Abstract
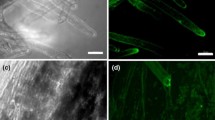
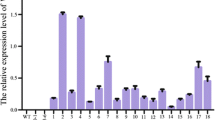
Because overexpression of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (Vgb) gene in plants can enhance tolerance to waterlogging, here Vgb was inserted into Populus alba × glandulosa to investigate its expression and effects on growth and physiological responses to waterlogging stress in the transgenic poplars. Southern blotting and RT-PCR analysis of Vgb-transgenic P. alba × glandulosa showed that the Vgb gene was integrated into the genome of the V13-81 and V13-85 transgenic lines and expressed. In greenhouse waterlogging stress tests, mortality of the transgenic poplar was significant lower than that of nontransgenic plants with increasing treatment time from 2 to 22 days. The transgenic plants had higher chlorophyll content and less chloroplast damage than in the control plants. Additionally, starch accumulation increased, and growth was enhanced in the transgenic plants, suggesting that the Vgb-expressing lines had improved energy reserves. Field trials of the transgenic poplar suggested that Vgb expression promotes growth and influences wood quality. Taken together, our results suggest that the expression of Vgb can increase the accumulation of chlorophyll and starch in the transgenic poplar, improve its ability to endure flooding, and improve growth and wood quality of the transgenic plants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brewin NJ, Flavell RB (1997) A cure for anemia in plants. Nat Biotechnol 15:222–223
Bülow L, Holmberg N, Lilius G, Bailey JE (1999) The metabolic effects of native and transgenic hemoglobins on plants. Trends Biotechnol 17:21–24
Chen FH, Hao YQ, Yin ZZ, Wu GB, Jiang XX (2017) Transcriptome of wax apple (syzygium samarangense) provides insights into nitric oxide-induced delays of postharvest cottony softening. Acta Physiol Plant 39(12):273
Dikshit RP, Dikshit KL, Liu Y, Webster DA (1992) The bacterial hemoglobin from Vitreoscilla can support the aerobic growth of Escherichia coli lacking terminal oxidases. Arch Biochem Biophys 293:241
Farrés J, Kallio PT (2002) Improved cell growth in tobacco suspension cultures expressing Vitreoscilla hemoglobin. Biotechnol Prog 18:229–233
Guo ZY, Tan HX, Lü ZY, Ji Q, Huang YX, Liu JJ, Chen DH, Diao Y, Si JP, Zhang L (2018) Targeted expression of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin improves the production of tropane alkaloids in Hyoscyamus niger hairy roots. Sci Rep 8:17969
Häggman H, Frey AD, Ryynänen L, Aronen T, Julkunen-Tiitto R, Tiimonen H, Pihakaski-Maunsbach K, Jokipii S, Chen X, Kallio PT (2003) Expression of Vitreoscilla haemoglobin in hybrid aspen (Populus tremula × tremuloides). Plant Biotechnol J 1:287–300
Hebelstrup KH, Igamberdiev AU, Hill RD (2007) Metabolic effects of hemoglobin gene expression in plants. Gene 398:86–93
Hebelstrup KH, Shah JK, Simpson C, Schjoerring JK, Mandon J, Cristescu SM, Harren FJ, Christiansen MW, Mur LA, Igamberdiev AU (2014) An assessment of the biotechnological use of hemoglobin modulation in cereals. Physiol Plant 150(4):593–603
Hermann K, Meinhard J, Dobrev P, Linkies A, Pesek B, Hess B, Macháčková I, Fischer U, Metzger GL (2007) 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid and abscisic acid during the germination of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.): a comparative study of fruits and seeds. J Exp Bot 58(11):3047–3060
Holmberg N, Lilius G, Bailey JE, Bülow L (1997) Transgenic tobacco expressing Vitreoscilla hemoglobin exhibits enhanced growth and altered metabolite production. Nat Biotechnol 15:244–247
Inskeep WP, Bloom PR (1985) Extinction coefficients of chlorophyll a and b in N,N-dimethylformamide and 80% acetone. Plant Physiol 77:483–485
Leiva EN, Reeder BJ, Wilson MT, Bülow L (2019) Sugar beet hemoglobins: reactions with nitric oxide and nitrite reveal differential roles for nitrogen metabolism. Biochem J 476(14):2111–2125
Leiva-Eriksson N, Pin PA, Kraft T, Dohm JC, Minoche AE, Himmelbauer H, Bülow L (2014) Differential expression patterns of non-symbiotic hemoglobins in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris ssp. vulgaris). Plant Cell Physiol 55(4):834–844
Lodhi MA, Ye GN, Weeden NF, Reisch B (1994) A simple and efficient method for DNA extraction from grapevine cultivars and Vitis species. Plant Mol Biol Report 12:6–13
Mao ZC, Hu YL, Zhong J, Wang LX, Guo JY, Lin ZP (2003) Improvement of the hydroponic growth and waterlogging tolerance of Petunias by the introduction of Vhb gene. Acta Bot Sin 45:205–210
Martinelli L, Vaccari I, Dallacosta L, Poletti V, Masuero D, Vrhovsek U (2013) Combining molecular and metabolomic analysis to evaluate transgenic Vitis vinifera plants expressing the Vitreoscilla haemoglobin (VHb). Vitis 52:77–84
Misra AN, Vladkova R, Singh R, Misra M, Dobrikova AG, Apostolova EL (2014) Action and target sites of nitric oxide in chloroplasts. Nitric Oxide 39:35–45
Rodrigo ML, Marvin M, Vikas Y, Marcelo FL (2015) Improved biomass and protein production in solid-state cultures of an Aspergillus sojae strain harboring the Vitreoscilla hemoglobin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:9699–9708
Shi XZ, Wang XL, Peng FT, Zhao Y (2012) Molecular cloning and characterization of a nonsymbiotic hemoglobin gene (GLB1) from Malus hupehensis Rehd. with heterologous expression in tomato. Mol Biol Rep 39:8075–8082
