Abstract
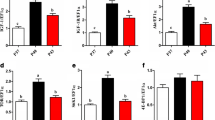
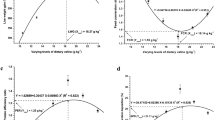
Amino acids can act as signaling molecules in protein synthesis and animal growth by regulating several genes in the target of rapamycin (TOR) pathway. An 8-week feeding trial was conducted to examine the effects of dietary proline on growth performance, body composition, amino acid profiles, blood-biochemistry and expression of TOR pathway-related genes in juvenile Nibea diacanthus. Fish (450 juvenile N. diacanthus) were assigned to six dietary proline supplementation groups (0, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 and 12.5 g kg−1 of dry diet). The results revealed that the growth performance and feed utilization of N. diacanthus were not significantly improved with dietary proline level (P > 0.05). Whole-body crude protein and some amino acids in muscle tissue were significantly (P < 0.05) affected by the supplemental dietary proline, while the levels of hepatic GOT and GPT increased significantly (P < 0.05) with increasing levels of dietary proline. The transcript level of TOR in muscle was significantly affected by dietary proline level, while the mRNA levels of 4EBP, S6K1, TSC and GTPBP in muscle were relatively unaffected. In conclusion, our results indicate that (1) dietary proline promotes protein synthesis, and (2) proline may promote protein synthesis by regulating the transcription of TOR but not 4EBP, S6K1, TSC and GTPBP.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboudi T, Mambrini M, Larondelle Y, Rollin X (2009) The effect of dispensable amino acids on nitrogen and amino acid losses in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fry fed a protein-free diet. Aquaculture 289:327–333
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) (1995) Official Methods of Analysis of Official Analytical Chemists International, 16th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, VA
Baker DH (2009) Advances in protein-amino acid nutrition of poultry. Amino Acids 37:29–41
Ball RO, Atkinson JL, Bayley HS (1986) Proline as an essential amino acid for the young pig. Br J Nutr 55:659–668
Barbul A (2024S) Proline precursors to sustain mammalian collagen synthesis. J Nutr 138:2021S–2024S
Ben-Sahra I, Manning BD (2017) mTORC1 signaling and the metabolic control of cell growth. Curr Opin Cell Biol 45:72–82
Chen GF, Feng L, Kuang SY, Liu Y, Jiang J, Hu K, Jiang WD, Li SH, Tang L, Zhou XQ (2012) Effect of dietary arginine on growth, intestinal enzyme activities and gene expression in muscle, hepatopancreas and intestine of juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Br J Nutr 108:195–207
Chen HD, Zheng JH, Shen ZK (2011) Technique for artificial breeding of spotted drum N. diacanthus. Fish Sci 30:501–504 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Deng JM, Kong LF, An QC, Bi BL, Tao LL, Zhang X (2011) Effect of dietary pH adjustment on the utilization of supplemental methionine and lysine by juvenile common carp, Cyprinus carpio. J World Aquac Soc 42:696–704
Ferreira AGK, Lima DD, Delwing D, Mackedanz V, Tagliari B, Kolling J, Schuck PF, Wajner M, Wyse ATS (2010) Proline impairs energy metabolism in cerebral cortex of young rats. Metab Brain Dis 25:161–168
Gorres KL, Raines RT (2010) Prolyl 4-hydroxylase. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 45:106–124
Graber G, Allen NK, Scott HM (1970) Proline essentiality and weight gain. Poult Sci 49:692–697
Habte-Tsion HM (2019) Fish nutritional response to essential amino acids in relation to TOR and GH/IGF-axis signaling molecules. EC Nutr ECO 2:13–15
He Y, Chi S, Tan B, Dong X, Yang Q, Liu H, Zhang S, Han F, Liu D (2019) DL-Methionine supplementation in a low-fishmeal diet affects the TOR/S6K pathway by stimulating ASCT2 amino acid transporter and insulin-like growth factor-I in the dorsal muscle of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Br J Nutr 122(7):734–744
Holeček M (2018) Branched-chain amino acids in health and disease: metabolism, alterations in blood plasma, and as supplements. Nutr Metabol 15:33
Holz MK, Ballif BA, Gygi SP, Blenis J (2005) mTOR and S6K1 mediate assembly of the translation preinitiation complex through dynamic protein interchange and ordered phosphorylation events. Cell 123:569–580
Hou YQ, Wu G (2017) Nutritionally nonessential amino acids: a misnomer in nutritional sciences. Adv Nutr 8:137–139
Hou YQ, Yao K, Yin YL, Wu G (2016) Endogenous synthesis of amino acids limits growth, lactation and reproduction of animals. Adv Nutr 7:331–342
Hu SD, Li XL, Rezaei R, Meininger CJ, McNeal CJ, Wu G (2015) Safety of long-term dietary supplementation with l-arginine in pigs. Amino Acids 47:925–936
