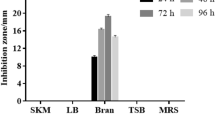
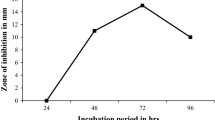
Abstract
Abamectin (ABA) constitutes a big commodity for pharmaceutical companies because it generates about one billion dollar annual sale. Avermectins (AVMs) and their naturally occurring analogues, milbemycins (MILs), meilingmycins (MEIs), ivermectin (IVE), abamectin (ABA), and nemadectin (NEM), represent one of the most developed antiparasitic agents. Abamectin is a mixture of avermectin B1a and avermectin B1b. The production of abamectin by Streptomyces avermitilis is a complicated process and separation of two fractions is quite difficult; commercial product contains more than 80% of Bla and less than 20% of B1b components. The main goal of the study was the identification and optimization of fermentation conditions to raise the production of abamectin from Egyptian S. avermitilis. The qualitative and quantitative analysis of avermectins was carried out by thin layer chromatography (TLC) and 6538 Q-TOF with Agilent 1290 UHPLC. The process of identification was carried out by using production medium containing 30 g/L corn starch, and 0.725 g/L CaCO3, pH 7, 8% inoculum size and incubated at 32.5 °C. The enhancement of the production of abamectin is a big challenge with commercial and industrial importance, as its output is insufficient for human consumption.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almalki MH, Mankai H, Slama N, Barkallah I, Limam F (2018) Production and optimization of thermophilic alkaline protease in solid-state fermentation by Streptomyces sp CN902. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 36(4):531–537
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 17:3389–3402
Alvinerie M, Sutra JF, Galtier P, Toutain PL (1987) Determination of ivermectin in milk by high performance liquid chromatography. Ann Rech Vet 18:269–274
Beg QK, Sahai V, Gupta R (2003) Statistical media optimization and alkaline protease production from Bacillus mojavensis in a bioreactor. Process Biochem 39(2):203–209
Campbell WC (2016) Lessons from the history of ivermectin and other antiparasitic agents. Annual Rev Animal Biosci 4:1–14
Cao J, Chen X, Ren H, Zhang J, Li L, Chen Y, Xiong J, Bai J, Ying H (2012) Production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate by Arthrobacter sp. A302 using fed batch fermentation with pH shift control. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28(1):121–127
Cheng KK, Wu J, Lin ZN, Zhang JA (2014) Aerobic and sequential anaerobic fermentation to produce xylitol and ethanol using non detoxified acid pretreated corncob. Biotech Biofuels 7:166
Clarridge JE (2004) Impact of 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis for identification of bacteria on clinical microbiology and infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev 4:840–862
Deepika KV, Kalam S, Sridhar PR, Podile AR, Bramhachari PV (2016) Optimization of rhamnolipid biosurfactant production by mangrove sediment bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa KVR-HR42 using response surface methodology. Biocatal agric Biotech 5:38–47
Deng Q, Zhou L, Luo M, Deng Z, Zhao C (2017) Heterologous expression of avermectins biosynthetic gene cluster by construction of a bacterial artificial chromosome library of the producers. Synth Syst Biotech 2:59–64
Deng Q, Xiao L, Liu Y, Zhang L, Deng Z, Zhao C (2019) Streptomyces avermitilis industrial strain as cell factory for ivermectin B1a production. Synth Syst Biotech 1:34–39
Dey A, Bhattacharya R, Mukherjee A, Pandey DK (2017) Natural products against Alzheimer’s disease: pharmaco-therapeutics and biotechnological interventions. Biotechnol Adv 35:178–216
Elibol M (2004) Optimization of medium composition for actinorhodin production by Streptomyces coelicolor A3 (2) with response surface methodology. Process Biochem 39:1057–1062
El-Naggar NE, Abdelwahed NA (2014) Optimization of process parameters to produce alkali-tolerant carboxymethyl cellulase by newly isolated Streptomyces sp. strain NEAE-D. Afr J Biotechnol 11(5):1185–1196
El-Naggar NE, Hamouda RA (2016) Antimicrobial potentialities of Streptomyces lienomycini NEAE-31 against human pathogen multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Pharmacol 12:769–788
El-Naggar NE, El-Bindary AA, Nour SN (2013a) Statistical optimization of process variables for antimicrobial metabolites production by Streptomyces anulatus NEAE-94 against some multidrug-resistant strains. Int J Pharmacol 9:322–334
El-Naggar NE, El-Bindary AA, Nour SN (2013b) Production of antimicrobial agent inhibitory to some human pathogenic multidrug-resistant bacteria and Candida albicans produced by Streptomyces sp. NEAE-1. Int J Pharmacol 9:335–347
El-Naggar NE, Mohamedin AH, Sherief AA, Hussien SM (2015) Optimization of bioactive metabolites production by a newly isolated marine Streptomyces sp using statistical approach. Biotech 14(5):211–224
El-Naggar NE, El-Shweihy NM, El-Ewasy SM (2016a) Identification and statistical optimization of fermentation conditions for a newly isolated extracellular cholesterol oxidase producing Streptomyces cavourensis strain NEAE. BMC Microbiol 42:16–2171
