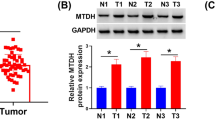
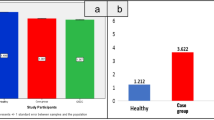
Abstract
Heparin-binding protein 17/fibroblast growth factor–binding protein-1 (HBp17/FGFBP-1) was purified from A431 cell-conditioned media based on its capacity to bind to fibroblast growth factor 1 and 2 (FGF-1 and FGF-2). HBp17/FGFBP-1 has been observed to induce the tumorigenic potential of epithelial cells and is highly expressed in oral cancer cell lines and tissues. HBp17/FGFBP-1 is also recognized as a pro-angiogenic molecule as a consequence of its interaction with FGF-2. We have previously reported that Eldecalcitol (ED-71), an analog of 1α,25(OH)2D3, downregulated the expression of HBp17/FGFBP-1 and inhibited the proliferation of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cells in vitro and in vivo through NF-κb inhibition. To explore the possibility of microRNA (miRNA) control of HBp17/FGFBP-1, we analyzed exosomal miRNAs from medium conditioned by A431 cells treated with ED-71. Microarray analysis revealed that 12 exosomal miRNAs were upregulated in ED-71-treated A431 cells. Among them, miR-6887-5p was identified to have a predicted mRNA target matching the 3′ untranslated region (3′-UTR) of HBp17/FGFBP-1. The 3′-UTR of HBp17/FGFBP-1 was confirmed to be a direct target of miR-6887-5p in SCC/OSCC cells, as assessed with a luciferase reporter assay. Functional assessment revealed that overexpression of miR-6887-5p in SCC/OSCC cells inhibited cell proliferation and colony formation in vitro, and inhibited tumor growth in vivo compared with control. In conclusion, our present study supports a novel anti-cancer mechanism involving the regulation of HBp17/FGFBP-1 function by exosomal miR-6887-5p in SCC/OSCC cells, which has potential utility as a miRNA-based cancer therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data will be made available upon reasonable request.
References
Alvarez-Diaz S, Valle N, Ferrer-Mayorga G, Lombardia L, Herrera M, Dominguez O, Segura MF, Bonilla F, Hernando E, Munoz A (2012) MicroRNA-22 is induced by vitamin D and contributes to its antiproliferative, antimigratory and gene regulatory effects in colon cancer cells. Hum Mol Genet 21:2157–2165
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355
Andaloussi EL, Mager I, Breakefield XO, Wood MJ (2013) Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:347–357
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Beer HD, Bittner M, Niklaus G, Munding C, Max N, Goppelt A, Werner S (2005) The fibroblast growth factor binding protein is a novel interaction partner of FGF-7, FGF-10 and FGF-22 and regulates FGF activity: implications for epithelial repair. Oncogene 24:5269–5277
Begum S, Zhang Y, Shintani T, Toratani S, Sato JD, Okamoto T (2007) Immunohistochemical expression of heparin-binding protein 17/fibroblast growth factor-binding protein-1 (HBp17/FGFBP-1) as an angiogenic factor in head and neck tumorigenesis. Oncol Rep 17:591–596
Colombo M, Raposo G, Thery C (2014) Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 30:255–289
Czubayko F, Liaudet-Coopman ED, Aigner A, Tuveson AT, Berchem GJ, Wellstein A (1997) A secreted FGF-binding protein can serve as the angiogenic switch in human cancer. Nat Med 3:1137–1140
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269
Fabricant RN, De Larco JE, Todaro GJ (1977) Nerve growth factor receptors on human melanoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74:565–569
Gilmore TD (1999) The Rel/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway: introduction. Oncogene 18:6842–6844
Giovannucci E, Liu Y, Willett WC (2006) Cancer incidence and mortality and vitamin D in black and white male health professionals. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 15:2467–2472
Gocek E, Wang X, Liu X, Liu CG, Studzinski GP (2011) MicroRNA-32 upregulation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in human myeloid leukemia cells leads to Bim targeting and inhibition of AraC-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 71:6230–6239
Hatakeyama S, Yoshino M, Eto K, Takahashi K, Ishihara J, Ono Y, Saito H, Kubodera N (2010) Synthesis and preliminary biological evaluation of 20-epi-eldecalcitol [20-epi-1alpha,25-dihydroxy-2beta-(3-hydroxypropoxy)vitamin D3: 20-epi-ED-71]. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 121:25–28
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5:522–531
Holick MF (2011) Vitamin D deficiency in 2010: health benefits of vitamin D and sunlight: a D-bate. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7:73–75
