Abstract
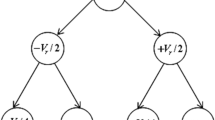
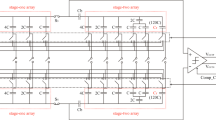
A combinational method, based on hybrid and junction splitting techniques, is used to realize a 4 bit high energy efficient SC SAR ADC. The hybrid switching scheme is very energy efficient in which the first three comparison cycles do not consume any energy. In junction split technique, the total value of capacitors does not remain constant. Rather capacitors are appended as bits are being determined successively. The present method combines the features of these two methods to realize an even more energy efficient SC SAR ADC. Reset energy, in some cases, can seriously impact the overall efficiency of a SC SAR ADC. A study has been made about the normal reset energy and two step reset energy for the different cases. A table has been drawn to show the overall energy efficiency for normal conversion, conversion with single step reset and lastly conversion with two step reset for all the architectures.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari M, Hashemipour O, Khateb F, Moradi F (2018) An energy-efficient DAC switching algorithm based on charge recycling method for SAR ADCs. Microelectron J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2018.10.011
Akbari M, Hashemipour O, Nazari M, Moradi F (2019a) A charge sharing-based switching scheme for SAR ADCs. Int J Circuit Theory Appl. https://doi.org/10.1002/cta.2635
Akbari M, Nazari M, Hashemipour O, Lee K-S (2019b) Energy-efficient and area-efficient switching schemes for SAR ADCs. In: IEEE International midwest symposium on circuits and systems—MWSCAS 2019, USA
Baek S-U, Lee S-W, Lee M (2018a) Scaled-down reference switching scheme for low-power SAR ADCs. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process 97(1):143–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1279-1
Baek S-U, Lee K-Y, Lee M (2018b) Energy-efficient switching scheme for SAR ADC using zero-energy dual capacitor switching. Analog Integr Circuits Sig Process 94(2):317–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-017-1101-5
Chang AHT (2013) Low-power high-performance SAR ADC with redundancy and digital background calibration. Doctorate of Philosophy Dissertation, MIT, 2013
Chen Y, Zhuang Y, Tang H (2019a) A highly energy-efficient, area-efficient switching scheme for SAR ADC in biomedical applications. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01502-1
Chen Y, Zhuang Y, Tang H (2019b) An ultra-low power consumption high-linearity switching scheme for SAR ADC. J Circuits Syst Comput. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126620500863
Chen Y, Zhuang Y, Tang H (2019c) A 99.8% energy-reduced two-stage mixed switching scheme for SAR ADC without reset energy. Circuits Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01151-9
Ding R, Dong S, Liu S, Sun D, Zhu Z (2019a) A novel split capacitor array switching scheme with proportional coefficient for SAR ADC. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 98(3):597–605
Ding R, Dong S, Sun D, Liu S, Zhu Z (2019b) Energy-efficient and two-step structure switching scheme based on reference-free for SAR ADC. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process 99(1):209–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01420-2
Ghasemi AR, Saberi M, Lofti R (2017) A low-power capacitor switching scheme with low common-mode voltage variation for successive approximation ADC. Microelectron J 61(10):15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2016.12.009
Ghoshal P, Moydudy M, Hossain M, Sen SK (2017) An energy and area efficient SC SAR ADC structure based on multi level capacitor switching technique. In: IEEE International conference: devices for integrated circuit (DevIC), pp 574–577, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/devic.2017.8074016
Ghoshal P, Dey C, Sen SK (2019) A 4 bit combinational hybrid-junction splitting technique for realization of an energy efficient SC SAR ADC. In: IEEE Conference, OPTRONIX, 2019
Ginsberg BP, Chandrakasan AP (2005) An energy-efficient charge recycling approach for a SAR converter with capacitive DAC. In: Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems, ISCAS, vol 1, pp 184–187, 2005
Ginsberg BP, Chandrakasan AP (2007) 500-MS/s 5-bit ADC in 65-nm CMOS with split capacitor array DAC. IEEE J Solid State Circuits 42(4):739–747
Hariprasath V, Guerber J, Lee S-H, Moon U-K (2010) Merged capacitor switching based SAR ADC with highest switching energy-efficiency. Electron Lett 46(9):620–621. https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2010.0706
Lee J-S, Park I-C (2008) Capacitor array structure and switch control for energy-efficient SAR analog-to-digital converters. 87(1). 978-1-4244-1684-4/08/$25.00 ©2008 IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0707-3
Liang H, Ding R, Liu S, Zhu Z (2018) Energy-efficient and area-saving asymmetric capacitor switching scheme for SAR ADCs. J Circuits Syst Comput. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126618501098
Liu J, Liu S, Huang L, Zhu Z (2018a) A highly energy-efficient switching scheme for SAR ADC with the redundant capacitance splitting technology. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process 97(4):89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1302-6
Liu S, Han H, Ding R (2018b) Energy-efficient switching scheme with 93.41% reduction in capacitor area for SAR ADC. J Circuits Syst Comput. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218126619300101
Liu J, Ding R, Liu S, Zhu Z (2018c) A highly energy-efficient, highly area-efficient capacitance multiplexing switching scheme for SAR ADC. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process 96(4):207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1217-2
Ma R, Bai WB, Zhu ZM (2015) An energy-efficient and highly linear switching capacitor procedure for SAR ADCs. J Semicond 36(5):05501401–05501406. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-4926/36/5/055014
Osipov D, Paul S (2016a) Two step reset method for energy efficient SAR ADC switching schemes. Electron Lett 52(10):816–817. https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2016.0890
Osipov D, Paul S (2016b) Two advanced energy-back SAR ADC architectures with 99.21 and 99.37% reduction in switching energy. Analog Integr Circuits Signals Process 87(1):81–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0707-3
Sanyal A, Sun N (2014) An energy-efficient low frequency-dependence switching technique for SAR ADCs. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs 61(11):294–298. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2014.2304890
Wang F, Wu J (2019) A low energy switching scheme for SAR ADC with MSB-splitting DAC structure. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process 100(6):79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01449-3
Wang H, Xie W, Chen Z, Cai S (2019) A capacitor-splitting switching scheme with low total power consumption for SAR ADCs. J Circuits Syst Comput. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126619200020
Xie L, Wen WJ, Liu J, Wang Y (2014) Energy efficient hybrid capacitor switching scheme for SAR ADC. Electron Lett 50(1):22–23. https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2013.279
Xie L, Nie W, Yang X, Zhou M (2018) A group reset method for energy-efficient SAR ADC switching schemes. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process 96:183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1201-x
Yue P, Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhu Z (2019) A 92.1% area-efficient charge sharing switching scheme with near zero reset energy for SAR ADCs. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process 101:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01522-x
Zhang M, Cai Q, Fan X (2018) A high-speed, high-linearity, and energy-efficient subranging single-side capacitor switching scheme for SAR ADCs. Analog Integr Circuits Signals Process 96(4):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1183-8
Zhou R, Liu S, Liu J, Ding R, Wang J, Huang S, Zhu Z (2019) A 96.88% area-saving and 99.72% energy-reduction switching scheme for SAR ADC with a novel two-step quantisation technique. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01455-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghoshal, P., Dey, C. & Sen, S.K. A 4 bit highly energy and area efficient SC SAR ADC based on a combinational technique with reduced reset energy. Microsyst Technol 26, 1395–1404 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04672-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04672-0