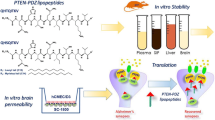
Abstract
Additional biological protection; blood brain barrier (BBB) to neuronal tissue is essential against invading infections and unwanted chemicals. However, such highly selective transport across the BBB often restricts entry of majority of drug molecules intended for various therapies including thrombotic cerebral ischemia. The inadequate permeation of drugs across BBB and subsequently failure of intended therapies result in finding an effective native transport mechanism. The computational approach in studying protein–protein interactions emerged as one of prospective hope for the identification of proteins (receptors/transporter) towards an effective drug delivery system. Interestingly, low-density lipoprotein receptor proteins-1 (LRP-1) express constitutively in many tissues including BBB plays an important role in the transport of peptides (hormones) believed a candidate transporter for drugs to the neuronal tissue. In this study, earthworm fibrinolytic enzyme (EFE); an effective thrombolyte and its interaction with LRP-1 suggests potential transport mechanism towards entry of drug molecule into neuronal tissue. Fibrinolytic enzyme (PDB Id-1M9U) was docked to LRP1 (PDB Id-1CR8) using Auto Dock tool. Virtual screening following by binding energy calculations suggest a promising interaction of EFE with LRP-1. Further, RMSD and RMSF calculations provide insights and extent of protein-protein interactions (PPIs). Molecular dynamic simulation (MDS) studies were carried out to predict the stability of docked cluster followed by binding mode and surface analysis. Interacting residues in various site/pose were compared with Novel LRP-1 binding peptide 57 and does not show significant similarity. The interacting residues and docking pose in docked cluster suggest LRP-1 a potential transport shuttle for the clot-dissolving drug molecules. We analyzed EFE-LRP-1 interaction and propose LPR-1 mediated endocytosis of EFE across BBB.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHA:
-
American Heart Association
- RSMD:
-
Root mean square deviation
- RSMF:
-
Root mean square fluctuations
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- EFE:
-
Earthworm fibrinolytic enzyme
- MDS:
-
Molecular dynamic simulations
- LPR:
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor protein
- PPIs:
-
Protein–protein interactions
- GROMACS :
-
Groningen machine for chemical simulations
- PDB:
-
Protein data bank
References
Adibhatla RM, Hatcher JF (2008) Tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) and matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of stroke: therapeutic strategies. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 7(3):243–253
Alkjaersig N, Fletcher AP, Sherry S (1959) The mechanism of clot dissolution by plasmin. J Clin Invest 38(7):1086–1095. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI103885
Balami JS, Chen R, Sutherland BA, Buchan AM (2013) Thrombolytic agents for acute ischemic stroke treatment: the past, present and future. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 12(2):145–54
Barreto AD (2011) Intravenous thrombolytics for ischemic stroke. Neurotherapeutic 8(3):388–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-011-0049-x
Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman M et al (2017) Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 135(10):e146–e603. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000485
Bertrand Y, Currie JC, Demeule M, Régina A, Ché C, Abulrob A (2010) Transport characteristics of a novel peptide platform for CNS therapeutics. J Cell Mol Med 14:2827–2839
Bertrand Y, Currie JC, Poirier J, Demeule M, Abulrob A, Fatehi D (2011) Influence of glioma tumour microenvironment on the transport of ANG1005 via low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1. Br J Cancer 105:1697–1707
Bres EE, Faissner A (2019) Low density receptor-related protein 1 interactions with the extracellular matrix: more than meets the eye. Front Cell Dev Biol 7:31. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2019.00031
Cesarman-Maus G, Hajjar KA (2005) Molecular mechanisms of fibrinolysis. Br J Haematol 129:307–321. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05444.x
Cheng NT, Kim AS (2015) Intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke within 3 hours versus between 3 and 4.5 hours of symptom onset. Neurohospitalist 5(3):101–109. https://doi.org/10.1177/1941874415583116
Chernyshev O, Martin-Schild S, Albright K et al (2010) Safety of t-PA in stroke mimics and neuroimaging-negative cerebral ischemia. Neurology 74(17):1340–1345
Cho IH, Cho ES, Lim HG, Lee HH (2004) Purification and characterization of six fibrinolytic serine-Proteases from earthworm Lumbricus rubellus. J Biochem Mol Biol 37(2):199–205