El-Naggar NE, Mohamedin AH, Sherief AA, Hussien SM (2016b) Optimization of fermentation conditions for production of bioactive metabolites effective against Staphylococcus epidermidis by a newly isolated Nocardiopsis chromatogenes strain SH89 using response surface methodology. J Pure Appl Sci 10(1):823–839
Gordon RE, Smith NR (1949) Aerobic spore forming bacteria capable of growth at high temperatures. J Bacteriol 58(3):327–340
Guo H, Liu M, Liu J, Dai H, Zhou X, Liu X, Zhuo Y, Zhang W, Zhang L (2009) Medium optimization for the production of avermectin B1a by Streptomyces avermitilis 14-12A using response surface methodology. Bioresource Tech 100:4012–4016
Homans A, Fuchs A (1970) Direct bioautography on thin layer chromatograms as a method for detecting fungitoxic substances. J Chromatogr A 51:327–329
Jia B, Jin ZH, Mei LH (2008) Medium optimization based on statistical methodologies for pristinamycins production by Streptomyces pristinaespiralis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2:133–143
Kim SM, Cho WJ, Song CM, Park WS, Kim K, Kim E, Nam JS, Oh HK, Yoon JY (2017) Engineered biosynthesis of milbemycins in the avermectin high producing strain Streptomyces avermitilis. Microb Cell Factories 16:9
Kokare C, Mahadik K, Kadam S, Chopade B (2004) Isolation, characterization and antimicrobial activity of marine halophilic Actinopolyspora sp AH1 from the west coast of India. Curr Sci 86(4):593–597
Kumar V, Bharti A, Gusain O, Bisht GS (2011) Scanning electron microscopy of Streptomyces without use of any chemical fixatives. Scan 33(6):446–449
Laing R, Gillan V, Devaney E (2017) Ivermectin–old drug, new tricks? Trends Parasitol 33(6):463–472
Lim LE, Vilcheze C, Ng C, Jacobs WR, Ramon-Garcia S, Thompson CJ (2013) Anthelmintic avermectins kill Mycobacterium tuberculosis, including multidrug resistant clinical strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:1040–1046
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) Unifrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 12:8228–8235
Maxwell RJ (1999) Light field. J Planar Chromatogram Mod TLC 12:109
Meng J, Kanzaki G, Meas D, Lam CK, Crummer H, Tain J, Xu HH (2012) A genome-wide inducible phenotypic screen identifies antisense RNA constructs silencing Escherichia coli essential genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 329(1):45–53
Plackett RL, Burman JP (1946) The design of optimum multifactorial experiments. Biometrika 33:305–325
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Shirling ET, Gottlieb D (1966) Methods for characterization of Streptomyces sp. Int J Syst Bacteriol 16(3):313–340
Siddique S, Syed Q, Adnan A, Nadeem M, Irfan M, Ashraf Qureshi F (2013) Production of avermectin B1b from Streptomyces avermitilis 41445 by batch submerged fermentation. J Microbiol 8:10–5812
Silverman RB, Holladay MW (2014) The organic chemistry of drug design and drug action. Third edition / ed.; Elsevier/AP, academic press, is an imprint of Elsevier: Amsterdam; Boston
Song S, Liu Z, He Z, Chen J, Li C (2009) Degradation of the biocide 4-chloro-3,5-dimethlphenol in aqueous medium with ozono in combination with ultraviolet irradiation; operating conditions influence and mechanism. Chemospere 77:1043–1051
Syed DG, Lee JC, Li WJ, Kim CJ, Agasar D (2009) Production, characterization and application of keratinase from Streptomyces gulbargensis. Bioresour Technol 5:1868–1871
Tresner H, Davies M, Backus E (1961) Electron microscopy of Streptomyces spore morphology and its role in species differentiation. J Bacteriol 81(1):70
Upadhyaya J, Kim MJ, Kim YH, Ko SR, Park HW, Kim MK (2016) Enzymatic formation of compound K from ginsenoside Rb1 by enzyme preparation from cultured mycelia of Armillaria mellea. J Ginseng Res 40:105–112
Waldia A, Gupta S, Issarani R, Nagori BP (2008) Validated liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous estimation of albendazole and ivermectin in tablet dosage form. Indian J Chem Tech 15:617–620
Wang SY, Chen JH, Li WJ, Liang JP, Bo YH, Ma X, Liu J (2011) Mutagenesis, screening and industrialization of high avermectin B1a producing strains from Streptomyces avermitilis irradiated by 12C ion beam. Adv Mater 339:652–655
Watve MG, Tickoo R, Jog MM, Bhole BD (2001) How many antibiotics are produced by the genus Streptomyces? Arch Microbiol 176:386–390
Yong JH, Byeon WH (2005) Alternative production of avermectin components in Streptomyces avermitilis by gene replacement. J Microbiol 3:277–284
Zheng ZM, Hu Q, Hao JF, Xu NM, Guo Y, Sun DH (2008) Statistical optimization of culture conditions for 1, 3-propanediol by Klebsiella pneumoniae AC 15 via central composite design. Bioresource Tech 99(5):1052–1056
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the Egyptian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research and Mansoura University that funded Miss Suzan Hussein for her training scholarship at proteomic facility in Montana State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osman, Y.A., Aldesuquy, H.S., Younis, S.A. et al. Characterization and optimization of abamectin—a powerful antiparasitic from a local Streptomyces avermitilis isolate. Folia Microbiol (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-020-00779-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-020-00779-4