Huang YS, Lin ZD, Rong H, Hao ML, Zou WG, Li SK, Wen XB (2017a) Cloning, tissue distribution, functional characterization and nutritional regulation of Δ6 fatty acyl desaturase in chu’s croaker Nibea coibor. Aquaculture 479:208–216
Huang YS, Wen XB, Li SK, Xuan XZ, Zhu DS (2017b) Effects of protein levels on growth, feed utilization, body composition, amino acid composition and physiology indices of juvenile chu’s croaker, Nibea coibor. Aquac Nutr 23:594–602
Karna E, Szoka L, Huynh TYL, Palka JA (2019) Proline-dependent regulation of collagen metabolism. Cell Mol Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03363-3
Kaul S, Sharma SS, Mehta IK (2008) Free radical scavenging potential of L-proline: evidence from in vitro assays. Amino Acids 34:315–320
Kirchgessner M, Fickler J, Roth FX (1995) Effect of dietary proline supply on N-balance of piglets, 3: communication on the importance of nonessential amino acids for protein retention. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 73:57–65
Li P, Mai KS, Trushenski J, Wu GY (2009) New developments in fish amino acid nutrition: towards functional and environmentally oriented aquafeeds. Amino Acids 37:43–53
Li P, Wu GY (2018) Roles of dietary glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline in collagen synthesis and animal growth. Amino Acids 50:29–38
Li WJ, Wen XB, Zhao J, Li SK, Zhu DS (2016) Effects of dietary protein levels on growth, feed utilization, body composition and ammonia–nitrogen excretion in juvenile Nibea diacanthus. Fish Sci 82:137–146
Li WJ, Wen XB, Huang YS, Zhao J, Li SK, Zhu DS (2017) Effects of varying protein and lipid levels and protein-to-energy ratios on growth, feed utilization and body composition in juvenile Nibea diacanthus. Aquac Nutr 23:1035–1047
Li XL, Rezaei R, Li P, Wu GY (2011) Composition of amino acids in feed ingredients for animal diets. Amino Acids 40:1159–1168
Liang H, Ren M, Habte-Tsion HM, Ge X, Xie J, Mi H, Xi B, Miao L, Liu B, Zhou Q, Fang W (2016) Dietary arginine affects growth performance, plasma amino acid contents and gene expressions of the TOR signaling pathway in juvenile blunt snout bream, Megalobrama amblycephala. Aquaculture 461:1–8
Lin ZD, Hao ML, Huang YS, Zou WG, Rong H, Wen XB (2018a) Cloning, tissue distribution and nutritional regulation of a fatty acyl Elovl4-like elongase in mud crab, Scylla paramamosain (Estampador, 1949). Comp Biochem Physiol Part B 217:70–78
Lin ZD, Huang YS, Zou WG, Rong H, Hao ML, Wen XB (2018b) Cloning, tissue distribution, functional characterization and nutritional regulation of a fatty acyl Elovl5 elongase in chu’s croaker Nibea coibor. Gene 659:11–21
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2(-ΔΔC(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Ma T, Zuazaga G (1942) Micro-Kjeldahl determination of nitrogen. A new indicator and an improved rapid method. Ind Eng Chem Anal Ed 14:280–282
Menon S, Dibble CC, Talbott G, Hoxhaj G, Valvezan AJ, Takahashi H, Cantley LC, Manning BD (2014) Spatial control of the TSC complex integrates insulin and nutrient regulation of mTORC1 at the lysosome. Cell 156:771–785
Metón I, Mediavilla D, Caseras A, Cantó E, Fernández F, Baanante I (1999) Effect of diet composition and ration size on key enzyme activities of glycolysis–gluconeogenesis, the pentose phosphate pathway and amino acid metabolism in liver of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Br J Nutr 82:223–232
National Research Council (NRC) (2011) Nutrient Requirements of Domestic Animals. Nutrient Requirements of Fish. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Peres H, Oliva-Teles A (2007) Effect of the dietary essential amino acid pattern on growth, feed utilization and nitrogen metabolism of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 267:119–128
Polak P, Hall MN (2009) mTOR and the control of whole body metabolism. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:209–218
Rezaei R, Wang WW, Wu ZL, Dai Z, Wang J, Wu G (2013) Biochemical and physiological bases for utilization of dietary amino acids by young pigs. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 4:7
Rong H, Zhang Y, Hao M, Zou W, Yu J, Yu C, Shi Q, Wen X (2019) Effects of dietary hydroxyproline on collagen metabolism, proline 4-hydroxylase activity, and expression of related gene in swim bladder of juvenile Nibea diacanthus. Fish Physiol Biochem 45(6):1779–1790
Shimobayashi M, Hall MN (2016) Multiple amino acid sensing inputs to mTORC1. Cell Res 26:7–20
Ren M, Habte-Tsion HM, Liu B, Miao L, Ge X, Xie J, Liang H, Zhou Q, Pan L (2015) Dietary leucine level affects growth performance, whole body composition, plasma parameters and relative expression of TOR and TNF-ɑ in juvenile blunt snout bream, Megalobrama amblycephala. Aquaculture 448:162–168
