Abstract
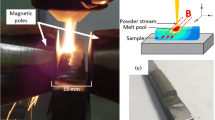
As a typical additive manufacturing technique, direct energy deposition is restricted from further application due to the presence of residual stress and the structural deformation. Thus, minimizing the residual stress plays a crucial role in additive manufacturing. In this work, a transverse static magnetic field is introduced in the laser remelting of Inconel 718 superalloy to investigate the effects on residual stress and microstructural change. The x-ray diffraction technique was used to examine the residual stress variation. Optical microscope and scanning electron microscope were applied to observe the microstructure evolution. It was found that the compressive residual stress of the remelted region was notably reduced from 392.50 to 315.45 MPa under the effect of the magnetic field of 0.55 T. Furthermore, it was observed that the average dendrite spacing was reduced by about 32% under the magnetic field. During the laser remelting process, the imposed electromagnetic force minimized the flow field within the molten pool, inhibiting the heat transfer and minimizing the cooling rate. These directly reduced the residual stresses. Based on research findings, the magnetic field can be a potential method to eliminate the residual stress in laser additive manufacturing components.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Yan, Q. Li, S. Yin, Z. Chen, R. Jenkins, C. Chen, J. Wang, W. Ma, R. Bolot, R. Lupoi, Z. Ren, H. Liao, and M. Liu, Mechanical and In Vitro Study of an Isotropic Ti6Al4 V Lattice Structure Fabricated Using Selective Laser Melting, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 782, p 209-223
T. DebRoy, H.L. Wei, J.S. Zuback, T. Mukherjee, J.W. Elmer, J.O. Milewski, A.M. Beese, A. Wilson-Heid, A. De, and W. Zhang, Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Components: Process, Structure And Properties, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2018, 92(Supplement C), p 112-224
D. Herzog, V. Seyda, E. Wycisk, and C. Emmelmann, Additive Manufacturing of Metals, Acta Mater., 2016, 117, p 371-392
C.L. Qiu, N.J.E. Adkins, and M.M. Attallah, Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Selectively Laser-Melted and of HIPed Laser-Melted Ti-6Al-4 V, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct., 2013, 578, p 230-239
G.-H. Meng, H. Liu, M.-J. Liu, T. Xu, G.-J. Yang, C.-X. Li, and C.-J. Li, Highly Oxidation Resistant MCrAlY Bond Coats Prepared by Heat Treatment Under Low Oxygen Content, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2019, 368, p 192-201
H. Fayazfar, M. Salarian, A. Rogalsky, D. Sarker, P. Russo, V. Paserin, and E. Toyserkani, A Critical Review of Powder-Based Additive Manufacturing of Ferrous Alloys: Process Parameters, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties, Mater. Des., 2018, 144, p 98-128
D.D. Gu, W. Meiners, K. Wissenbach, and R. Poprawe, Laser Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Components: Materials, Processes and Mechanisms, Int. Mater. Rev., 2013, 57(3), p 133-164
Q. Jia and D. Gu, Selective Laser Melting Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718 Superalloy Parts: Densification, Microstructure and Properties, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 585, p 713-721
S. Luo, W. Huang, H. Yang, J. Yang, Z. Wang, and X. Zeng, Microstructural Evolution and Corrosion Behaviors of Inconel 718 Alloy Produced by Selective Laser Melting Following Different Heat Treatments, Addit. Manuf., 2019, 30, p 100875
W. Ma, Y. Xie, C. Chen, H. Fukanuma, J. Wang, Z. Ren, and R. Huang, Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of High-Performance Inconel 718 Alloy by Cold Spraying, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 792, p 456-467
R. Vilar and A. Almeida, Repair and Manufacturing of Single Crystal Ni-Based Superalloys Components by Laser Powder Deposition—A Review, J. Laser Appl., 2015, 27(S1), p S17004
D. Zhang, Z. Feng, C. Wang, W. Wang, Z. Liu, and W. Niu, Comparison of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Inconel 718 Alloy Processed by Selective Laser Melting and Casting, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 724, p 357-367
G.H. Cao, T.Y. Sun, C.H. Wang, X. Li, M. Liu, Z.X. Zhang, P.F. Hu, A.M. Russell, R. Schneider, D. Gerthsen, Z.J. Zhou, C.P. Li, and G.F. Chen, Investigations of γ′, γ″ and δ Precipitates in Heat-Treated Inconel 718 Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting, Mater. Charact., 2018, 136, p 398-406