Stark BC, Pagilla KR, Dikshit KL (2015) Recent applications of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin technology in bioproduct synthesis and bioremediation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1627–1636
Sturms R, DiSpirito AA, Fulton DB, Hargrove MS (2011) Hydroxylamine reduction to ammonium by plant and cyanobacterial hemoglobins. Biochemistry 50:10829–10835
Su XH, Chu YG, Li H, Hou YJ, Zhang BY, Huang QJ, Hu ZM, Huang RF, Tian YC (2011) Expression of multiple resistance genes enhances tolerance to environmental stressors in transgenic poplar (Populus × euramericana ‘Guariento’). PLoS ONE 6:e24614. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0024614
Tang QY, Feng MG (2002) DPS data processing system for practical statistics. Science Press, Beijing
Thiel J, Rolletschek H, Friedel S, Lunn JE, Nguyen TH, Feil R, Tschiersch H, Muller M, Borisjuk L (2011) Seed-specific elevation of non-symbiotic hemoglobin AtHb1: beneficial effects and underlying molecular networks in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 11:48
Trevisan S, Manoli A, Begheldo M, Nonis A, Enna M, Vaccaro S, Caporale G, Ruperti B, Quaggiotti S (2011) Transcriptome analysis reveals coordinated spatiotemporal regulation of hemoglobin and nitrate reductase in response to nitrate in maize roots. New Phytol 192:338–352
Tsai PS, Rao G, Bailey JE (1995) Improvement of Escherichia coli microaerobic oxygen metabolism by Vitreoscilla hemoglobin: new insights from NAD(P)H fluorescence and culture redox potential. Biotechnol Bioeng 47:347–354
Tsai P, Hatzimanikatis V, Bailey JE (1996) Effect of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin dosage on microaerobic Escherichia coli carbon and energy metabolism. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:139–150
Tsai PS, Nageli M, Bailey JE (2002) Intracellular expression of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin modifies microaerobic Escherichia coli metabolism through elevated concentration and specific activity of cytochrome o. Biotechnol Bioeng 79:558–567
Vigeolas H, Huhn D, Geigenberger P (2011) Nonsymbiotic hemoglobin-2 leads to an elevated energy state and to a combined increase in polyunsaturated fatty acids and total oil content when overexpressed in developing seeds of transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Physiol 155:1435–1444
Wakabayashi S, Matsubara H, Webster DA (1986) Primary sequence of a diametric bacterial hemoglobin from Vitreoscilla. Nature 322:481–483
Wang ZN, Xiao Y, Chen WS, Tang KX, Zhang L (2009) Functional expression of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin (VHb) In Arabidopsis relieves submergence, nitrosative, photo-oxidative stress and enhances antioxidants metabolism. Plant Sci 176:66–77
Wang XT, Ding YT, Gao XY, Liu HH, Zhao K, Gao YQ, Qiu LY (2019) Promotion of the growth and plant biomass degrading enzymes production in solid-state cultures of Lentinula edodes expressing Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene. J Biotechnol 302:42–47
Webster DA (1987) Structure and function of bacterial hemoglobin and related proteins. In: Eichorn GC, Marzilli LG (eds) Advances in inorganic biochemistry, vol 7. Elsevier, New York, pp 245–265
Zelasco S, Reggi S, Callihari P, Balestrazzi A, Bongiorni C, Quattrini E, Delia G, Bisoffi S, Fogher C, Confalonieri M (2006) Expression of the Vitreoscilla hemoglobin (VHb)-encoding gene in transgenic white poplar: plant growth and biomass production, biochemical characterization and cell survival under submergence, oxidative and nitrosative stress conditions. Mol Breed 17:201–216
Zhang BY, Su XH, Li YL, Huang QJ, Zhang XH, Zhang L (2005) Regeneration of vgb-transgenic poplar (populus alba × p. glandulosa) and the primary observation of its growth. J Agric Biotechnol 13:288–293
Zhou ZZ, Zhou YG, He CZ, Mang KQ, Tian YC (2004) Expression of cry3A and vhb genes in transgenic potato plants. Prog Biochem Biophys 31:741–745
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL Li and WX Zhang projected and implemented all the experiments and drafted the manuscript. YL Li and WX Zhang are contributed equally to this work. XH Su, WX Zhu, BY Zhang, QJ Huang were involved in devising and directing the experiments and proofreading the manuscript. XH Su contributed to the concept of the research, gave constructive advice on the experiments, and finally completed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project funding: The work was supported by the Basic Research Fund of RIF (Grant No. CAFYBB2017ZA001-3) the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31700589) and the Forestry Genetic Breeding National Key Laboratory (Chinese Academy of Forestry Sciences) Open Project (Grant No. TGB 2013005).
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com
Corresponding editor: Tao Xu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhang, W., Zhu, W. et al. Waterlogging tolerance and wood properties of transgenic Populus alba × glandulosa expressing Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (Vgb). J. For. Res. 32, 831–839 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-020-01121-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-020-01121-x