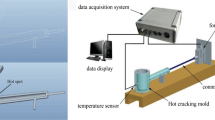
The effects of different Sn additions (0, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0 wt%) on hot tearing susceptibility (HTS) of Mg–Zn–Zr alloy were studied using a “T-shaped” hot tearing mold in a pouring temperature of 700 °C and a mold temperature of 270 °C. The “Clyne–Davies” hot tearing prediction model and commercial simulation software, Procast, were used to characterize the HTS of alloys. The dendrite coherency temperature was obtained by means of differential thermal analysis. The phases evolution, microstructures and morphology of the crack zone of Mg–4Zn–xSn–0.6Zr alloys were investigated by using X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope. The experimental results show that the HTS of Mg–4Zn–xSn–0.6Zr alloys decreases with Sn additions up to 1.0 wt%, and then exhibits a slight increase with further Sn additions up to 3.0 wt%. The Sn additions into Mg–4Zn–0.6Zr alloy can form Mg2Sn phase with high melting point. Appropriate addition of Sn can refine grain size, decrease the dendrite coherency temperature, increase the thickness of liquid film and the feeding ability at the end of solidification, which reduce the HTS of the alloy. However, excessive Sn addition will make Mg2Sn aggregate and grow up, and hinder the residual liquid-phase feeding in the late solidification stage, resulting in an increase in HTS of the alloy. The order of HTS of studied alloys is: CSC(Mg–4Zn–0.6Zr) > CSC(Mg–4Zn–0.5Sn–0.6Zr) > CSC(Mg–4Zn–3Sn–0.6Zr) > CSC(Mg–4Zn–2Sn–0.6Zr) > CSC(Mg–4Zn–1Sn–0.6Zr).














Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.S. Pan, M.B. Yang, D.F. Zhang, L.Y. Wang, P.D. Ding, Research and development of wrought magnesium alloys in China. Mater. Sci. Forum 488–489, 413–418 (2005)
G.H. Wu, M. Sun, W. Wang, W.J. Ding, New research development on purification technology of magnesium alloys. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 20(6), 1021–1031 (2010)
Z. Liu, S.B. Zhang, P.L. Mao, F. Wang, Effects of Y on hot tearing susceptibility of Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(4), 907–914 (2014)
K. Hantzsche, J. Bohlena, J. Wendt, K.U. Kainer, S.B. Yi, D. Letzig, Effect of rare earth additions on microstructure and texture development of magnesium alloy sheets. Scr. Mater. 63(7), 725–730 (2010)
S.B. Yi, J. Bohlen, F. Heinemann, D. Letzig, Mechanical anisotropy and deep drawing behavior of AZ31 and ZE10 magnesium alloy sheets. Acta Mater. 58(2), 592–605 (2010)
Z. Wang, S. Yao, Y. Feng, Z. Liu, Y.Z. Li, F. Wang, P.L. Mao, Solidification pathways and hot tearing susceptibility of MgZnxY4Zr0.5 alloys. China Foundry 15(2), 124–131 (2018)
Y. Zhou, P.L. Mao, Z. Wang, Y.Z. Li, Z. Liu, F. Wang, Effects of copper content and mold temperature on the hot tearing susceptibility of Mg–7Zn–xCu–0.6Zr alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49, 3444–3455 (2018)
H. Huang, P.H. Fu, Y.X. Wang, L.M. Peng, H.Y. Jiang, Effect of pouring and mold temperatures on hot tearing susceptibility of AZ91D and Mg–3Nd–0.2Zn–Zr Mg alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(4), 922–929 (2014)
J.F. Song, Z. Wang, Y.D. Huang, A. Srinivasan, F. Beckmann, K.U. Kainer, H. Norbert, Effect of Zn addition on hot tearing behaviour of Mg–0.5Ca–xZn alloys. Mater. Des. 87(15), 157–170 (2015)
J.H. Chen, Z.H. Chen, H.G. Yan, F.Q. Zhang, K. Liao, Effects of Sn addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Al alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 461, 209–215 (2008)
Z. Liu, Y. Zhang, P.L. Mao, C.H. Yang, Effects of Sn on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Ca magnesium alloys. Spec. Cast. Nonferrous Alloys 32(11), 999–1001 (2012)
S. Wei, T. Zhu, M. Hodgson, W. Gao, Effects of Sn addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast, rolled and annealed Mg–4Zn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 585(12), 139–148 (2013)
C.F. Fang, D.D. Song, G.X. Liu, H. Huang, X.L. Dong, X.G. Zhang, Effects of Sn addition forms on microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater. Res. Innov. 19(10), 273–276 (2015)
G.G. Zhang, J.H. Chen, H.G. Yan, B. Su, X. He, M. Ran, Effects of artificial aging on microstructure and mechanical properties of the Mg–4.5Zn–4.5Sn–2Al alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 592(15), 250–257 (2014)
