Abstract
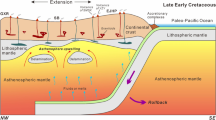
The North China Craton (NCC) is the best example of an Archean craton that has lost its stability in the Late Mesozoic. Although the cratonic destruction is generally considered to have occurred in the Eastern Block and reached a peak in the Early Cretaceous, the exact areal extent of cratonic destruction is debated, especially the southern and northern margin of the NCC. Here we report geochronology, geochemical and Hf isotopic data of the Late Mesozoic granitoids from Lushi polymetal mineralization area (LPMA) in the southern margin of NCC. These results provide new insights into the destruction in the southern margin of the NCC during the Late Mesozoic. Zircon U-Pb dating indicates that eight granitoids intruded in the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous (136.8–154.1 Ma), respectively. Geochemical signatures define these granitoids being A-type or I-type granite that formed in an extension setting. In addition, Hf isotopic compositions of zircons from these granitoids vary in a relatively large range, with εHf(t) values and TDM2 ages ranginge from -26.1 to +15.2 and 215 to 2 849 Ma, respectively. The parental magmas were likely derived from diverse sources, including materials of the partial melting of ancient lower crust and mantle-derived mafic magmas in various proportions. Combining with previous studies on the contemporaneous magma-tectonic activities in circum of NCC, we suggest that the rim of NCC was already unstabilized from the Late Jurassic in the LPMA. The subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate was the main trigger to the destruction of the southern margin of NCC, which was responsible for the lithospheric extension and thinning, extensive magmatism and mineralization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao, Z. W., Wang, C. Y., Zhao, T. P., et al., 2014. Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic Granites and Mo Mineralization of the Luanchuan Ore Field in the East Qinling Mo Mineralization Belt, Central China. Ore Geology Reviews, 57: 132–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.09.008
Bao, Z. W., Zeng, Q. S., Zhao, T. P., et al., 2009. Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Ore-Related Nannihu and Shangfanggou Granite Porphyries from East Qinling Belt and Their Constraints on the Molybdenum Mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25: 2523–2536 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Blichert-Toft, J., Albarède, F., 1998. The Lu-Hf Isotope Geochemistry of Chondrites and the Evolution of the Mantle-Crust System. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 148(1/2): 243–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(97)00040-x
Bryant, D. L., Ayers, J. C., Gao, S., et al., 2004. Geochemical, Age, and Isotopic Constraints on the Location of the Sino-Korean/Yangtze Suture and Evolution of the Northern Dabie Complex, East Central China. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 116(5): 698–717. https://doi.org/10.1130/b25302.2
Chen, L., 2009. Lithospheric Structure Variations between the Eastern and Central North China Craton from S- and P-Receiver Function Migration. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 173(3/4): 216–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pepi.2008.11.011
Chen, Y. J., Li, C., Zhang, J., et al., 2000. Sr and O Isotopic Characteristics of Porphyries in the Qinling Molybdenum Deposit Belt and Their Implication to Genetic Mechanism and Type. Science China Earth Sciences, 43(S1): 82–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02911935
Ding, L. X., Ma, C. Q., Li, J. W., et al., 2011. Timing and Genesis of the Adakitic and Shoshonitic Intrusions in the Laoniushan Complex, Southern Margin of the North China Craton: Implications for Post-Collisional Magmatism Associated with the Qinling Orogen. Lithos, 126(3/4): 212–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2011.07.008
Dong, Y. P., Liu, X. M., Zhang, G. W., et al., 2012. Triassic Diorites and Granitoids in the Foping Area: Constraints on the Conversion from Subduction to Collision in the Qinling Orogen, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 47: 123–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.06.005
Dong, Y. P., Santosh, M., 2016. Tectonic Architecture and Multiple Orogeny of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China. Gondwana Research, 29(1): 1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.009
Dong, Y. P., Zhang, G. W., Neubauer, F., et al., 2011. Tectonic Evolution of the Qinling Orogen, China: Review and Synthesis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(3): 213–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.002
