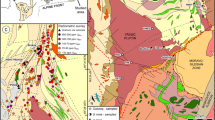
Abstract
A detailed study on petrology and mineral chemistry of 12 mantle xenoliths from Late Cretaceous basaltic lava flows at Daxizhuang has been conducted to constrain the nature and secular evolution of the Mesozoic lithospheric mantle beneath the eastern North China Craton (NCC). The Daxizhuang mantle xenoliths are mainly anhydrous spinel lherzolite, with subordinate olivine websterite and rare spinel wehrlite. Based on petrographic and geochemical characteristics, the Daxizhuang spinel lherzolite can be subdivided into two groups. Group 1 lherzolite has olivine with Fo contents from 89.4 to 90.6 and LREE-depleted through spoon-shaped to LREE-enriched REE (rare earth element) patterns in clinopyroxene grains, reflecting variable degrees of partial melt extraction (up to 18%) overprinted by later incipient metasomatism. In contrast, Group 2 lherzolite is strongly metasomatized and enriched in iron, as evidenced by relatively lower Fo contents of olivine (84.9 to 88.2) than that from the Group 1 lherzolite and convex-upward trace element patterns in clinopyroxene grains. The Daxizhuang olivine websterite and spinel wehrlite are rich in Fe, Al and low Mg# in olivine and pyroxenes, and slight Ti-enrichment in spinel. Numerical modeling of the Mg# shows that the Daxizhuang olivine websterite and wehrlite may have resulted from the reaction between host residual lherzolite and evolved, silicate melts at high melt/rock ratios. The result of this study indicates that the lithospheric mantle beneath Daxizhuang underwent multiple metasomatism through asthenosphere-lithosphere interaction, which plays an important role in the transformation of the lithospheric mantle of the NCC at least during Late Cretaceous time.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman L, Jelinek E, Medaris G, Ježek J, Siebel W, Strnad L (2009) Geochemistry of Fe-rich peridotites and associated pyroxenites from Horní Bory, bohemian massif: insights into subduction-related melt-rock reactions. Chem Geol 259(3):152–167
Anders E, Grevesse N (1989) Abundances of the elements: meteoritic and solar. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53(1):197–214
Arai S (1992) Chemistry of chromian spinel in volcanic rocks as a potential guide to magma chemistry. Mineral Mag 56(383):173–184
Arai S (1994) Characterization of spinel peridotites by olivine-spinel compositional relationships: review and interpretation. Chem Geol 113(3–4):191–204
Aulbach S, Stachel T, Viljoen KS, Brey GP, Harris JW (2002) Eclogitic and websteritic diamond sources beneath the Limpopo belts slab-melting the link? Contrib Mineral Petrol 143:56–70
Ballhaus C (1993) Redox states of the lithospheric and asthenospheric upper mantle. Contrib Mineral Petrol 114:331–348
Ballhaus C, Berry RF, Green DH (1991) High pressure experimental calibration of the olivine-orthopyroxene-spinel oxygen geobarometer implications for the oxidation-state of the upper mantle. Contrib Mineral Petrol 107(1):27–40
Beard AD, Downes H, Mason PRD, Vetrin VR (2007) Depletion and enrichment processes in the lithospheric mantle beneath the Kola peninsula (Russia): evidence from spinel peridotite and wehrlite xenoliths. Lithos 94(1–4):1–24
Bianchini G, Yoshikawa M, Sapienza GT (2010) Comparative study of ultramafic xenoliths and associated lavas from south-eastern Sicily: nature of the lithospheric mantle and insights on magma genesis. Mineral Petrol 98:111–121
Bodinier JL, Garrido CJ, Chanefo I, Bruguier O, Gervilla F (2008) Origin of Pyroxenite-Peridotite veined mantle by Refertilization reactions: evidence from the Ronda Peridotite (southern Spain). J Petrol 49(49):999–1025
Bodinier JL, Menzies MA, Shimizu N, Frey FA, McPherson E (2004) Silicate, hydrous and carbonate metasomatism at Lherz, France: contemporaneous derivatives of silicate melt-harzburgite reaction. J Petrol 45:299–320
Bodinier JL, Vasseur G, Vernieres J, Dupuy C, Fabries J (1990) Mechanisms of mantle Metasomatism: geochemical evidence from the Lherz Orogenic Peridotite. J Petrol 31(3):597–628
