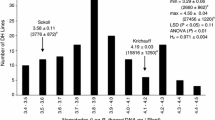
Abstract
Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) is an important agronomic crop and model system for studies of plant-pathogen interactions. Black shank, caused by Phytophthora nicotianae, is an important disease affecting tobacco production worldwide. In this study, a mapping population of 177 F7:8-9 recombinant inbred lines was generated from a cross between the highly resistant cultivar ‘Yunyan 85’ and a susceptible line ‘Dabaijin 599’. A high-density genetic linkage map containing 7734 single-nucleotide polymorphic markers based on restriction site-associated DNA tag sequencing technology was used to finely map quantitative trait loci (QTL) for resistance to P. nicotianae. A total of 10 QTLs were detected as being associated with resistance to P. nicotianae across multiple environments, and two major QTL qBS7 and qBS14 were repeatedly identified under all five environments. They explained 16.48-62.20% and 3.94-11.29% of the phenotypic variance with high LOD score, respectively. One hundred thirty-eight candidate genes were identified for two major QTLs qBS7 and qBS14, and annotation analysis showing that several predicted genes encoded proteins associated with plant defense response to pathogens. This high-density single-nucleotide polymorphic genetic linkage map of flue-cured tobacco based on restriction site-associated DNA sequencing was useful in the QTL finely mapping of resistance to P. nicotianae. This study increases our understanding of the genetics of resistance to P. nicotianae and aids in marker-assisted selection.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- RIL:
-
Recombinant inbred line
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- NBS-LRR:
-
Nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat
- LOD:
-
Log-likelihood
References
Apple JL (1962) Transfer of resistance to black shank (Phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae) from Nicotiana plumbaginifolia to N. tabacum. Phytopathology 52:1
Baird NA, Etter PD, Atwood TS, Currey MC, Shiver AL, Lewis ZA, Selker EU, Cresko WA, Johnson EA (2008) Rapid SNP discovery and genetic mapping using sequenced RAD markers. PLoS One 3(10):e3376. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003376
Ballvora A, Ercolano MR, Weiss J, Meksem K, Bormann CA, Oberhagemann P, Salamini F, Gebhardt C (2002) The R1 gene for potato resistance to late blight (Phytophthora infestans) belongs to the leucine zipper/NBS/LRR class of plant resistance genes. Plant J 30(3):361-371
Bindler G, Plieske J, Bakaher N, Gunduz I, Ivanov N, Van der Hoeven R, Ganal M, Donini P (2011) A high density genetic map of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) obtained from large scale microsatellite marker development. Theor Appl Genet 123(2):219-230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1578-8
Bittner-Eddy PD, Crute IR, Holub EB, Beynon JL (2000) RPP13 is a simple locus in Arabidopsis thaliana for alleles that specify downy mildew resistance to different avirulence determinants in Peronospora parasitica. Plant J 21(2):177-188. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00664.x
Bombarely A, Rosli HG, Vrebalov J, Moffett P, Mueller LA, Martin GB (2012) A draft genome sequence of Nicotiana benthamiana to enhance molecular plant-microbe biology research. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 25(12):1523-1530. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-06-12-0148-TA
Chaplin JF (1962) Transfer of black shank resistance from Nicotiana plumbaginifolia to flue-cured N. tabacum. Tob Sci 6:184-189
Chaplin JF (1966) Comparison of tobacco black shank (Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae) resistance from four sources. Tob Sci 10:55-58
DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, Garimella KV, Maguire JR, Hartl C, Philippakis AA, del Angel G, Rivas MA, Hanna M, McKenna A, Fennell TJ, Kernytsky AM, Sivachenko AY, Cibulskis K, Gabriel SB, Altshuler D, Daly MJ (2011) A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet 43(5):491-498. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.806
Drake K, Lewis RS (2013) An introgressed Nicotiana rustica genomic region confers resistance to Phytophthora nicotianae in cultivated tobacco. Crop Sci 53(4):1366-1374. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2012.10.0605
Drake KE, Moore JM, Bertrand P, Fortnum B, Peterson P, Lewis RS (2015) Black shank resistance and agronomic performance of flue-cured tobacco lines and hybrids carrying the introgressed Nicotiana rustica region, Wz. Crop Sci 55(1):79-86. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2014.02.0164