Eby, G. N., 1990. The A-Type Granitoids: A Review of their Occurrence and Chemical Characteristics and Speculations on Their Petrogenesis. Lithos, 26(1/2): 115–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-4937(90)90043-z
Eby, G. N., 1992. Chemical Subdivision of the A-Type Granitoids: Petrogenetic and Tectonic Implications. Geology, 20(7): 641–644. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:csotat>2.3.co;2
Gao, S., Rudnick, R. L., Carlson, R. W., et al., 2002. Re-Os Evidence for Replacement of Ancient Mantle Lithosphere beneath the North China Craton. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 198(3/4): 307–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(02)00489-2
Gao, S., Zhang, J. F., Xu, W. L., et al., 2009. Delamination and Destruction of the North China Craton. Science Bulletin, 54(19): 3367–3378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0395-9
Griffin, W. L., O’Reilly, S. Y., Afonso, J. C., et al., 2009. The Composition and Evolution of Lithospheric Mantle: A Re-Evaluation and Its Tectonic Implications. Journal of Petrology, 50(7): 1185–1204. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egn033
Griffin, W. L., Pearson, N. J., Belousova, E., et al., 2000. The Hf Isotope Composition of Cratonic Mantle: LAM-MC-ICPMS Analysis of Zircon Megacrysts in Kimberlites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(1): 133–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-7037(99)00343-9
Griffin, W. L., Wang, X., Jackson, S. E., et al., 2002. Zircon Chemistry and Magma Mixing, SE China: In-situ Analysis of Hf Isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan Igneous Complexes. Lithos, 61(3/4): 237–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-4937(02)00082-8
Griffin, W. L., Zhang, A. D., O’Reilly, S. Y., et al., 1998. Phanerozoic Evolution of the Lithosphere beneath the Sino-Korean Craton. In: Flower, M., Chung, S.-L., Lo, C.-H., Lee, T.-Y., eds., Mantle Dynamics and Plate Interactions in East Asia. American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C.. 107–126
Hawkesworth, C. J., Kemp, A. I. S., 2006. Using Hafnium and Oxygen Isotopes in Zircons to Unravel the Record of Crustal Evolution. Chemical Geology, 226(3/4): 144–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.09.018
Hu, H., Li, J. W., McFarlane, C. R. M., et al., 2017. Textures, Trace Element Compositions, and U-Pb Ages of Titanite from the Mangling Granitoid Pluton, East Qinling Orogen: Implications for Magma Mixing and Destruction of the North China Craton. Lithos, 284-285: 50–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2017.03.025
Hu, H., Li, J. W., Deng, X. D., 2011. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating of Granitoid Intrusions in the Luonan-Lushi Area, Southern North China Craton: Implications for the Timing of Decratonization. Mineral Deposits, 30: 979–1001 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Huang, X. L., Zhong, J. W., Xu, Y. G., 2012. Two Tales of the Continental Lithospheric Mantle Prior to the Destruction of the North China Craton: Insights from Early Cretaceous Mafic Intrusions in Western Shandong, East China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 96: 193–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2012.08.014
King, S., 2005. Archean Cratons and Mantle Dynamics. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 234(1/2): 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.03.007
Koschek, G., 1993. Origin and Significance of the SEM Cathodoluminescence from Zircon. Journal of Microscopy, 171(3): 223–232. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2818.1993.tb03379.x
Li, J. W., Bi, S. J., Selby, D., et al., 2012a. Giant Mesozoic Gold Provinces Related to the Destruction of the North China Craton. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 349-350: 26–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2012.06.058
Li, J. W., Li, Z. K., Zhou, M. F., et al., 2012b. The Early Cretaceous Yangzhaiyu Lode Gold Deposit, North China Craton: A Link between Craton Reactivation and Gold Veining. Economic Geology, 107(1): 43–79. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.107.1.43
Li, N., Chen, Y. J., Pirajno, F., et al., 2012. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating, Trace Element and Hf Isotope Geochemistry of the Heyu Granite Batholith, Eastern Qinling, Central China: Implications for Mesozoic Tectono-Magmatic Evolution. Lithos, 142-143: 34–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2012.02.013