Huang Q, Yang J, Zheng J, Hsueh C, Guo Y, Zhou L (2018) Characterization of selective exosomal microRNA expression profile derived from laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma detected by next generation sequencing. Oncol Rep 40:2584–2594
Janjetovic Z, Tuckey RC, Nguyen MN, Thorpe EM Jr, Slominski AT (2010) 20,23-dihydroxyvitamin D3, novel P450scc product, stimulates differentiation and inhibits proliferation and NF-kappaB activity in human keratinocytes. J Cell Physiol 223:36–48
Kehl T, Backes C, Kern F, Fehlmann T, Ludwig N, Meese E, Lenhof HP, Keller A (2017) About miRNAs, miRNA seeds, target genes and target pathways. Oncotarget 8:107167–107175
Kia V, Sharif Beigli M, Hosseini V, Koochaki A, Paryan M, Mohammadi-Yeganeh S (2018) Is miR-144 an effective inhibitor of PTEN mRNA: a controversy in breast cancer. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 54:621–628
Kimura Y (1978) Studies on lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes in a cell line (Ca 9-22) derived from carcinoma of the gingiva (author's transl). Kokubyo Gakkai Zasshi 45:20–35
Kramer-Albers EM, Hill AF (2016) Extracellular vesicles: interneural shuttles of complex messages. Curr Opin Neurobiol 39:101–107
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75:843–854
Li C, Qin F, Hu F, Xu H, Sun G, Han G, Wang T, Guo M (2018) Characterization and selective incorporation of small non-coding RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer extracellular vesicles. Cell Biosci 8:2
Liu X, Shi S, Chen J-H, Wu D, Kan M, Myoken Y, Okamoto T, Sato JD (2002) Human fibroblast growth factor-binding protein HBp17 enhances the tumorigenic potential of immortalized squamous epithelial cells. In: Shirahata S, Teruya K, Katakura Y (eds) Animal cell technology: basic & applied aspects: proceedings of the thirteenth annual meeting of the Japanese Association for Animal Cell Technology (JAACT), Fukuoka-Karatsu, November 16–21, 2000. Springer, Netherlands, pp 343–352
Liu Y, Hu Y, Ni D, Liu J, Xia H, Xu L, Zhou Q, Xie Y (2019) miR-194 regulates the proliferation and migration via targeting Hnf1beta in mouse metanephric mesenchyme cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 55:512–521
Lobb RJ, Becker M, Wen SW, Wong CS, Wiegmans AP, Leimgruber A, Moller A (2015) Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J Extracell Vesicles 4:27031
Maleklou N, Allameh A, Kazemi B (2016) Targeted delivery of vitamin D3-loaded nanoparticles to C6 glioma cell line increased resistance to doxorubicin, epirubicin, and docetaxel in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 52:989–1000
Melo SA, Luecke LB, Kahlert C, Fernandez AF, Gammon ST, Kaye J, LeBleu VS, Mittendorf EA, Weitz J, Rahbari N, Reissfelder C, Pilarsky C, Fraga MF, Piwnica-Worms D, Kalluri R (2015) Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature 523:177–182
Michimukai E, Kitamura N, Zhang Y, Wang H, Hiraishi Y, Sumi K, Hayashido Y, Toratani S, Okamoto T (2001) Mutations in the human homologue of the Drosophila segment polarity gene patched in oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 37:459–464
Miyauchi S, Moroyama T, Kyoizumi S, Asakawa J, Okamoto T, Takada K (1988) Malignant tumor cell lines produce interleukin-1-like factor. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 24:753–758
Myoken Y, Myoken Y, Okamoto T, Kan M, Sato JD, Takada K (1994a) Release of fibroblast growth factor-1 by human squamous cell carcinoma correlates with autocrine cell growth. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 30a:790–795
Myoken Y, Myoken Y, Okamoto T, Sato JD, Takada K (1994b) Immunocytochemical localization of fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF-1) and FGF-2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). J Oral Pathol Med 23:451–456
Nishii Y, Okano T (2001) History of the development of new vitamin D analogs: studies on 22-oxacalcitriol (OCT) and 2beta-(3-hydroxypropoxy)calcitriol (ED-71). Steroids 66:137–146
Okamoto T, Tanaka Y, Kan M, Sakamoto A, Takada K, Sato JD (1996a) Expression of fibroblast growth factor binding protein HBp17 in normal and tumor cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 32:69–71
Okamoto T, Tani R, Yabumoto M, Sakamoto A, Takada K, Sato GH, Sato JD (1996b) Effects of insulin and transferrin on the generation of lymphokine-activated killer cells in serum-free medium. J Immunol Methods 195:7–14
Padi SK, Zhang Q, Rustum YM, Morrison C, Guo B (2013) MicroRNA-627 mediates the epigenetic mechanisms of vitamin D to suppress proliferation of human colorectal cancer cells and growth of xenograft tumors in mice. Gastroenterology 145:437–446