Tang L, Feng L, Sun CY, Chen GF, Jiang WD, Hu K, Liu Y, Jiang J, Li SH, Kuang SY, Zhou XQ (2013) Effect of tryptophan on growth, intestinal enzyme activities and TOR gene expression in juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian): studies in vivo and in vitro. Aquaculture 412:23–33
van Meijl LEC, Popeijus HE, Mensink RP (2010) Amino acids stimulate Akt phosphorylation, and reduce IL-8 production and NF-kappaB activity in HepG2 liver cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 54:1568–1573
Wen J, Zeng L, Chen ZM, Xu YH (2016) Comparison of nutritional quality in fish maw product of croaker Protonibea diacanthus and perch Lates niloticus. J Ocean Univ China 15:726–730
Wu G, Bazer FW, Burghardt RC, Johnson GA, Kim SW, Knabe DA, Li P, Li XL, McKnight JR, Satterfield MC, Spencer TE (2011) Proline and hydroxyproline metabolism: implications for animal and human nutrition. Amino Acids 40:1053–1063
Wu G, Bazer FW, Datta S, Johnson GA, Li P, Satterfield MC, Spencer TE (2008) Proline metabolism in the conceptus: implications for fetal growth and development. Amino Acids 35:691–702
Wu G, Bazer FW, Davis TA, Kim SW, Li P, Rhoads JM, Satterfield MC, Smith SB, Spencer TE, Yin YL (2009) Arginine metabolism and nutrition in growth, health and disease. Amino Acids 37:153–168
Wu G, Meininger CJ (2009) Nitric oxide and vascular insulin resistance. BioFactors 35:21–27
Wu G, Morris SM Jr (1998) Arginine metabolism: nitric oxide and beyond. Biochem J 336:1–17
Wu M, Lu S, Wu X, Jiang S, Luo Y, Yao W, Jin Z (2017) Effects of dietary amino acid patterns on growth, feed utilization and hepatic IGF-I, TOR gene expression levels of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀× Epinephelus lanceolatus♂) juveniles. Aquaculture 468:508–514
Wu M, Wu X, Lu S, Gao Y, Yao W, Li X, Dong Y, Jin Z (2018) Dietary arginine affects growth, gut morphology, oxidation resistance and immunity of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀× Epinephelus lanceolatus♂) juveniles. Br J Nutr 120(3):269–282
Wu ZL, Hou YQ, Hu SD, Bazer FW, Meininger CJ, McNeal CJ, Wu G (2016) Catabolism and safety of supplemental l-arginine in animals. Amino Acids 48:1541–1552
Xie SW, Tian LX, Li YM, Zhou WW, Zeng SL, Yang HJ, Liu YJ (2015) Effect of proline supplementation on anti-oxidative capacity, immune response and stress tolerance of juvenile Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 448:105–111
Yoon MS, Choi CS (2016) The role of amino acid-induced mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling in insulin resistance. Exp Mol Med 48:e201
Zhang KK, Mai KS, Xu W, Zhou HH, Liufu ZG, Zhang YJ, Peng M, Ai QH (2015) Proline with or without hydroxyproline influences collagen concentration and regulates prolyl 4-hydroxylase α (I) gene expression in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). J Ocean Univ China 14:541–548
Zhang Y, Dabrowski K, Hliwa P, Gomulka P (2006) Indispensable amino acid concentrations decrease in tissues of stomachless fish, common carp in response to free amino acid- or peptide-based diets. Amino Acids 31:165–172
Zhou Z, Wang X, Wu X, Gao Y, Li X, Dong Y, Yao W (2019) Effects of dietary leucine levels on growth, feed utilization, neuro-endocrine growth axis and TOR-related signaling genes expression of juvenile hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀× Epinephelus lanceolatus♂). Aquaculture 504:172–181
Zou T, Cao SP, Han D, Liu HK, Yang YX, Jin JY, Zhu XM, Xie SQ (2018) Effects of dietary leucine levels on growth, tissue protein content and relative expression of genes related to protein synthesis in juvenile gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio var. CAS III). Aquac Res 49(6):2240–2248
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all laboratory members for technical advice and valuable help during the feeding trial and sample analysis. This research was supported by grant no. 2016ZR14 from the Natural Science Youth Research Foundation of Yunnan Agricultural University, grant no. 2018FG001-044 from the Yunnan Province Agricultural Basic Research Joint Project and grant no. 2016KQNCX058 from Young Creative Talents, Major Scientific Research Projects of Guangdong University Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rong, H., Lin, F., Zhang, Y. et al. Effects of dietary proline on growth, physiology, biochemistry and TOR pathway-related gene expression in juvenile spotted drum Nibea diacanthus. Fish Sci 86, 495–506 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-020-01414-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-020-01414-4