Boyd FR (1989) Compositional distinction between oceanic and cratonic lithosphere. Earth Planet Sci Lett 96(1–2):15–26
Brey GP, Köhler T (1990) Geothermobarometry in four-phase peridotite II: new thermobarometers, and practical assessment of existing thermobarometers. J Petrol 31(6):1353–1378
Chen MM, Tian W, Suzuki K, Tejada MLG, Liu FL, Senda R, Wei CJ, Chen B, Chu ZY (2014) Peridotite and pyroxenite xenoliths from Tarim, NW China: evidences for melt depletion and mantle refertilization in the mantle source region of the Tarim flood basalt. Lithos 204(0): 97–111
Chung SL (1999) Trace element and isotope characteristics of Cenozoic basalts around the tan lu fault with implications for the eastern plate boundary between north and South China. Geology 107(3):301–312
Coltorti M, Bonadiman C, Hinton RW, Siena F, Upton BGJ (1999) Carbonatite metasomatism of the oceanic upper mantle: evidence from clinopyroxenes and glasses in ultramafic xenoliths of Grande Comore, Indian Ocean. J Petrol 40(1):133–165
Dantas C, Ceuleneer G, Grégoire M, Python M, Freydier R, Warren J, Dick HJB (2007) Pyroxenites from the southwest Indian ridge, 9°–16°E: cumulates from incremental melt fractions produced at the top of a cold melting regime. J Petrol 48:647–660
Dantas C, Grégoire M, Koester E, Conceio RV, Rieck N (2009) The peridotite-websterite xenolith suite from northern Patagonia (Argentina): evidence of mantle-melt reaction processes. Lithos 107(1):107–120
Dautria JM, Dupuy C, Takherist D, Dostal, J. (1992) Carbonate metasomatism in the lithospheric mantle: peridotitic xenoliths from a melilititic district of the Sahara basin. Contrib Mineral Petrol 111(1): 37–52
Dobbs PN, Duncan DJ, Hu S, Shee SR, Colgan E, Brown MA, Smith CB, Allsopp HL (1994) The geology of the Mengyin kimberlites, Shandong, China. In: Meyer HOA, Leonardos OH (eds) Diamonds: characterization, genesis and exploration. CPRM, Brasilia, pp 106–115
Downes H (2001) Formation and modification of the shallow subcontinental lithospheric mantle: a review of geochemical evidence from ultramafic xenolith suites and tectonically emplaced ultramafic massifs of western and Central Europe. J Petrol 42:233–250
Downes H (2007) Origin and significance of spinel and garnet pyroxenites in the shallow lithospheric mantle: ultramafic massifs in orogenic belts in Western Europe and NW Africa. Lithos 99(1):1–24
Fan WM, Menzies MA (1992) Destruction of aged lower lithosphere and accretion of asthenosphere mantle beneath eastern China. Geotecton Metallog 16(3–4):171–180
Fan WM, Zhang HF, Baker J, Jarvis KE, Mason PRD, Menzies MA (2000) On and off the North China Craton: where is the Archaean keel? J Petrol 41(7):933–950
Faure M, Lin W, Breton NL (2001) Where is the North China-South China boundary in eastern China. Geology 29(2):119–122
Frey FA, Prinz M (1978) Ultramafic inclusions from San Carlos, Arizona: petrologic and geochemical data bearing on their petrogenesis. Earth Planet Sci Lett 38(1):129–176
Frost DJ, McCammon CA (2008) The redox state of Earth’s mantle. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 36(1):389–420
Gao S, Rudnick RL, Carlson RW, McDonough WF, Liu YS (2002) Re-Os evidence for replacement of ancient mantle lithosphere beneath the North China craton. Earth Planet Sci Lett 198(3–4):307–322
Gao S, Rudnick RL, Yuan HL, Liu XM, Liu YS, Xu WL, Ling WL, Ayers J, Wang XC, Wang QH (2004) Recycling lower continental crust in the North China craton. Nature 432(7019):892–897
Gilder SA, Leloup PH, Courtillot V, Chen Y, Coe RS (1999) Tectonic evolution of the Tancheng-Lujiang (tan-Lu) fault via middle Triassic to early Cenozoic paleomagnetic data. J Geophys Res Atmos 1041(B7):15365–15390
Grégoire M, Bell D, Le Roex A (2002) Trace element geochemistry of phlogopite-rich mafic mantle xenoliths: their classification and their relationship to phlogopite-bearing peridotites and kimberlites revisited. Contrib Mineral Petrol 142(5):603–625
Grégoire M, Chevet J, Maaloe S (2010) Composite xenoliths from Spitsbergen: evidence of the circulation ofMORB-related melts within the uppermantle. Geol Soc Lond, Spec Publ 337:71–86