Drake-Stowe K, Bakaher N, Goepfert S, Philippon B, Mark R, Peterson P, Lewis RS (2017) Multiple disease resistance loci affect soilborne disease resistance in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Phytopathology 107(9):1055-1061
Edwards KD, Fernandez-Pozo N, Drake-Stowe K, Humphry M, Evans AD, Bombarely A, Allen F, Hurst R, White B, Kernodle SP, Bromley JR, Sanchez-Tamburrino JP, Lewis RS, Mueller LA (2017) A reference genome for Nicotiana tabacum enables map-based cloning of homeologous loci implicated in nitrogen utilization efficiency. BMC Genomics 18(1):448. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-3791-6
Gallup CA, Shew HD (2010) Occurrence of race 3 of Phytophthora nicotianae in North Carolina, the causal agent of black shank of tobacco. Plant Dis 94:557-562
Gong D, Huang L, Xu X, Wang C, Ren M, Wang C, Chen M (2016) Construction of a high-density SNP genetic map in flue-cured tobacco based on SLAF-seq. Mol Breed 36(7):100
Heggestad H, Lautz W (1957) Some results of studies on resistance to tobacco black shank. Phytopathology 47:452-452
Huang X, Zhao Y, Wei X, Li C, Wang A, Zhao Q, Li W, Guo Y, Deng L, Zhu C, Fan D, Lu Y, Weng Q, Liu K, Zhou T, Jing Y, Si L, Dong G, Huang T, Lu T, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li J, Han B (2011) Genome-wide association study of flowering time and grain yield traits in a worldwide collection of rice germplasm. Nat Genet 44(1):32-39. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.1018
Jansen J, Jong A, Ooijen J (2001) Constructing dense genetic linkage maps. Theor Appl Genet 102:10
Jiang R, Li JC, Tian ZD, Du J, Armstrong M, Baker K, Lim JTY, Vossen JH, He H, Portal L, Zhou J, Bonierbale M, Hein I, Lindqvist-Kreuze H, Xie CH (2018) Potato late blight field resistance from QTL dPI09c is conferred by the NB-LRR gene R8. J Exp Bot 69(7):1545-1555. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery021
Kosambi D (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugenics 12:172-175
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25(14):1754-1760. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Li H, Ye G, Wang J (2007) A modified algorithm for the improvement of composite interval mapping. Genetics 175(1):361-374. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.106.066811
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R, Genome Project Data Processing S (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25(16):2078-2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Liu D, Ma C, Hong W, Huang L, Liu M, Liu H, Zeng H, Deng D, Xin H, Song J, Xu C, Sun X, Hou X, Wang X, Zheng H (2014) Construction and analysis of high-density linkage map using high-throughput sequencing data. PLoS One 9(6):e98855. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0098855
Ma JM, Heim C, Humphry M, Nifong JM, Lewis RS (2019) Genetic analysis of Phn7.1, a major QTL conferring partial resistance to Phytophthora nicotianae in Nicotiana tabacum. Mol Breed 39(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-018-0923-x
McCorkle KL, Drake-Stowe K, Lewis RS, Shew D (2018) Characterization of Phytophthora nicotianae resistance conferred by the Introgressed Nicotiana rustica region, Wz, in flue-cured tobacco. Plant Dis 102(2):309-317. https://doi.org/10.1094/Pdis-03-17-0339-Re
McDonald BA, Linde C (2002) Pathogen population genetics, evolutionary potential, and durable resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 40:349. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.40.120501.101443
McIntyre JL, Taylor GS (1978) Race 3 of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae. Phytopathology 68:35-38
Meng L, Li HH, Zhang LY, Wang JK (2015) QTL IciMapping: integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J 3(3):269-283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2015.01.001
Nielsen M (1992) Sources of resistance to black shank and black root rot diseases. CORESTA Inf Bull 3(4):144-150
Sierro N, Battey JN, Ouadi S, Bovet L, Goepfert S, Bakaher N, Peitsch MC, Ivanov NV (2013) Reference genomes and transcriptomes of Nicotiana sylvestris and Nicotiana tomentosiformis. Genome Biol 14(6):R60. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2013-14-6-r60
Sierro N, Battey JND, Ouadi S, Bakaher N, Bovet L, Willig A, Goepfert S, Peitsch MC, Ivanov NV (2014) The tobacco genome sequence and its comparison with those of tomato and potato. Nat Commun 5(5):3833. https://doi.org/10.1038/Ncomms4833