D. Tomus, Y. Tian, P.A. Rometsch, M. Heilmaier, and X.H. Wu, Influence of Post Heat Treatments on Anisotropy of Mechanical Behaviour and Microstructure of Hastelloy-X Parts Produced by Selective Laser Melting, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct., 2016, 667, p 42-53
I. Lopez-Galilea, B. Ruttert, J. He, T. Hammerschmidt, R. Drautz, B. Gault, and W. Theisen, Additive Manufacturing of CMSX-4 Ni-Base Superalloy by Selective Laser Melting: Influence of Processing Parameters and Heat Treatment, Addit. Manuf., 2019, 30, p 100874
J. Liang, Y. Liu, J. Li, Y. Zhou, and X. Sun, Epitaxial Growth and Oxidation Behavior of an Overlay Coating on a Ni-Base Single-Crystal Superalloy by Laser Cladding, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, 35(2), p 344-350
R.J. DiMelfi, P.G. Sanders, B. Hunter, J.A. Eastman, K.J. Sawley, K.H. Leong, J.M. Kramer, Mitigation of Subsurface Crack Propagation in Railroad Rails by Laser Surface Modification, in This Paper was Presented at the 1997 International Conference on Metallurgical Coatings and Thin Films, Session E1, held 21–25 April 1997, Town and Country Hotel, San Diego, CA, USA. Surf Coat Technol 106(1) (1998), pp 30-43
B. Ahmad, S.O. van der Veen, M.E. Fitzpatrick, and H. Guo, Residual Stress Evaluation in Selective-Laser-Melting Additively Manufactured Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) and Inconel 718 Using the Contour Method and Numerical Simulation, Addit. Manuf., 2018, 22, p 571-582
L. Parry, I.A. Ashcroft, and R.D. Wildman, Understanding the Effect of Laser Scan Strategy on Residual Stress in Selective Laser Melting Through Thermo-Mechanical Simulation, Addit. Manuf., 2016, 12, p 1-15
C. Qiu, H. Chen, Q. Liu, S. Yue, and H. Wang, On the Solidification Behaviour and Cracking Origin of a Nickel-Based Superalloy During Selective Laser Melting, Mater. Charact., 2019, 148, p 330-344
Z. Shuangyin, L. Xin, C. Jing, and H. Weidong, Influence of Heat Treatment on Residual Stress of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy by Laser Solid Forming, Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 2009, 5, p 774-778
P. Farahmand and R. Kovacevic, An Experimental–Numerical Investigation of Heat Distribution and Stress Field in Single-and Multi-track Laser Cladding by a High-Power Direct Diode Laser, Opt. Laser Technol., 2014, 63, p 154-168
M. Labudovic, D. Hu, and R. Kovacevic, A Three Dimensional Model for Direct Laser Metal Powder Deposition and Rapid Prototyping, J. Mater. Sci., 2003, 38(1), p 35-49
E. Savitsky, R. Torchinova, and S. Turanov, Effect of Crystallization in Magnetic Field on the Structure and Magnetic Properties of Bi-Mn Alloys, J. Cryst. Growth, 1981, 52, p 519-523
A. Goetz and M.F. Hasler, The Thermoanalysis of Metal Single Crystals and a New Thermoelectric Effect of Bismuth Crystals Grown in Magnetic Fields, Phys. Rev., 1930, 36(12), p 1752
W. Tiller, K. Jackson, J. Rutter, and B. Chalmers, The Redistribution of Solute Atoms During the Solidification of Metals, Acta Metall., 1953, 1(4), p 428-437
X. Li, A. Gagnoud, Y. Fautrelle, Z. Ren, R. Moreau, Y. Zhang, and C. Esling, Dendrite Fragmentation and Columnar-to-Equiaxed Transition During Directional Solidification at Lower Growth Speed Under a Strong Magnetic Field, Acta Mater., 2012, 60(8), p 3321-3332
X. Li, Y. Fautrelle, K. Zaidat, A. Gagnoud, Z. Ren, R. Moreau, Y. Zhang, and C. Esling, Columnar-to-Equiaxed Transitions in Al-Based Alloys During Directional Solidification Under a High Magnetic Field, J. Cryst. Growth, 2010, 312(2), p 267-272
G. Oreper and J. Szekely, The Effect of an Externally Imposed Magnetic Field on Buoyancy Driven Flow in a Rectangular Cavity, J. Cryst. Growth, 1983, 64(3), p 505-515
A. Witt, C.J. Herman, and H. Gatos, Czochralski-Type Crystal Growth in Transverse Magnetic Fields, J. Mater. Sci., 1970, 5(9), p 822-824
P. Lehmann, R. Moreau, D. Camel, R. Bolcato, Modification of Interdendritic Convection by a Magnetic Field. Mater Sci Forum, Trans Tech Publ, 1996, pp. 235-240
S.N. Tewari, R. Shah, and H. Song, Effect of Magnetic Field on the Microstructure and Macrosegregation in Directionally Solidified Pb-Sn Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1994, 25(7), p 1535-1544
J. Wang, Y. Fautrelle, Z. Ren, X. Li, H. Nguyen-Thi, N. Mangelinck-Noël, G. Salloum Abou Jaoude, Y. Zhong, I. Kaldre, and A. Bojarevics, Thermoelectric Magnetic Force Acting on the Solid During Directional Solidification Under a Static Magnetic Field, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, 101(25), p 251904