Grégoire M, Langlade JA, Delpech G, Dantas C, Ceuleneer G (2009) Nature andevolution of the lithospheric mantle beneath the passive margin of East Oman: evidence from mantle xenoliths sampled by Cenozoic alkaline lavas. Lithos 112:203–216
Grégoire M, Cottin JY, Giret A, Mattielli N, Weis D (1998) The metaigneous xenoliths from Kerguelen archipelago: evidence of a continent nucleation in an oceanic setting. Contrib Mineral Petrol 133:259–283
Grégoire M, McInnes BIA, O'Reilly SY (2001) Hydrous metasomatism of oceanic subarc mantle, Lihir, Papua New Guinea. Part 2. Trace element characteristics of slab derived fluids. Lithos 59:91–108
Grégoire M, Moine BN, O'Reilly SY, Cottin JY, Giret A (2000) Trace element residence and partitioning in mantle xenoliths metasomatized by highly alkaline, silicate- and carbonate-rich melts (Kerguelen Islands, Indian Ocean). J Petrol 41:477–509
Griffin WL, O’Reilly SY, Ryan CG (1999) The composition and origin of sub-continental lithospheric mantle. In: Fei Y, Bertka CM, MysenBJ (eds) Mantle petrology: field observations and high-pressure experimentations: a tribute to Francis R. (Joe) Boyd. The GeochemicalSociety Special Publications, Houston, pp 13–45
Griffin WL, O'Reilly SY, Ryan CG (1992) Composition and thermal structure of the lithosphere beneath South Africa, Siberia and China: proton microprobe studies. International symposium on Cenozoic volcanic rocks and deep-seated xenoliths of China and its environs. Beijing, 65−66
Griffin WL, Zhang AD, O’Reilly SY, Ryan CG (1998) Phanerozoic evolution of the lithosphere beneath the Sino-Korean Craton (eds. Flower MFJ, Chung SL, Lo CH, Lee TY) am Geophys union, Washington, DC, Geodyn Ser 7:107–126
Hart SR, Dunn T (1993) Experimental cpx/melt partitioning of 24 trace elements. Contrib Mineral Petrol 113(1):1–8
Hauri EH, Hart SR (1994) Constraints on melt migration from mantle plumes: a trace element study of peridotite xenoliths from Savai'i, Western Samoa. J Geophys Res-Sol Earth 99(B12):24301–24321
Hauri EH, Shimizu N, Dieu JJ, Hart SR (1993) Evidence for hotspot-related carbonatite metasomatism in the oceanic upper mantle. Nat Int W J Sci 365(6443):221–227
Hellebrand E, Snow JE, Dick HJ, Hofmann AW (2001) Coupled major and trace elements as indicators of the extent ofmelting in mid-ocean-ridge peridotites. Nature 410:677–681
Ionov DA, Chanefo I, Bodinier JL (2005) Origin of Fe-rich peridotite and wehrlites from Tok, SE Siberia by reactive melt percolation in refractory mantle peridotites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 150(3):335–353
Jacob D (2004) Nature and origin of eclogite xenoliths from kimberlites. Lithos 77:295–316
Johnson KTM (1998) Experimental determination of partition coefficients for rare earth and high-field-strength elements between clinopyroxene, garnet, and basaltic melt at high pressures. Contrib Mineral Petrol 133(1–2):60–68
Johnson KTM, Dick HJB, Shimizu N (1990) Melting in the oceanic upper mantle: an ion microprobe study of diopsides in abyssal peridotites. J Geophys Res 95:2661–2678
Kelemen PB, Joyce DB, Webster JD, Holloway JR (1990) Reaction between ultramafic rock and fractionating basaltic magma II. Experimental investigation of reaction between olivine Tholeiite and Harzburgite at 1150-1050°C and 5 kb. J Petrol 31(1):99–134
Li ZX (1994) Collision between the north and South China blocks: crustal-detachment model for suturing in the region east of the tan-Lu fault. Geology 22(8):739–742
Liu DY, Nutman AP, Compston W, Wu JS, Shen QH (1992) Remnants of ≥ 3800 Ma crust in the Chinese part of the Sino-Korean craton. Geology 20(4):339–342
Liu YS, Gao S, Lee CTA, Hu SH, Liu XM, Yuan HL (2005) Melt-peridotite interactions: links between garnet pyroxenite and high-mg# signature of continental crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett 234(1):39–57
Mattielli N, Weis D, Gregoire M, Mennessier J, Cottin J, Giret A (1996) Kerguelen basic and ultrabasic xenoliths: evidence for long-lived Kerguelen hotspot activity. Lithos 37(1):261–280
