Abstract
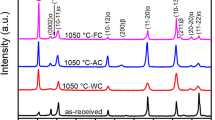
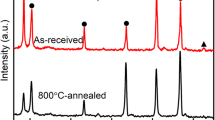
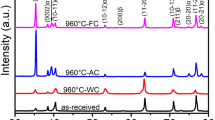
The microstructure and hot tensile behaviors of the different heat-treated Ti2AlNb sheets were investigated by backscattered electron image (BSE), electron backscattering diffraction (EBSD), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and tensile tests. The grain sizes and contents of α2, B2/β and O phases were quantitatively studied. As the heating time increases at 970 °C, the mean grain size and content of α2-phase increased. The grain shapes and distributions of the O-phase lamellar grains were affected by the heat treatments. The plastic deformation promoted the O → B2/β phase transition and the globularization of O-phase lamellar grains at 970 °C. Calculated by the creep equation and the iso-stress method, the grain size exponent was \(\mu = 1.1\) and the relationship between the material constants of B2/β and O phase was \(K_{{\text{O}}} = 1.14K_{{{\text{B}}2/\upbeta }}\).













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shao HP, Wang Z, Lin T, Ye Q, Guo ZM. Preparation of TiAl alloy powder by high-energy ball milling and diffusion reaction at low temperature. Rare Met. 2018;37(1):21.
He YS, Hu R, Luo WZ, He T, Lai YJ, Du YJ, Liu XH. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a new Ti2AlNb-based alloy after aging treatment. Rare Met. 2018;37(11):942.
Chowdhary NS, Graham HC, Hinze JW. Properties of high temperature alloys. Princeton: Electrochemical Society; 1977. 668.
Banerjee D, Gogia AK, Nandy TK, Joshi VA. A new ordered orthorhombic phase in a Ti2AlNb alloy. Acta Mater. 1988;36(4):871.
Boehlert CJ. Part III. The tensile behavior of Ti–Al–NbO+BCC orthorhombic alloys. Metall Trans A. 2001;2(8):1977.
Chen W, Zhang JW, Xu L, Lu B. Development of Ti2AINb alloys: opportunities and challenges. Adv Mater Process. 2014;172(5):23.
Boehlert CJ, Majumdar BS, Seetharaman V, Miracle DB. Part I. The microstructural evolution in Ti-Al-Nb O + BCC orthorhombic alloys. Metall Trans A. 1999;30(9):2305.
Jiao XY, Wang DJ, Yang JL, Liu ZQ, Liu G. Microstructure analysis on enhancing mechanical properties at 750 °C and room temperature of Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo alloy tubes fabricated by hot gas forming. J Alloy Compd. 2019;789:639.
Cheng YJ, Li SQ, Liang XB, Zhang JW. Effect of deformed microstructure on mechanical properties of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2006;16(A03):2058.
Shagiev MR, Galeyev RM, Valiakhmetov OR, Safiullin RV. Improved mechanical properties of Ti2AlNb-based intermetallic alloys and composites. Adv Mater Res. 2009;59:105.
Zhang ZX, Qu SJ, Feng AH, Shen J, Chen DL. Hot deformation behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy: Effect of initial microstructure. J Alloy Compd. 2017;718(25):170.
Beer AG, Barnett MR. Influence of initial microstructure on the hot working flow stress of Mg-3Al-1Zn. Mat Sci Eng A. 2006;423(1):292.
Lin YC, Jiang XY, Shuai CJ, Zhao CY, He DG, Chen MS, Chen C. Effects of initial microstructures on hot tensile deformation behaviors and fracture characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Mat Sci Eng A. 2018;711(10):293.
Kong BB, Liu G, Wang DJ, Wang KH, Yuan SJ. Microstructural investigations for laser welded joints of Ti–22Al–25Nb alloy sheets upon large deformation at elevated temperature. Mater Design. 2016;90(15):723.
Lin P, He ZB, Yuan SJ, Shen J. Tensile deformation behavior of Ti–22Al–25Nb alloy at elevated temperatures. Mat Sci Eng A. 2012;556:617.
Lin P, He Z, Yuan S, Shen J, Huang Y, Liang X. Instability of the O-phase in Ti–22Al–25Nb alloy during elevated-temperature deformation. J Alloy Compd. 2013;578(25):96.
Wu Y, Liu G, Liu ZQ, Tang ZJ, Wang B. Microstructure, mechanical properties and post-weld heat treatments of dissimilar laser-welded Ti2AlNb/Ti60 sheet. Rare Met. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-1047-5.
