Abstract
Background
Environmental exposure and genotype variation influence DNA methylation. Studies on the effects of genotype variation were performed mainly on European ancestries. We analyzed the genetic effects on cord blood methylation of Koreans.
Methods
As part of the Korean Exposome study project, DNA was extracted from 192 cord blood samples for analysis. Cord blood samples were genotyped via Asian Precision Medicine Research Array analysis and methylation was measured using the Methylation EPIC Beadchip kits. The associations between genotypes and CpG methylation were analyzed with matrix eQTL.
Results
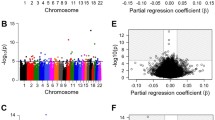
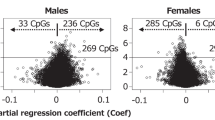
Conditional analysis revealed 34,425 methylation quantitative trait loci (mQTLs), and trans-mQTLs constituted 7.2% of all the associated CpG sites. About 80% of the total trans-associations were trans-chromosomal and the related SNPs were concentrated on chromosome 19. According to the results of DAVID, cis-mQTL-related SNPs resulting in amino acid substitutions were related to signal peptides or glycosylation.
Conclusion
We identified genotype variations associated with DNA methylation in the cord blood obtained from Koreans.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aryee MJ, Jaffe AE, Corrada-Bravo H, Ladd-Acosta C, Feinberg AP, Hansen KD, Irizarry RA (2014) Minfi: a flexible and comprehensive Bioconductor package for the analysis of Infinium DNA methylation microarrays. Bioinformatics 30:1363–1369
Bakulski KM, Feinberg JI, Andrews SV, Yang J, Brown S, McKenney SL, Witter F, Walston J, Feinberg AP, Fallin MD (2016) DNA methylation of cord blood cell types: applications for mixed cell birth studies. Epigenetics 11:354–362
Banovich NE, Lan X, McVicker G, van de Geijn B, Degner JF, Blischak JD, Roux J, Pritchard JK, Gilad Y (2014) Methylation qtls are associated with coordinated changes in transcription factor binding, histone modifications, and gene expression levels. PLoS Genet 10:e1004663
Bell JT, Pai AA, Pickrell JK, Gaffney DJ, Pique-Regi R, Degner JF, Gilad Y, Pritchard JK (2011) DNA methylation patterns associate with genetic and gene expression variation in HapMap cell lines. Genome Biol 12:R10
Boks MP, Derks EM, Weisenberger DJ, Strengman E, Janson E, Sommer IE, Kahn RS, Ophoff RA (2009) The relationship of DNA methylation with age, gender and genotype in twins and healthy controls. PLoS ONE 4:e6767
Carlson CS, Matise TC, North KE, Haiman CA, Fesinmeyer MD, Buyske S, Schumacher FR, Peters U, Franceschini N, Ritchie MD et al (2013) Generalization and dilution of association results from European GWAS in populations of Non-European ancestry: the PAGE study. PLoS Biol 11:e1001661
Chang CC, Chow CC, Tellier LC, Vattikuti S, Purcell SM, Lee JJ (2015) Second-generation PLINK: rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 4:7
Chen W, Liu J, Yuan D, Zuo Y, Liu Z, Liu S, Zhu Q, Qiu G, Huang S, Giampietro PF (2016) Progress and perspective of TBX6 gene in congenital vertebral malformations. Oncotarget 7:57430
Consortium EP (2012) An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 489:57
Consortium TMs (1999) Complete sequence and gene map of a human major histocompatibility complex. Nature 401:921
Delaneau O, Marchini J, Zagury J-F (2012) A linear complexity phasing method for thousands of genomes. Nat Methods 9:179
den Dekker HT, Burrows K, Felix JF, Salas LA, Nedeljkovic I, Yao J, Rifas-Shiman SL, Ruiz-Arenas C, Amin N, Bustamante M et al (2019) Newborn DNA-methylation, childhood lung function, and the risks of asthma and COPD across the life course. Eur Respir J 53:1801795
Feinberg AP (2018) The key role of epigenetics in human disease prevention and mitigation. New Engl J Med 378:1323–1334
Ferguson-Smith AC (2011) Genomic imprinting: the emergence of an epigenetic paradigm. Nat Rev Genet 12:565
Gaunt TR, Shihab HA, Hemani G, Min JL, Woodward G, Lyttleton O, Zheng J, Duggirala A, McArdle WL, Ho K et al (2016) Systematic identification of genetic influences on methylation across the human life course. Genome Biol 17:61
Gordon L, Joo JE, Powell JE, Ollikainen M, Novakovic B, Li X, Andronikos R, Cruickshank MN, Conneely KN, Smith AK et al (2012) Neonatal DNA methylation profile in human twins is specified by a complex interplay between intrauterine environmental and genetic factors, subject to tissue-specific influence. Genome Res 22:1395–1406
Gu Z, Gu L, Eils R, Schlesner M, Brors B (2014) circlize implements and enhances circular visualization in R. Bioinformatics 30:2811–2812
Hannon E, Spiers H, Viana J, Pidsley R, Burrage J, Murphy TM, Troakes C, Turecki G, O’Donovan MC, Schalkwyk LC et al (2015) Methylation QTLs in the developing brain and their enrichment in schizophrenia risk loci. Nat Neurosci 19:48
Houseman EA, Accomando WP, Koestler DC, Christensen BC, Marsit CJ, Nelson HH (2012) DNA methylation arrays as surrogate measures of cell mixture distribution. BMC Bioinformatics 13:86
Howie BN, Donnelly P, Marchini J (2009) A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet 5:e1000529
Howie B, Marchini J, Stephens M (2011) Genotype imputation with thousands of genomes. G3 Genes Genomes Genet 1:457–470