McDonough WF, Sun SS (1995) The composition of the earth. Chem Geol 120(3–4):223–253
Menzies MA, Fan WM, Zhang M (1993) Paleozoic and Cenozoic lithoprobes and the loss of >120 km of Archean lithosphere, Sino-Korean craton, China. In: Prichard, H. M., alabaster, T., Harris, N. B. W., and Neary, C. R. Eds., magmatic processes and plate tectonics. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 76(1):71–81
Menzies MA, Xu YG, Zhang HF, Fan WM (2007) Integration of geology, geophysics and geochemistry: a key to understanding the North China Craton. Lithos 96(1–2):1–21
Morishita T, Arai S (2003) Evolution of spinel–pyroxene symplectite in spinel– lherzolites from the Horoman complex, Japan. Contrib Mineral Petrol 144:509–522
Navon O, Stolper E (1987) Geochemical consequences of melt percolation: the upper mantle as a chromatographic column. J Geol 95(3):285–307
Nimis P, Taylor WR (2000) Single clinopyroxene thermobarometry for garnet peridotites. Part I Calibration and testing of a Cr-in-Cpx barometer and an enstatite-in-Cpx thermometer. Contrib Mineral Petrol 139 (5):541–554
Okay AI, Celal AM, Şengör (1992) Evidence for intracontinental thrust-related exhumation of the ultra-high-pressure rocks in China. Geology 20(5):411–414
Pearson DG, Nowell GM (2004) Re-Os and Lu-Hf isotope constraintson the origin and age of pyroxenites from the Beni Bousera peridotite massif implications for mixed peridotite-pyroxenite mantle sources. J Petrol 45(2):439–455
Peslier AH, Francis D, Ludden J (2002) The lithospheric mantle beneath continental margins: melting and melt-rock reaction in Canadian cordillera xenoliths. J Petrol 43(11):2013–2047
Pouchou JL, Pichoir F (1991) Quantitative analysis of homogeneous or stratified microvolumes applying the model “PAP”. In: Heinrich KFJ, Newbury DE (eds) Electron probe quantification. Plenum, New York, pp 31–75
Qi L, Grégoire DC (2000) Determination of trace elements in twenty six Chinese geochemistry reference materials by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Geostand Geoanal Res 24(1):51–63
Rudnick RL, McDonough WF, Chappell BW (1993) Carbonatite metasomatism in the northern Tanzanian mantle: petrographic and geochemical characteristics. Earth Planet Sci Lett 114(4):463–475
Stagno V, Ojwang DO, McCammon CA, Frost DJ (2013) The oxidation state of the mantle and the extraction of carbon from Earth’s interior. Nature 493(7430):84–88
Streckeisen A (1976) To each plutonic rock its proper name. Earth Sci Rev 12(1):1–33
Tang YJ, Zhang HF, Ying JF, Su BX (2013) Widespread refertilization of cratonic and circum-cratonic lithospheric mantle. Earth Sci Rev 118:45–68
Teitchou MI, Grégoire M, Temdjim R, Ghogomu RT, Ngwa C, Aka FT (2011) Mineralogical and geochemical fingerprints of mantle metasomatism beneath Nyos volcano (Cameroon volcanic line). Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 478:193–210
Tursack E, Liang Y (2012) A comparative study of melt–rock reactions in the mantle: laboratory dissolution experiments and geological field observations. Contrib Mineral Petrol 163:861–876
Ulmer P (1989) The dependence of the Fe2+-mg cation-partitioning between olivine and basaltic liquid on pressure, temperature and composition. Contrib Mineral Petrol 101(3):261–273
Vernières L, Godard M, Bodinier JL (1997) Plate model for the simulation of trace element fractionation during partial melting and magma transport in the Earth's upper mantle. J Geophys Res 102:24771–24784
Walter MJ (2003) Melt extraction and compositional variability in mantle lithosphere. Treatise on geochemistry 2(1):363–394
Wells PRA (1977) Pyroxene thermometry in simple and complex systems. Contrib Mineral Petrol 62(2):129–139
Wilshire HG, Shervais JW (1975) Al-augite and Cr-diopside ultramafic xenoliths in basaltic rocks from western United States. Phys Chem Earth 9(2):257–272
Witteickschen G, Seck HA (1991) Solubility of Ca and Al in orthopyroxene from spinel peridotite: an improved version of an empirical geothermometer. Contrib Mineral Petrol 106(4):431–439
Wood BJ (1990) An experimental test of the spinel peridotite oxygen barometer. J Geophys Res 95(B10):15845–15851