R. Moreau, O. Laskar, M. Tanaka, and D. Camel, Thermoelectric Magnetohydrodynamic Effects on Solidification of Metallic Alloys in the Dendritic Regime, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1993, 173(1-2), p 93-100
S. Kuroda, T. Fukushima, and S. Kitahara, Simultaneous Measurement of Coating Thickness and Deposition Stress During Thermal Spraying, Thin Solid Films, 1988, 164, p 157-163
Y.C. Tsui and T.W. Clyne, An Analytical Model for Predicting Residual Stresses in Progressively Deposited Coatings Part 1: Planar Geometry, Thin Solid Films, 1997, 306(1), p 23-33
T.W. Clyne and S.C. Gill, Residual Stresses in Thermal Spray Coatings and Their Effect on Interfacial Adhesion: A Review of Recent Work, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 1996, 5(4), p 401
J. Liu, R. Bolot, and S. Costil, Residual Stresses and Final Deformation of an Alumina Coating: Modeling and Measurement, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2015, 268, p 241-246
P. Royston, Approximating the Shapiro–Wilk W-Test for Non-normality, Stat. Comput. Control Eng. J., 1992, 2(3), p 117-119
C. Panwisawas, C.L. Qiu, Y. Sovani, J.W. Brooks, M.M. Attallah, and H.C. Basoalto, On the Role of Thermal Fluid Dynamics into the Evolution of Porosity During Selective Laser Melting, Scr. Mater., 2015, 105, p 14-17
H. Harada, T. Toh, T. Ishii, K. Kaneko, and E. Takeuchi, Effect of Magnetic Field Conditions on the Electromagnetic Braking Efficiency, ISIJ Int., 2001, 41(10), p 1236-1244
J. Favier and D. Camel, Analytical and Experimental Study of Transport Processes During Directional Solidification and Crystal Growth, J. Cryst. Growth, 1986, 79(1-3), p 50-64
Y. Fautrelle, J. Wang, G. Salloum-Abou-Jaoude, L. Abou-Khalil, G. Reinhart, X. Li, Z.M. Ren, and H. Nguyen-Thi, Thermo-Electric-Magnetic Hydrodynamics in Solidification: In Situ Observations and Theory, JOM, 2018, 70(5), p 764-771
X.-H. Tian, W.-Y. Shi, T. Tang, L. Feng, Influence of Vertical Static Magnetic Field on Behavior of Rising Single Bubble in a Conductive Fluid. ISIJ Int (2015) ISIJINT-2015-493
X. Li, A. Gagnoud, Z. Ren, Y. Fautrelle, and R. Moreau, Investigation of Thermoelectric Magnetic Convection and Its Effect on Solidification Structure During Directional Solidification Under a Low Axial Magnetic Field, Acta Mater., 2009, 57(7), p 2180-2197
H. Liu, W. Xuan, X. Xie, C. Li, J. Wang, J. Yu, X. Li, Y. Zhong, and Z. Ren, Columnar-to-Equiaxed Transition and Equiaxed Grain Alignment in Directionally Solidified Ni 3 Al Alloy Under an Axial Magnetic Field, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, 48(9), p 4193-4203
S. Eckert, P.A. Nikrityuk, D. Räbiger, K. Eckert, and G. Gerbeth, Efficient Melt Stirring Using Pulse Sequences of a Rotating Magnetic Field: Part I. Flow Field in a Liquid Metal Column, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2007, 38(6), p 977-988
W. Xuan, Z. Ren, and C. Li, Effect of a High Magnetic Field on Microstructures of Ni-Based Superalloy During Directional Solidification, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 620, p 10-17
J.H. Martin, B.D. Yahata, J.M. Hundley, J.A. Mayer, T.A. Schaedler, and T.M. Pollock, 3D Printing of High-Strength Aluminium Alloys, Nature, 2017, 549(7672), p 365
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51604171, 51690162 and 51701112), the Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (Nos. 17JC1400602 and 19DZ1100704), Shanghai Sailing Program (Grant Nos. 19YF1415900), Chinese National Science and Technology Major Project “Aeroengine and Gas Turbine” (2017-VII-0008-0102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of a special topical focus in the Journal of Thermal Spray Technology on Advanced Residual Stress Analysis in Thermal Spray and Cold Spray Processes. This issue was organized by Dr. Vladimir Luzin, Australian Centre for Neutron Scattering; Dr. Seiji Kuroda, National Institute of Materials Science; Dr. Shuo Yin, Trinity College Dublin; and Dr. Andrew Ang, Swinburne University of Technology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, J., Chen, C., Shuai, S. et al. Effect of Static Magnetic Field on the Evolution of Residual Stress and Microstructure of Laser Remelted Inconel 718 Superalloy. J Therm Spray Tech 29, 1410–1423 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-020-01039-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-020-01039-0