Li, N., Chen, Y. J., Ni, Z. H., et al., 2009. Characteristics of Ore Forming Fluid of the Yuchiling Porphyry Mo Deposit, Songxian County, Henan Province, and Its Geological Significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25: 2509–2522 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, N., Chen, Y. J., Zhang, H., et al., 2007. Molybdenum Deposits in East Qinling. Earth Science Frontiers, 14: 186–198 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, S. G., Xiao, Y. L., Liou, D. L., et al., 1993. Collision of the North China and Yangtse Blocks and Formation of Coesite-Bearing Eclogites: Timing and Processes. Chemical Geology, 109(1/2/3/4): 89–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(93)90063-o
Li, T. G., Wu, G., Chen, Y. C., et al., 2013. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Yinjiagou Complex in Western Henan Province, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29: 46–66 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Liu, R., Li, J. W., Bi, S. J., et al., 2013. Magma Mixing Revealed from in-situ Zircon U-Pb-Hf Isotope Analysis of the Muhuguan Granitoid Pluton, Eastern Qinling Orogen, China: Implications for Late Mesozoic Tectonic Evolution. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 102(6): 1583–1602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-013-0900-x
Liu, X. C., Jahn, B. M., Li, S. Z., et al., 2013. U-Pb Zircon Age and Geochemical Constraints on Tectonic Evolution of the Paleozoic Accretionary Orogenic System in the Tongbai Orogen, Central China. Tectonophysics, 599: 67–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2013.04.003
Liu, Y. S., Zong, K. Q., Kelemen, P. B., et al., 2008. Geochemistry and Magmatic History of Eclogites and Ultramafic Rocks from the Chinese Continental Scientific Drill Hole: Subduction and Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphism of Lower Crustal Cumulates. Chemical Geology, 247(1/2): 133–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.016
Ludwig, K. R. 2003. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel (No. 4). Berkeley Geochronology Center, Berkeley
Ma, C. Q., Ming, H. L., Yang, K. G., 2004. An Ordovician Magmatic Arc at the Northern Foot of Dabie Mountains: Evidence from Geochronology and Geochemistry of Intrusive Rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20: 393–402 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Maniar, P. D., Piccoli, P. M., 1989. Tectonic Discrimination of Granitoids. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101(5): 635–643. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:tdog>2.3.co;2
Mao, J. W., Pirajno, F., Xiang, J. F., et al., 2011. Mesozoic Molybdenum Deposits in the East Qinling-Dabie Orogenic Belt: Characteristics and Tectonic Settings. Ore Geology Reviews, 43(1): 264–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.07.009
Mao, J. W., Xie, G. Q., Bierlein, F., et al., 2008. Tectonic Implications from Re-Os Dating of Mesozoic Molybdenum Deposits in the East Qinling-Dabie Orogenic Belt. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72(18): 4607–4626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2008.06.027
Mao, J. W., Xie, G. Q., Pirajno, F., et al., 2010. Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous Granitoid Magmatism in Eastern Qinling, Central-Eastern China: SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Ages and Tectonic Implications. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 57(1): 51–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/08120090903416203
Mao, J. W., Xie, G. Q., Zhang, Z. H., et al., 2005. Mesozoic Large-Scale Metallogenic Pulses in North China and Corresponding Geodynamic Settings. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21: 169–188 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Mao, J. W., Ye, H. S., Wang, T., et al., 2009. Mineral Deposit Model of Mesozoic Porphyry Mo and Vein-Type Pb-Zn-Ag Ore Deposits in the Eastern Qinling, Central China and Its Implication for Prospecting. Geological Bulletin of China, 28: 72–79 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
McDonough, W. F., Sun, S. S., 1995. The Composition of the Earth. Chemical Geology, 120(3/4): 223–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(94)00140-4
Menzies, M. A., Fan, W. M., Zhang, M., 1993. Palaeozoic and Cenozoic Lithoprobes and the Loss of >120 km of Archaean Lithosphere, Sino-Korean Craton, China. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 76(1): 71–81. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.1993.076.01.04