Collen D, Lijnen HR (2005) Thrombolytic agents. Thromb Haemost 93(4):627–630
Colman RW (1968) Activation of plasminogen by human plasma kallikreins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 35:273–279
Dehouck B, Fenart L, Dehouck MP, Pierce M, Torpier G, Cecchelli R (1997) A new function for the LDL receptor; transcytosis of LDL across the blood–brain barrier. J Cell Biol 138:877–889
Demeule M, Currie JC, Bertrand Y, Ché C, Nguyen T, Régina A (2008) Involvement of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in the transcytosis of the brain delivery vector angiopep-2. J Neurochem 106:1534–1544
Demeule M, Régina A, Ché C, Poirier J, Nguyen T, Gabathuler R (2008) Identification and design of peptides as a new drug delivery system for the brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 324:1064–1072
Fan Q, Wu C, Li L, Fan R, Wu C, Hou Q, He R (2001) Some features of intestinal absorption of intact fibrinolytic enzyme III-1 from Lumbricus rubellus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1526(3):286–292
Georgieva JV, Hoekstra D, Zuhorn IS (2014) Smuggling drugs into the brain: an overview of ligands targeting transcytosis for drug delivery across the blood–brain barrier. Pharmaceutics 6(4):557–583. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics6040557
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL et al (2014) Heart disease and stroke statistics-2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Sub-committee. Circulation 129(3):e28–e292
Gray D (2005) Thrombolysis: past, present, and future. Postgrad Med J 82(968):372–375. https://doi.org/10.1136/pgmj.2005.033266
Greenberg CS, Miraglia CC, Rickles FR, Shuman MA (1985) Cleavage of blood coagulation factor XIII and fibrinogen by thrombin during in vitro clotting. J Clin Invest 75(5):1463–1470. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI111849
Halade GV, Black M, Verma MK (2018) Paradigm shift: metabolic transformation of docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acids to bio-actives exemplify the promise of fatty acid drug discovery. Biotechnol Adv 36(4):935–953
Heo L, Shin WH, Lee MS, Seok S (2014) GalaxySite: ligand-binding-site prediction by using molecular docking. Nucleic Acids Res 42:W210–W214. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku321
Holmes WE, Nelles L, Lijnen HR (1987) Primary structure of human alpha2-antiplasmin, a serine protease inhibitor (serpin). J Biol Chem 262:1659–1664
Hospital A, Ramon J, Modesto G, Josep O, Gelpí L (2015) Molecular dynamics simulations: advances and applications. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem 8:37–47
Ji H, Wang L, Bi H, Sun L, Cai B, Wang Y, Zhao J, Du Z (2008) Mechanisms of lumbrokinase in protection of cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol 590(1–3):281–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.05.037
Kingwell K (2016) New targets for drug delivery across the BBB. Nat Rev Drug Discov 15:84–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.14
Libertiny G, Hands L (1999) Deep venous thrombosis in peripheral vascular disease. Br J Surg 86(7):907–910
Lijnen HR, Collen D (1998) Mechanisms of plasminogen activation by mammalian plasminogen activators. Enzyme 40(2–3):90–96
Makarewicz T, Kaźmierkiewicz R (2013) Molecular dynamics simulation by GROMACS using GUI plugin for PyMOL. J Chem Inf Model 53(5):1229–1234. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci400071x
McGuffin LG, Bryson K, Jones DT (2000) The PSIPRED protein structure prediction server. Bioinformatics 16(4):404–405
Mihara H, Sumi H, Akazawa K (1983) Fibrinolytic enzyme extracted from the earthworm. Thromb Haemost 50:58
Mihara H, Sumi H, Yoneta T, Mizumoto H, Ikeda R, Seikl M, Maruyama M (1991) A novel fibrinolytic enzyme extracted from the earthworm, Lumbricus rubellus . Jpn J Physiol 41:461–472
Mihara H, Nakajima N, Sumi H (1993) Characterization of protein fibrinolytic enzyme in earthworm, Lumbricus rubellus. Biosci Biotech Biochem 57:1726–1731
Mutch NJ, Moore NR, Wang E, Booth NA (2003) Thrombus lysis by uPA, scuPA and tPA is regulated by plasma TAFI. J Thromb Haemost 1(9):2000–2007
Nagareddy P, Smyth SS (2014) Inflammation and thrombosis in cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Hematol 20(5):457–463. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOH.0b013e328364219d
Nakajima N, Mihara H, Sumi H (1993) Characterization of potent fibrinolytic enzymes in earthworm, Lumbricus rubellus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 57(10):1726–1730
Oller-Salvia B, Sánchez-Navarro M, Giralt E, Teixidó M (2016) Blood–brain barrier shuttle peptides: an emerging paradigm for brain delivery. Chem Soc Rev 45:4690–4707
Pardridge WM (2012) Drug transport across the blood–brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32(11):1959–1972