Sullivan MJ, Melton TA, Shew HD (2005) Managing the race structure of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae with cultivar rotation. Plant Dis 89:1285-1294
Tan C, Li Y, Wang Y, Ma W, Lei Y (1997) Breeding and selecting a new variety of flue-cured tobacco Yunyan 85 and its characteristics. Chin Tobacco Sci 1:7-10
Tisdale WB (1931) Development of strains of cigar wrapper tobacco resistant to black shank (Phytophthora nicotianae Breda de Haan). Florida Univ Agr Expt Stat Bull 226:1-45
Valleau WD, Stokes GW, Johnson EM (1960) Nine years experience with the Nicotiana longiflora factor for resistance to Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae in the control of black shank. Tob Sci 4:92-94
van Jaarsveld E, Wingfield MJ, Drenth A (2002) Evaluation of tobacco varieties for resistance to races of Phytophthora nicotianae in South Africa. J Phytopathol 150:456-462
Van Ooijen JW (2011) Multipoint maximum likelihood mapping in a full-sib family of an outbreeding species. Genet Res 93(5):343-349. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0016672311000279
van Os H, Stam P, Visser RG, van Eck HJ (2005) SMOOTH: a statistical method for successful removal of genotyping errors from high-density genetic linkage data. Theor Appl Genet 112(1):187-194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0124-y
Vontimitta V, Lewis RS (2012a) Growth chamber evaluation of a tobacco ‘Beinhart 1000’ × ‘Hicks’ mapping population for quantitative trait loci affecting resistance to multiple races of Phytophthora nicotianae. Crop Sci 52(1):91-98
Vontimitta V, Lewis RS (2012b) Mapping of quantitative trait loci affecting resistance to Phytophthora nicotianae in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) line Beinhart-1000. Mol Breed 29(1):89-98
West MA, van Leeuwen H, Kozik A, Kliebenstein DJ, Doerge RW, St Clair DA, Michelmore RW (2006) High-density haplotyping with microarray-based expression and single feature polymorphism markers in Arabidopsis. Genome Res 16(6):787-795. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.5011206
Wills W (1971) A comparison of black shank resistance of tobacco measured in inoculated whole plants and excised leaf tissue. Tob Sci 15:47-50
Xiao BG, Drake K, Vontimitta V, Tong ZJ, Zhang XT, Li MY, Leng XD, Li YP, Lewis RS (2013) Location of genomic regions contributing to phytophthora nicotianae resistance in tobacco cultivar Florida 301. Crop Sci 53(2):473-481. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2012.06.0376
Zhang YS, Guo X, Yan XX, Ren M, Jiang CH, Cheng YZ, Wen LY, Liu D, Zhang Y, Sun MM, Feng QF, Yang AG, Cheng LR (2018) Identification of stably expressed QTL for resistance to black shank disease in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) line Beinhart 1000-1. Crop J 6(3):282-290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2017.12.002
Funding
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Non-profit Scientific Institution (1610232017009 and 1610232017012) and the Science Foundation for Young Scholars of Tobacco Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (2015B01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS, YZ, and XX collected the plant materials used in this study. DG and MC carried out the determination of resistance to black shank. DG, MC, and XZ analyzed data and prepared the manuscript. DG and XX planned and supervised this work and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Table S1.
The RIL population genotype of mapped markers (XLSX 4961 kb)
Table S2.
The markers and their genetic distance in the genetic map. (XLSX 162 kb)
Table S3.
The functional annotation of the candidate genes of the major QTLs. (XLSX 15 kb)
Figure S1.
Haplotype maps of the RIL population. Green represents ‘Yunyan 85’, blue represents ‘Dabaijin 599’, white means the parent could not be estimated, gray represents deletions, and red indicates heterozygosity. (PDF 5026 kb)
Figure S2.
Heat maps of pair-wise recombination of the tobacco. Each cell represents the recombination rate of two markers. Yellow indicates a lower recombination rate and purple a higher one. (PDF 12403 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, D., Chen, M., Sun, Y. et al. Fine mapping of QTLs for resistance to Phytophthora nicotianae in flue-cured tobacco using a high-density genetic map. Mol Breeding 40, 45 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-020-01126-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-020-01126-8