Ratschbacher, L., Hacker, B. R., Calvert, A., et al., 2003. Tectonics of the Qinling (Central China): Tectonostratigraphy, Geochronology, and Deformation History. Tectonophysics, 366(1/2): 1–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-1951(03)00053-2
Ren, J. S., Chen, T. Y., 1989. Tectonic Evolution of the Continental Lithosphere in Eastern China and Adjacent Areas. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 3(1/2/3/4): 17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/0743-9547(89)90006-8
Ren, J. S., Chen, T. Y., Niu, B. G., 1992. Tectonic Evolution of the Continental Lithosphere of the East China and Adjacent Area and Relevant Mineralization. Science Press, Beijing. 230 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Rudnick, R. L., Fountain, D. M., 1995. Nature and Composition of the Continental Crust: A Lower Crustal Perspective. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(3): 267–310. https://doi.org/10.1029/95rg01302
Shu, T., Xu, H. J., Zhang, J. F., et al., 2019. Deformation Characteristics and Time of Taipingshan Folds in Fangshan Area, Beijing: Implications for Early Cretaceous Compressional Tectonics of North China Craton. Earth Science, 44(5): 1734–1748 (in Chinese with English Abstract) https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2018.119
Söderlund, U., Patchett, P. J., Vervoort, J. D., et al., 2004. The 176Lu Decay Constant Determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb Isotope Systematics of Precambrian Mafic Intrusions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 219(3/4): 311–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(04)00012-3
Sun, W. D., Ding, X., Hu, Y. H., et al., 2007. The Golden Transformation of the Cretaceous Plate Subduction in the West Pacific. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 262(3/4): 533–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2007.08.021
Tang, Y. J., Zhang, H. F., Deloule, E., et al., 2012. Slab-Derived Lithium Isotopic Signatures in Mantle Xenoliths from Northeastern North China Craton. Lithos, 149: 79–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2011.12.001
Wang, X. X., Wang, T., Jahn, B. M., et al., 2007. Tectonic Significance of Late Triassic Post-Collisional Lamprophyre Dykes from the Qinling Mountains (China). Geological Magazine, 144(5): 837–848. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0016756807003548
Wang, X. X., Wang, T., Ke, C. H., et al., 2015. Nd-Hf Isotopic Mapping of Late Mesozoic Granitoids in the East Qinling Orogen, Central China: Constraint on the Basements of Terranes and Distribution of Mo Mineralization. Acta Geologica Sinica—English Edition, 88(S2): 625–625. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.12374_60
Wang, X. X., Wang, T., Zhang, C. L., 2013. Neoproterozoic, Paleozoic, and Mesozoic Granitoid Magmatism in the Qinling Orogen, China: Constraints on Orogenic Process. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 72: 129–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.037
Wang, X., Griffin, W. L., Wang, Z. C., et al., 2003. Hf Isotope Composition of Zircons and Implication for the Petrogenesis of Yajiangqiao Granite, Hunan Province, China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(10): 995–998. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03184214
Wang, X. X., Wang, T., Qi, Q. J., et al., 2011. Temporal Spatial Varitions, Origin and Their Tectonic Significance of the Late Mesozoic Granites in the Qinling, Central China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27: 1573–1593 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Whalen, J. B., Currie, K. L., Chappell, B. W., 1987. A-Type Granites: Geochemical Characteristics, Discrimination and Petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00402202
Wilde, S. A., Zhou, X. H., Nemchin, A. A., et al., 2003. Mesozoic Crust-Mantle Interaction beneath the North China Craton: A Consequence of the Dispersal of Gondwanaland and Accretion of Asia. Geology, 31(9): 817–820. https://doi.org/10.1130/g19489.1
Wilson, M., 1989. Igneous Petrogenesis. Unwin Hyman Press, London
Wu, F. Y., Yang, Y. H., Xie, L. W., et al., 2006. Hf Isotopic Compositions of the Standard Zircons and Baddeleyites Used in U-Pb Geochronology. Chemical Geology, 234(1/2): 105–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.003
Wu, F., Lin, J., Wilde, S., et al., 2005. Nature and Significance of the Early Cretaceous Giant Igneous Event in Eastern China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 233(1/2): 103–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.019