Pigati L, Yaddanapudi SC, Iyengar R, Kim DJ, Hearn SA, Danforth D, Hastings ML, Duelli DM (2010) Selective release of microRNA species from normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells. PLoS One 5:e13515
Pucci F, Garris C, Lai CP, Newton A, Pfirschke C, Engblom C, Alvarez D, Sprachman M, Evavold C, Magnuson A, von Andrian UH, Glatz K, Breakefield XO, Mempel TR, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ (2016) SCS macrophages suppress melanoma by restricting tumor-derived vesicle-B cell interactions. Science 352:242–246
Rosli SN, Shintani T, Hayashido Y, Toratani S, Usui E, Okamoto T (2013) 1alpha,25OH2D3 down-regulates HBp17/FGFBP-1 expression via NF-kappaB pathway. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 136:98–101
Rosli SN, Shintani T, Toratani S, Usui E, Okamoto T (2014) 1alpha,25(OH)(2)D(3) inhibits FGF-2 release from oral squamous cell carcinoma cells through down-regulation of HBp17/FGFBP-1. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 50:802–806
Sanford M, McCormack PL (2011) Eldecalcitol: a review of its use in the treatment of osteoporosis. Drugs 71:1755–1770
Sato JD, Kawamoto T, Okamoto T (1987) Cholesterol requirement of P3-X63-Ag8 and X63-Ag8.653 mouse myeloma cells for growth in vitro. J Exp Med 165:1761–1766
Shintani T, Rosli SNZ, Takatsu F, Choon YF, Hayashido Y, Toratani S, Usui E, Okamoto T (2016) Eldecalcitol (ED-71), an analog of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 as a potential anti-cancer agent for oral squamous cell carcinomas. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 164:79–84
Shintani T, Takatsu F, Rosli SNZ, Usui E, Hamada A, Sumi K, Hayashido Y, Toratani S, Okamoto T (2017) Eldecalcitol (ED-71), an analog of 1alpha,25(OH)2D3, inhibits the growth of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cells in vitro and in vivo by down-regulating expression of heparin-binding protein 17/fibroblast growth factor-binding protein-1 (HBp17/FGFBP-1) and FGF-2. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 53:810–817
Sporn MB (2006) The early history of TGF-beta, and a brief glimpse of its future. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17:3–7
Ting HJ, Messing J, Yasmin-Karim S, Lee YF (2013) Identification of microRNA-98 as a therapeutic target inhibiting prostate cancer growth and a biomarker induced by vitamin D. J Biol Chem 288:1–9
Tkach M, Thery C (2016) Communication by extracellular vesicles: where we are and where we need to go. Cell 164:1226–1232
Trams EG, Lauter CJ, Salem N Jr, Heine U (1981) Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 645:63–70
Wang Q, Lv L, Li Y, Ji H (2018a) MicroRNA655 suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma by directly targeting metadherin and regulating the PTEN/AKT pathway. Mol Med Rep 18:3106–3114
Wang Z, Yan J, Zou T, Gao H (2018b) MicroRNA-1294 inhibited oral squamous cell carcinoma growth by targeting c-Myc. Oncol Lett 16:2243–2250
Wu DQ, Kan MK, Sato GH, Okamoto T, Sato JD (1991) Characterization and molecular cloning of a putative binding protein for heparin-binding growth factors. J Biol Chem 266:16778–16785
Yoshioka Y, Konishi Y, Kosaka N, Katsuda T, Kato T, Ochiya T (2013) Comparative marker analysis of extracellular vesicles in different human cancer types. J Extracell Vesicles 2
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2007) microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol 302:1–12
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Emiko Usui for her valuable advice. We also thank Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. for the generous gift of ED-71.
Funding
This research was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to T.O. (grant number: 15H05043) and T. S. (grant number: 16K11723). A part of this work was carried out at Natural Science Center for Basic Research and Development, Hiroshima University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Editor: J Denry Sato
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 557 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Higaki, M., Shintani, T., Hamada, A. et al. Eldecalcitol (ED-71)-induced exosomal miR-6887-5p suppresses squamous cell carcinoma cell growth by targeting heparin-binding protein 17/fibroblast growth factor–binding protein-1 (HBp17/FGFBP-1). In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 56, 222–233 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-020-00440-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-020-00440-x