Xiao Y, Teng FZ, Zhang HF, Yang W (2013) Large magnesium isotope fractionation in peridotite xenoliths from eastern North China craton: product of melt–rock interaction. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 115:241–261
Xiao Y, Zhang HF, Fan WM, Ying JF, Zhang J, Zhao XM, Su BX (2010) Evolution of lithospheric mantle beneath the tan-Lu fault zone, eastern North China Craton: evidence from petrology and geochemistry of peridotite xenoliths. Lithos 117(1):229–246
Xu WL, Zhou QJ, Pei FP, Yang DB, Gao S, Li QL, Yang YH (2013) Destruction of the North China Craton: delamination or thermal/chemical erosion? Mineral chemistry and oxygen isotope insights from websterite xenoliths. Gondwana Res 23(1):119–129
Xu XS, O'Reilly SY, Griffin WL, Zhou, XM, Huang, XL (1998) The nature of the Cenozoic lithosphere of Nushan, Eastern China (eds. Flower MFJ, Chung SL, Lo CH, Lee TY) Am Geophys Union, Washington, DC, Geodyn Ser 27:167–196
Xu YG (2001) Thermo-tectonic destruction of the Archean lithospheric keel beneath the Sino-Korean Craton in China: evidence, timing and mechanism. Phys Chem Earth Part A Solid Earth Geod 26(9):747–757
Xu YG, Lin CY, Shi LB (1999) The geotherm of the lithosphere beneath Qilin, SE China: a re-appraisal and implications for P-T estimation of Fe-rich pyroxenites. Lithos 47(3):181–193
Xu YG, Mercier J, Menzies MA, Ross JV, Harte B, Lin CY, Shi LB (1996) K-rich glass-bearing wehrlite xenoliths from Yitong, northeastern China: petrological and chemical evidence for mantle metasomatism. Contrib Mineral Petrol 125(4):406–420
Xu YG, Sun M, Yan W, Liu Y, Huang XL (2002) Xenolith evidence for polybaric melting and stratification of the upper mantle beneath South China. J Asian Earth Sci 20(8):937–954
Yan J, Chen JF, Xie Z, Zhou TX (2003) Mantle xenoliths from late cretaceous basalt in eastern Shandong Province: new constraint on the timing of lithospheric thinning in eastern China. Chin Sci Bull 48(19):2139–2144
Yang JH, Wu FY, Wilde SA (2003) A review of the geodynamic setting of large-scale late Mesozoic gold mineralization in the North China Craton: an association with lithospheric thinning. Ore Geol Rev 23(3–4):125–152
Yang JH, Wu FY, Wilde SA, Belousova E, Griffin WL (2008) Mesozoic decratonization of the North China block. Geology 36:467–470
Yaxley GM, Crawford AJ, Green DH (1991) Evidence for carbonatite metasomatism in spinel peridotite xenoliths from western Victoria, Australia. Earth Planet Sci Lett 107(2):305–317
Yin A, Nie S (1993) An indentation model for the North China and South China collision and the development of the tan-Lu and Honam fault systems, East Asia. Tectonics 12(4):801–813
Ying J, Zhang H, Tang Y, Su B, Zhou X (2013) Diverse crustal components in pyroxenite xenoliths from Junan, Sulu orogenic belt: implications for lithospheric modification invoked by continental subduction. Chem Geol 356(3):181–192
Ying JF, Zhang HF, Kita N, Morishita Y, Shimoda G (2006) Nature and evolution of late cretaceous lithospheric mantle beneath the eastern North China Craton: constraints from petrology and geochemistry of peridotitic xenoliths from Jünan, Shandong Province, China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 244(3):622–638
Ying JF, Zhou XH, Zhang HF (2004) Geochemical and isotopic investigation of the Laiwu-Zibo carbonatites from western Shandong Province, China, and implications for their petrogenesis and enriched mantle source. Lithos 75(3–4):413–426
Yu SY, Xu YG, Ma JL, Zheng YF, Kuang YS, Hong LB, Ge WC, Tong LX (2010) Remnants of oceanic lower crust in the subcontinental lithospheric mantle: trace element and Sr-Nd-O isotope evidence from aluminous garnet pyroxenite xenoliths from Jiaohe, Northeast China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 297(3–4):413–422
Zhang HF (2005) Transformation of lithospheric mantle through peridotite-melt reaction: a case of Sino-Korean craton. Earth Planet Sci Lett 237(3):768–780
Zhang HF (2009) Peridotite-melt interaction: a key point for the destruction of cratonic lithospheric mantle. Chin Sci Bull 54:3417–3437