Wu, F. Y., Ge, W. C., Sun, D. Y., et al., 2003a. Discussions on the Lithospheric Thinning in Eastern China. Earth Science Frontiers, 10: 51–60 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wu, F. Y., Walker, R. J., Ren, X. W., et al., 2003b. Osmium Isotopic Constraints on the Age of Lithospheric Mantle beneath Northeastern China. Chemical Geology, 196(1/2/3/4): 107–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-2541(02)00409-6
Wu, F. Y., Xu, Y. G., Gao, S., et al., 2008. Lithospheric Thinning and Destruction of the North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24: 1145–1174 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Xiao, Y., Zhang, H. F., Fan, W. M., et al., 2010. Evolution of Lithospheric Mantle beneath the Tan-Lu Fault Zone, Eastern North China Craton: Evidence from Petrology and Geochemistry of Peridotite Xenoliths. Lithos, 117(1/2/3/4): 229–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2010.02.017
Xie, L. W., Zhang, Y. B., Zhang, H. H., et al., 2008. In-situ Simultaneous Determination of Trace Elements, U-Pb and Lu-Hf Isotopes in Zircon and Baddeleyite. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53: 1565–1573 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Xu, W. L., Yang, D. B., Gao, S., et al., 2010. Geochemistry of Peridotite Xenoliths in Early Cretaceous High-Mg# Diorites from the Central Orogenic Block of the North China Craton: The Nature of Mesozoic Lithospheric Mantle and Constraints on Lithospheric Thinning. Chemical Geology, 270(1/2/3/4): 257–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.12.006
Xu, Y. G., 2001. Thermo-Tectonic Destruction of the Archaean Lithospheric Keel beneath the Sino-Korean Craton in China: Evidence, Timing and Mechanism. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A: Solid Earth and Geodesy, 26(9/10): 747–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1464-1895(01)00124-7
Xu, Y. G., Li, H. Y., Pang, C. J., et al., 2009. On the Timing and Duration of the Destruction of the North China Craton. Science Bulletin, 54(19): 3379–3396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0346-5
Xu, Y. G., Zhang, H. H., Qiu, H. N., et al., 2012. Oceanic Crust Components in Continental Basalts from Shuangliao, Northeast China: Derived from the Mantle Transition Zone?. Chemical Geology, 328: 168–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.01.027
Yan, G. L., Ren, J. G., Xiao, G. F., et al., 2013. Geochemical Characteristics of Granite Porphyry of Yechangping Molybdenum Deposit and the Analysis on Its Relationship with Mineralization, Western Henan. Mineral Exploration, 4: 154–166 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yang, J. H., Wu, F. Y., Chung, S. L., et al., 2006. A Hybrid Origin for the Qianshan A-Type Granite, Northeast China: Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopic Evidence. Lithos, 89(1/2): 89–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2005.10.002
Yang, J. H., Wu, F. Y., Wilde, S. A., 2003. A Review of the Geodynamic Setting of Large-Scale Late Mesozoic Gold Mineralization in the North China Craton: An Association with Lithospheric Thinning. Ore Geology Reviews, 23(3/4): 125–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-1368(03)00033-7
Yang, J. H., Wu, F. Y., Wilde, S. A., et al., 2008. Mesozoic Decratonization of the North China Block. Geology, 36(6): 467–470. https://doi.org/10.1130/g24518a.1
Yang, Q. L., Zhao, Z. F., Zheng, Y. F., 2012. Modification of Subcontinental Lithospheric Mantle above Continental Subduction Zone: Constraints from Geochemistry of Mesozoic Gabbroic Rocks in Southeastern North China. Lithos, 146-147: 164–182
Yang, Y., Wang, X. X., Ke, C. H., et al., 2014. Zircon U-Pb Ages, Geochemistry and Evolution of Mangling Pluton in North Qinling Mountains. Mineral Deposits, 33: 14–36 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Ye, H. S., Sun, J., Wang, S., et al., 2014. Geology and Genesis of the World-Class Donggou Porphyry Molybdenum Deposit, Henan Province, East Qinling Metallogenic Belt, Central China. Acta Geologica Sinica—English Edition, 88(s2): 635–636. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.12374_65
Ye, H. S., Mao, J. W., Li, Y. F., et al., 2006. Characteristics and Metallogenic Mechanism of Mo-W and Pb-Zn-Ag Deposits in Nannihu Ore Field, Western Henan Province. Geoscience, 20: 165–174 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Ye, H. S., Wang, Y. T., Ding, J. H., et al., 2016. Geological Characteristics of Minerogenesis and Prospecting of Qinling Au-Pb-Zn Metallogenic Belt. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90: 1423–1446 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yuan, H. L., Gao, S., Liu, X. M., et al., 2004. Accurate U-Pb Age and Trace Element Determinations of Zircon by Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 28(3): 353–370. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-908x.2004.tb00755.x