Wu Y, Liu G, Liu ZQ, Wang B. Formability and microstructure of Ti-22Al-24.5Nb-0.5Mo rolled sheet within hot gas bulging tests at constant equivalent strain rate. Mater Design. 2016;108(15):298.
Du Z, Jiang S, Zhang K, Lu Z, Li B, Zhang D. The structural design and superplastic forming/diffusion bonding of Ti2AlNb based alloy for four-layer structure. Mater Design. 2016;104(15):242.
Wang CW, Zhao T, Wang G, Gao J, Fang H. Superplastic forming and diffusion bonding of Ti–22Al–24Nb alloy. J Mater Process Tech. 2015;222:122.
Lin J. Selection of material models for predicting necking in superplastic forming. Int J Plast. 2003;19(4):469.
Yang L, Wang B, Liu G, Zhao H, Xiao W. Behavior and modeling of flow softening and ductile damage evolution in hot forming of TA15 alloy sheets. Mater Design. 2015;85:135.
Ji H, Liu J, Wang B, Fu X, Xiao W, Hu Z. A new method for manufacturing hollow valves via cross wedge rolling and forging: Numerical analysis and experiment validation. J Mater Process Tech. 2017;240:1.
Sagar PK, Banerjee D, Muraleedharan K, Prasad YVRK. High-temperature deformation processing of Ti-24Al-20Nb. Metall Trans A. 1996;27(9):2593.
Muraleedharan K, Nandy TK, Banerjee D, Lele S. Phase stability and ordering behaviour of the O phase in Ti-Al-Nb alloys. Intermetallics. 1995;3(3):187.
Muraleedharan K, Banerjee D, Banerjee S, Lele S. The α2 to O transformation in Ti–Al–Nb alloys. Philos Mag. 1995;71(5):1011.
Dang W, Li J, Zhang T, Kou H. Microstructure and phase transformation in Ti-22Al-(27–x)Nb-xZr alloys during continuous heating. J Mater Eng Perform. 2015;24(10):3951.
Sherby OD, Klundt RH, Miller AK. Flow stress, subgrain size, and subgrain stability at elevated temperature. Metall Trans A. 1977;8(6):83.
Wang SH, Kao PW. The strengthening effect of TiAl3 in high temperature deformation of Al–TiAl3 composites. Acta Mater. 1998;46(8):2675.
Alabort E, Putman D, Reed RC. Superplasticity in Ti–6Al–4V: characterisation, modelling and applications. Acta Mater. 2015;95(15):428.
Boehlert CJ. The phase evolution and microstructural stability of an orthorhombic Ti-23Al-27Nb alloy. J Phase Equilib. 1999;20(2):101.
Cao Y, Ni S, Liao X, Song M, Zhu Y. Structural evolutions of metallic materials processed by severe plastic deformation. Mat Sci Eng R. 2018;133:1.
Mukherjee AK, Bird JE, Dorn JE. The stress/creep rate behavior of precipitation-hardened alloys. Trans ASM. 1969;62:155.
Wu Y, Wang D, Liu Z, Liu G. A unified internal state variable material model for Ti2AlNb-alloy and its applications in hot gas forming. Int J Mech Sci. 2019;164:105.
Ghosh AK, Hamilton CH. Mechanical behavior and hardening characteristics of a superplastic Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Metall Trans A. 1979;10(6):699.
Bai Q, Lin J, Dean TA, Balint DS, Gao T, Zhang Z. Modelling of dominant softening mechanisms for Ti-6Al-4V in steady state hot forming conditions. Mat Sci Eng A. 2013;559(1):352.
Wang KH, Liu G, Zhao J, Huang K, Wang LL. Experimental and modelling study of an approach to enhance gas bulging formability of TA15 titanium alloy tube based on dynamic recrystallization. J Mater Process Tech. 2018;259:387.
Li HW, Wu C, Yang H. Crystal plasticity modeling of the dynamic recrystallization of two-phase titanium alloys during isothermal processing. Int J Plast. 2013;51:271.
Cheong BH, Lin J, Ball AA. Modelling the effects of grain-size gradients on necking in superplastic forming. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2003;134(1):10.
Bae DH, Ghosh AK. Grain size and temperature dependence of superplastic deformation in an Al–Mg alloy under isostructural condition. Acta Mater. 2000;48(48):1207.
Langdon TG. A unified approach to grain boundary sliding in creep and superplasticity. Acta Mater. 1994;42(7):2437.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51805256).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Fan, RL., Zhou, XJ. et al. Microstructure and hot flow stress at 970 °C of various heat-treated Ti2AlNb sheets. Rare Met. 39, 695–706 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01408-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01408-2