Zhang HF, Goldstein S, Zhou XH, Sun M, Zheng JP, Cai Y (2008) Evolution of subcontinental lithospheric mantle beneath eastern China: re-Os isotopic evidence from mantle xenoliths in Paleozoic kimberlites and Mesozoic basalts. Contrib Mineral Petrol 155(3):271–293
Zhang HF, Nakamura E, Kobayashi K, Ying JF, Tang YJ (2010) Recycled crustal melt injection into lithospheric mantle: implication from cumulative composite and pyroxenite xenoliths. Int J Earth Sci 99(6):1167–1186
Zhang HF, Nakamura E, Kobayashi K, Zhang J, Ying JF, Tang YJ, Niu LF (2007) Transformation of subcontinental lithospheric mantle through peridotite-melt reaction: evidence from a highly fertile mantle xenolith from a highly fertile mantle xenolith from the North China craton. Int Geol Rev 49(7):658–679
Zhang HF, Sun M, Zhou XH, Fan WM, Zhai MG, Ying JF (2002) Mesozoic lithosphere destruction beneath the North China Craton: evidence from major-, trace-element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotope studies of Fangcheng basalts. Contrib Mineral Petrol 144(2):241–253
Zhang HF, Ying JF, Xu P, Ma YG (2004) Mantle olivine xenocrysts entrained in Mesozoic basalts from the North China craton: implication for replacement process of lithospheric mantle. Chin Sci Bull 49(9):961–966
Zhang J, Zhang HF, Kita N, Gen SM, Morishita Y, Ying JF, Tang YJ (2011) Secular evolution of the lithospheric mantle beneath the eastern North China craton: evidence from peridotitic xenoliths from late cretaceous mafic rocks in the Jiaodong region, east-Central China. Int Geol Rev 53(2):182–211
Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA, Li SZ (2005) Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: key issues revisited. Precambrian Res 136(2):177–202
Zhao XM, Zhang HF, Zhu XK, Zhu B, Cao HH (2015) Effects of melt percolation on iron isotopic variation in peridotites from Yangyuan, North China Craton. Chem Geol 401:96–110
Zheng JP, Griffin WL, O’Reilly SY, Yu CM, Zhang HF, Pearson N, Zhang M (2007) Mechanism and timing of lithospheric modification and replacement beneath the eastern North China Craton: Peridotitic xenoliths from the 100 Ma Fuxin basalts and a regional synthesis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71(21):5203–5225
Zheng JP, Griffin WL, O'Reilly SY, Yang J, LI TF (2006) Mineral chemistry of Peridotites from Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic lithosphere: constraints on mantle evolution beneath eastern China. J Petrol 47(11):2233–2256
Zheng JP, O'reilly SY, Griffin WL, Lu FX, Zhang M (1998) Nature and evolution of Cenozoic lithospheric mantle beneath Shandong peninsula, Sino-Korean Craton, eastern China. Int Geol Rev 40(6):471–499
Zhi XC, Song Y, Frey FA, Feng J, Zhai M (1990) Geochemistry of Hannuoba basalts, eastern China: constraints on the origin of continental alkalic and tholeiitic basalt. Chem Geol 88:1–33
Zhu R, Xu YG, Zhu G, Zhang HF, Xia QK, Zheng TY (2012) Destruction of the North China Craton. Sci China Earth Sci 55:1565–1587
Zhu RX, Chen L, Wu FY, Liu JL (2011) Timing, scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton. Sci China Earth Sci 54:789–797
Acknowledgements
We thank Qian Mao and YuGuang Ma for microprobe analyses at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. This work was financially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (41673021 and 41973015 to XinMiao Zhao; 41688103 to HongFu Zhang). We warmly thank Michel Grégoire and Elena Shchukina for their constructive comments and suggestions, and associate editor Shah Wali Faryad for his excellent editorial work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: S. W. Faryad
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Wang, H., Li, Z. et al. Multi-stage metasomatism of lithospheric mantle by asthenosphere-derived melts: evidence from mantle xenoliths in daxizhuang at the eastern North China craton. Miner Petrol 114, 141–159 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-020-00697-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-020-00697-w