Zeng, L. J., Xing, Y. C., Zhou, D., et al., 2013a. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Age and Hf Isotope Composition of the Babaoshan Granite Porphyries in Lushi County, Henan Province. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 37: 65–77 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zeng, L. J., Zhou, D., Xing, Y. C., et al., 2013b. Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Babaoshan Granite Porphyry in Lushi County, Henan Province. Geochimica, 42: 242–261 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zeng, Q. D., Guo, W. K., Chu, S. X., et al., 2015. Late Jurassic Granitoids in the Xilamulun Mo Belt, Northeastern China: Geochronology, Geochemistry, and Tectonic Implications. International Geology Review, 58(5): 588–602. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2015.1099479
Zhai, M. G., Fan, Q. C., Zhang, H. F., et al., 2007. Lower Crustal Processes Leading to Mesozoic Lithospheric Thinning beneath Eastern North China: Underplating, Replacement and Delamination. Lithos, 96(1/2): 36–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2006.09.016
Zhang, G. W., Meng Q. R., Yu Z. P., et al., 1996. Orogenic Processes and Dynamics of the Qinling. Science in China (Series D), 39: 225–234
Zhang, G. W., Yu, Z. P., Dong, Y. P., et al., 2000. On Precambrian Framework and Evolution of the Qinling Belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 16: 11–21 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, G. W., Zhang, B. R., Yuan, X. R., et al., 2001. Qinling Orogenic Belt and Continental Dynamics. Science Publishing House, Beijing. 320–321, 430–431 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, H. F., 2007. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Mesozoic Mafic Magmatism in the North China Craton and Implications for Secular Lithospheric Evolution. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 280(1): 35–54. https://doi.org/10.1144/sp280.2
Zhang, H. F., Goldstein, S. L., Zhou, X. H., et al., 2008. Evolution of Subcontinental Lithospheric Mantle beneath Eastern China: Re-Os Isotopic Evidence from Mantle Xenoliths in Paleozoic Kimberlites and Mesozoic Basalts. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 155(3): 271–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-007-0241-5
Zhang, H. F., Goldstein, S. L., Zhou, X. H., et al., 2009. Comprehensive Refertilization of Lithospheric Mantle beneath the North China Craton: Further Os-Sr-Nd Isotopic Constraints. Journal of the Geological Society, 166(2): 249–259. https://doi.org/10.1144/0016-76492007-152
Zhang, H. F., Sun, M., Zhou, M. F., et al., 2004. Highly Heterogeneous Late Mesozoic Lithospheric Mantle beneath the North China Craton: Evidence from Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopic Systematics of Mafic Igneous Rocks. Geological Magazine, 141(1): 55–62. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0016756803008331
Zhang, H. F., Sun, M., Zhou, X. H., et al., 2002. Mesozoic Lithosphere Destruction beneath the North China Craton: Evidence from Major-, Trace-Element and Sr-Nd-Pb Isotope Studies of Fangcheng Basalts. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 144(2): 241–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-002-0395-0
Zhang, H. F., Sun, M., Zhou, X. H., et al., 2003. Secular Evolution of the Lithosphere beneath the Eastern North China Craton: Evidence from Mesozoic Basalts and High-Mg Andesites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(22): 4373–4387. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-7037(03)00377-6
Zhang, S. H., Zhao, Y., Davis, G. A., et al., 2014. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Mesozoic Magmatism and Deformation in the North China Craton: Implications for Lithospheric Thinning and Decratonization. Earth-Science Reviews, 131: 49–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.12.004
Zhao, G. C., Wilde, S. A., Cawood, P. A., et al., 2001. Archean Blocks and Their Boundaries in the North China Craton: Lithological, Geochemical, Structural and P-T Path Constraints and Tectonic Evolution. Precambrian Research, 107: 45–73
Zhao, T. P., Xu, Y. H., Zhai, M. G., 2007. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Setting of the Paleoproterozoic Xiong’er Group in the Southern Part of the North China Craton: A Review. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13: 191–206 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhao, X. F., Li, Z. K., Zhao, S. R., et al., 2019. Early Cretaceous Regional-Scale Magmatic-Hydrothermal Metallogenic System at the Southern Margin of the North China Carton. Earth Science, 44(1): 52–68 (in Chinese with English Abstract) https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2018.372