Howie B, Fuchsberger C, Stephens M, Marchini J, Abecasis GR (2012) Fast and accurate genotype imputation in genome-wide association studies through pre-phasing. Nat Genet 44:955
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2008) Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 37:1–13
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protocols 4:44
Johnson WE, Li C, Rabinovic A (2007) Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics 8:118–127
Joubert BR, Felix JF, Yousefi P, Bakulski KM, Just AC, Breton C, Reese SE, Markunas CA, Richmond RC, Xu C-J et al (2016) DNA methylation in newborns and maternal smoking in pregnancy: genome-wide Consortium Meta-analysis. Am J Hum Genet 98:680–696
Koh EJ, Hwang SY (2019) Multi-omics approaches for understanding environmental exposure and human health. Mol Cell Toxicol 15:1–7
Küpers LK, Monnereau C, Sharp GC, Yousefi P, Salas LA, Ghantous A, Page CM, Reese SE, Wilcox AJ, Czamara D et al (2019) Meta-analysis of epigenome-wide association studies in neonates reveals widespread differential DNA methylation associated with birthweight. Nat commun 10:1893
Mackay DJ, Callaway JL, Marks SM, White HE, Acerini CL, Boonen SE, Dayanikli P, Firth HV, Goodship JA, Haemers AP (2008) Hypomethylation of multiple imprinted loci in individuals with transient neonatal diabetes is associated with mutations in ZFP57. Nat Genet 40:949
McRae AF, Powell JE, Henders AK, Bowdler L, Hemani G, Shah S, Painter JN, Martin NG, Visscher PM, Montgomery GW (2014) Contribution of genetic variation to transgenerational inheritance of DNA methylation. Genome Biol 15:R73
McRae AF, Marioni RE, Shah S, Yang J, Powell JE, Harris SE, Gibson J, Henders AK, Bowdler L, Painter JN et al (2018) Identification of 55,000 replicated DNA methylation QTL. Sci Rep 8:17605
Min JL, Hemani G, Davey Smith G, Relton C, Suderman M (2018) Meffil: efficient normalization and analysis of very large DNA methylation datasets. Bioinformatics 34:3983–3989
Moon DH, Kwon SO, Kim WJ, Hong Y (2019) Identification of serial DNA methylation changes in the blood samples of patients with lung cancer. Tuberc Respir Dis 82:126–132
Richardson TG, Shihab HA, Hemani G, Zheng J, Hannon E, Mill J, Carnero-Montoro E, Bell JT, Lyttleton O, McArdle WL et al (2016) Collapsed methylation quantitative trait loci analysis for low frequency and rare variants. Hum Mol Genet 25:4339–4349
Shabalin AA (2012) Matrix eQTL: ultra fast eQTL analysis via large matrix operations. Bioinformatics 28:1353–1358
Shi J, Marconett CN, Duan J, Hyland PL, Li P, Wang Z, Wheeler W, Zhou B, Campan M, Lee DS et al (2014) Characterizing the genetic basis of methylome diversity in histologically normal human lung tissue. Nat commun 5:3365
Stricker SH, Köferle A, Beck S (2016) From profiles to function in epigenomics. Nat Rev Genet 18:51
Takahashi N, Coluccio A, Thorball CW, Planet E, Shi H, Offner S, Turelli P, Imbeault M, Ferguson-Smith AC, Trono D (2019) ZNF445 is a primary regulator of genomic imprinting. Genes Dev 33:49–54
Teschendorff AE, Marabita F, Lechner M, Bartlett T, Tegner J, Gomez-Cabrero D, Beck S (2012) A beta-mixture quantile normalization method for correcting probe design bias in Illumina Infinium 450 k DNA methylation data. Bioinformatics 29:189–196
Turnbull J, Girard J-M, Lohi H, Chan EM, Wang P, Tiberia E, Omer S, Ahmed M, Bennett C, Chakrabarty A (2012) Early-onset Lafora body disease. Brain 135:2684–2698
Turner SD (2018) qqman: an R package for visualizing GWAS results using Q-Q and manhattan plots. J Open Source Softw 3:731. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.00731
Wu N, Ming X, Xiao J, Wu Z, Chen X, Shinawi M, Shen Y, Yu G, Liu J, Xie H (2015) TBX6 null variants and a common hypomorphic allele in congenital scoliosis. New Engl J Med 372:341–350
Xu Z, Niu L, Li L, Taylor JA (2015) ENmix: a novel background correction method for Illumina HumanMethylation450 BeadChip. Nucleic Acids Res 44:e20–e20
Yang J, Lee SH, Goddard ME, Visscher PM (2011) GCTA: a tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. Am J Hum Genet 88:76–82
Yang J, Ferreira T, Morris AP, Medland SE, Madden PA, Heath AC, Martin NG, Montgomery GW, Weedon MN, Loos RJ (2012) Conditional and joint multiple-SNP analysis of GWAS summary statistics identifies additional variants influencing complex traits. Nat Genet 44:369
Funding
This study was supported by the Korean Environment Industry & Technology Institute (KEITI) through “the Environmental Health Action Program”, funded by Korea Ministry of Environment (2017001360005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Statement of human and animal rights
This study received ethical approval of the Kangwon National University Hospital IRB (B-2017-11-006).
Informed consent
Written informed consent was provided by each participant.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J., Kwon, S.O., Kim, SH. et al. Methylation quantitative trait loci analysis in Korean exposome study. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 16, 175–183 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-019-00068-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-019-00068-3