Peng LX, Hsu MT, Bonomi M, Agardand DA, Jacobson MP (2014) The free energy profile of tubulin straight-bent conformational changes, with implications for microtubule assembly and drug discovery. PLoS Comput Biol 10(2):e1003464. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003464
Previtali E, Bucciarelli P, Passamonti SM, Martinelli I (2011) Risk factors for venous and arterial thrombosis. Blood Transfus 9(2):120–138. https://doi.org/10.2450/2010.0066-10
Ptitsyn OB (1995) Molten globule and protein folding. Adv Protein Chem 47:229
Pulicherla KK, Verma MK (2015) Targeting therapeutics across the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB), Prerequisite towards thrombolytic therapy for cerebrovascular disorders: an overview and advancements. AAPS Pharm Sci Technol 16(2):223–233
Régina A, Demeule M, Ché C, Lavallée I, Poirier J, Gabathuler R (2008) Antitumour activity of ANG1005, a conjugate between paclitaxel and the new brain delivery vector Angiopep-2. Br J Pharmacol 155:185–197
Roth GA, Johnson C, Abajobir A, Abd-Allah F et al (2017) Global, regional, and national burden of cardiovascular diseases for 10 causes, 1990 to 2015. J Am Coll Cardiol 70(1):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2017.04.052
Sakamoto K, Shinohara T, Adachi Y, Asami T, Ohtaki T (2017) A novel LRP1-binding peptide L57 that crosses the blood brain barrier. Biochem Biophys Rep 2:135–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2017.07.003
Shenkman B, Livnat T, Budnik I, Tamarin I, Einav Y, Martinowitz Y (2012) Plasma tissue-type plasminogen activator increases fibrinolytic activity of exogenous urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 23(8):729–733. https://doi.org/10.1097/MBC.0b013e32835897d5
Sidelmann JJ, Gram J, Jespersen J, Kluft C (2000) Fibrin clot formation and lysis: basic mechanisms. Semin Thromb Hemost 26(6):605–618
Sikri N, Bardia A (2007) A history of streptokinase use in acute myocardial infarction. Tex Heart Inst J 34(3):318–327
Sreerama N, Woody RW (2000) Estimation of protein secondary structure from circular dichroism spectra: comparison of CONTIN, SELCON, and CDSSTR methods with an expanded reference set. Anal Biochem 287(2):252–260
Tang Y, Liang D, Jiang T, Zhang J, Gui L, Chang W (2002) Crystal structure of earthworm fibrinolytic enzyme component a: revealing the structural determinants of its dual fibrinolytic activity. J Mol Biol 321:57–68
Thornton JM, Jones DT, MacArthur MW, Orengo CM, Swindells MB (1995) Protein folds: towards an understanding of folding from inspection of native structures. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 348:71–79
Unger R, Ussman JL (1993) The importance of short structural motifs in protein structure analysis. J Comput Aided Mol Des 7:457–472
Verma MK, Pulicherla KK (2011) Lumbrokinase; a potent and stable fibrin–specific plasminogen activator. Int J Bio-Sci Bio-Technol 3(2):57–70
Verma MK, Pulicherla KK (2016) Enzyme promiscuity in earthworm serine protease-substrate versatility and therapeutic potential. Amino Acids 48(4):941–948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2162-3
Verma MK, Pulicherla KK (2017) Broad substrate affinity and catalytic diversity of fibrinolytic enzyme from Pheretima posthumous: purification and molecular characterization study. Int J Biol Macromol 95:1011–1021
Violi F, Cangemi R, Calvieri C (2014) Pneumonia, thrombosis and vascular disease. J Thromb Haemost 12(9):1391–1400. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.12646
Wang C, Wang F, Li M, Tang Y, Zhang J, Gui LL, An X, Chang WR (2004) Structural basis for broad substrate specificity of earthworm fibrinolytic enzyme component A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 325:877–882
Wong ND (2014) Epidemiological studies of CHD and the evolution of preventive cardiology. Nat Rev Cardiol 11(5):276–289. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2014.26
Xu J, Zhang Y (2010) How significant is a protein structure similarity with TM-score = 0.5? Bioinformatics 26(7):889–895. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq066
Zhang F, Xu CL, Liu CM (2015) Drug delivery strategies to enhance the permeability of the blood–brain barrier for treatment of glioma. Drug Des Dev Ther 9:2089–2100. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S79592
Acknowledgements
The author would like to acknowledge Department of Biotechnology, Acharya Nagarjuna University, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India for kind support and providing a facility for proposed study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, M.K., Shakya, S. LRP-1 Mediated Endocytosis of EFE Across the Blood–Brain Barrier; Protein–Protein Interaction and Molecular Dynamics Analysis. Int J Pept Res Ther 27, 71–81 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10065-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10065-z