Zhao, Y., Chen, B., Zhang, S. H., et al., 2010. Pre-Yanshanian Geological Events in the Northern Margin of the North China Craton and Its Adjacent Areas. Geology in China, 37: 900–915 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zheng, J. P., 2009. Comparison of Mantle-Derived Matierals from Different Spatiotemporal Settings: Implications for Destructive and Accretional Processes of the North China Craton. Science Bulletin, 54(19): 3397–3416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0308-y
Zheng, J. P., Griffin, W. L., O’Reilly, S. Y., et al., 2007. Mechanism and Timing of Lithospheric Modification and Replacement beneath the Eastern North China Craton: Peridotitic Xenoliths from the 100 Ma Fuxin Basalts and a Regional Synthesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(21): 5203–5225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2007.07.028
Zheng, J. P., Griffin, W. L., O’Reilly, S. Y., et al., 2006. Mineral Chemistry of Peridotites from Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic Lithosphere: Constraints on Mantle Evolution beneath Eastern China. Journal of Petrology, 47(11): 2233–2256. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egl042
Zheng, J. P., O’Reilly, S. Y., Griffin, W. L., et al., 2001. Relict Refractory Mantle beneath the Eastern North China Block: Significance for Lithosphere Evolution. Lithos, 57(1): 43–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-4937(00)00073-6
Zhu, G., Wang, Y. S., Wang, W., et al., 2017. An Accreted Micro-Continent in the North of the Dabie Orogen, East China: Evidence from Detrital Zircon Dating. Tectonophysics, 698: 47–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2017.01.004
Zhu, L. M., Zhang, G. W., Guo, B., et al., 2008. U-Pb (LA-ICP-MS) Zircon Dating for the Large Jinduicheng Porphyry Mo Deposit in the East China, and Its Metallogenic Setting. Acta Geology Sinica, 82: 204–220 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhu, R. X., Chen, L., Wu, F. Y., et al., 2011. Timing, Scale and Mechanism of the Destruction of the North China Craton. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(6): 789–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-011-4203-4
Zhu, R. X., Fan, H. R., Li, J. W., et al., 2015. Decratonic Gold Deposits. Science China Earth Sciences, 58(9): 1523–1537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-015-5139-x
Zhu, R. X., Xu, Y. G., Zhu, G., et al., 2012a. Destruction of the North China Craton. Science China Earth Sciences, 55(10): 1565–1587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-012-4516-y
Zhu, R. X., Yang, J. H., Wu, F. Y., 2012b. Timing of Destruction of the North China Craton. Lithos, 149: 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2012.05.013
Zhu, R. X., Zheng, T. Y., 2009. Destruction Geodynamics of the North China Craton and Its Paleoproterozoic Plate Tectonics. Science Bulletin, 54(19): 3354–3366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0451-5
Acknowledgments
Yueheng Yang from the laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) laboratory at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences is thanked for U-Pb zircon dating and Hf isotope analyses. We are also grateful to Dingshuai Xue of the Rock-Mineral Preparation and Analysis Lab, IGGCAS, for their advice in the major element analysis, and Wuhan Sample Solution Analytical Technology Co. Ltd., for their assistance in the trace element analysis. Two anonymous reviewers are thanked for their constructive and valuable comments which greatly contributed to the improvement of the manuscript. This work was financially supported by the National Key R & D Program of China (No. 2016YFC0600109) and the State Key Laboratory of Lithospheric Evolution, IGGCAS (No. SKL-Z201905). This work was also financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41602099), and the State Key Laboratory of Lithospheric Evolution, IGGCAS (No. SPECIAL201606). The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1277-y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, Y., Gao, S., Zeng, Q. et al. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Hf Isotope of the Late Mesozoic Granitoids from the Lushi Polymetal Mineralization Area: Implication for the Destruction of Southern North China Craton. J. Earth Sci. 31, 313–329 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1277-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1277-y