T. Zhang, J. Shen, J.X. Sang, Y. Li, P.P. He, Effects of Sn addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg–6Zn–3Cu–xSn magnesium alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46(8), 3732–3743 (2015)
M.B. Yang, F.S. Pan, Effects of Sn addition on as-cast microstructure, mechanical properties and casting fluidity of ZA84 magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 31(1), 68–75 (2010)
H.K. Dong, F. Wang, Z. Wang, J.K. Liu, Z. Liu, P.L. Mao, Effect of Sn addition on hot tearing susceptibility of AXJ530 alloy. Mater. Res. Express 5(3), 036513 (2018)
B. Wang, Z. Liu, P.L. Mao, Z. Wang, F. Wang, Hot tearing susceptibility of Mg–Al–Ca alloy with different Sn additions. Chin. J. Rare Met. 244(7), 647–653 (2016)
M. Pokorny, C. Monroe, C. Beckermann, L. Bichler, C. Ravindran, Prediction of hot tear formation in a magnesium alloy permanent mold casting. Int. J. Metalcast. 2(4), 41–53 (2008)
M.R. Nasresfahani, M.J. Rajabloo, Research on the effect of pouring temperature on hot-tear susceptibility of A206 alloy by simulation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45(5), 1827–1833 (2014)
J.Z. Zhu, J.Z. Guo, M. Samonds, Numerical modeling of hot tearing formation in metal casting and its validations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 87, 289–308 (2011)
Y.Q. Li, J.F. Wang, W.J. Gou, Electron theory analysis on Sn improving property of Mg–Al alloy. Foundry 61(9), 995–997 (2012)
T.W. Clyne, G.J. Davies, Volume contractions accompanying solidification of aluminium–copper alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 12(5), 233–238 (1978)
Z. Wang, Y.D. Huang, A. Srinivasan, Z. Liu, F. Beckmann, K.U. Kainer, N. Hort, Experimental and numerical analysis of hot tearing susceptibility for Mg–Y alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 49(1), 353–362 (2014)
Z. Wang, Y.D. Huang, A. Srinivasan, Z. Liu, F. Beckmann, K.U. Kainer, N. Hort, Hot tearing susceptibility of binary Mg–Y alloy castings. Mater. Des. 47, 90–100 (2013)
J. Li, R. Chen, Y. Ma, W. Ke, Hot tearing of sand cast Mg-5 wt.% Y-4 wt.% RE (WE54) alloy. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 26(6), 728–734 (2013)
D.T. Zhang, M. Suzuki, K. Maruyama, Study on the texture of a friction stir welded Mg–Al–Ca alloy. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 19(5), 335–340 (2006)
Y.S. Wang, Q.D. Wang, W.J. Ding, C. Lu, Development of hot tear mechanism for cast alloys. Spec. Cast. Nonferrous Alloys 12(2), 48–50 (2000)
H. Ding, H.Z. Fu, Z.G. Liu, R.Z. Chen, B.C. Liu, Z.G. Zhong, D.Z. Tang, Compensation of solidification contraction and hot cracking tendency of alloys. Acta Metall. Sin. 33(9), 921–926 (1997)
Z.M. Zhang, T. Lii, C.J. Xu, X.F. Guo, Microstructure of binary Mg–Al eutectic alloy wires produced by the Ohno continuous casting process. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 21(4), 275–281 (2008)
Q.Y. Sun, D. Liu, L.P. Wang et al., Influences of rod diameter and sand-mould strength on hot tearing in Mg WE43A constrained rod castings. Int. J. Metalcast. 13, 407–416 (2019)
W.L. Cheng, M. Wang, Z.P. Que, C.X. Xu, J.S. Zhang, W. Liang, B.S. You, S.S. Park, Microstructure and mechanical properties of high speed indirect-extruded Mg–5Sn–(1,2,4) Zn alloys. J. Cent. South Univ. 20, 2643–2649 (2013)
W.L. Cheng, S.S. Park, W.N. Tang, Influence of rare earth on the microstructure and age hardening response of indirect-extruded Mg–5Sn–4Zn alloy. J. Rare Earths 28(5), 785–789 (2010)
W.L. Cheng, S.S. Park, W.N. Tang, B.S. You, B.H. Koo, Influence of alloying elements on microstructure and microhardness of Mg–Sn–Zn-based alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 20(12), 2246–2252 (2010)
G. Zhu, Z. Wang, W. Qiu et al., Effect of yttrium on hot tearing susceptibility of Mg–6Zn–1Cu–0.6Zr alloys. Int. J. Metalcast 14, 179–190 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by LiaoNing Revitalization Talents Program (No. XLYC1807021), Joint Research Fund Liaoning-Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science (2019JH3/30100014), and Technologies for Young and Middle-aged Scientists of Shenyang (No. RC180111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leng, F., Wang, F., Wang, Z. et al. Hot Tearing Behavior of \(\text{Mg}{-}4\text{Zn}{-}x\text{Sn}{-}0.6\text{Zr}\) Alloys. Inter Metalcast 15, 292–305 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00464-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00464-9