Abstract
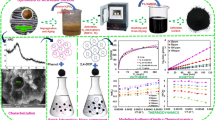
The use of low-cost adsorbents produced from rice husks that can selectively remove zinc (II) ion from wastewater effluent has been investigated. The disorder and fatal diseases can be triggered in living organisms by accumulating the heavy metals in the wastewater. Adsorption is an operative cleansing and separation method used in the industry to remove contaminants from effluents. In order to convert the rice husk to the adsorbent, digestion and carbonization processes were performed. Rice husks digested nitric acid at 1.0 M to reduce the organic constituents and further carbonized at 400, 600 and 800 °C to eliminate the non-carbon element in rice husks. The physiochemical characteristics of the digested and carbonized rice husks were analyzed using scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and atomic adsorption spectrophotometer (AAS). The SEM morphological characteristics showed the high pyrolysis effect on the organic matter left the samples with more pores and cavities, which enhanced the surface area and uptake, especially for 800 °C carbonized samples. The samples’ physical characteristics using XRD showed that the treatment with HNO3 illustrated a pattern close to the activated carbon with slightly lower intensities. The applied feed-forward back-propagation neural network algorithm showed high validity (R2 ≈ 0.9686) for the tested experimental data sets and hence can be applied for forthcoming studies with nearby conditions. The outcomes showed that the increment of the carbonization temperature is correlated with the contact time and can increase the metal uptake percentage and adsorption capacity. The adsorption followed the Langmuir isotherm, which indicates monolayer coverage. The data showed that adsorption kinetics follow the pseudo-second-order rate expression.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Kareem FA, Shariff AM, Ullah S, Garg S, Dreisbach F, Keong LK, Mellon N (2017) Experimental and neural network modeling of partial uptake for a carbon dioxide/methane/water ternary mixture on 13X zeolite. Energy Technol-Ger 5:1373–1391
Abdul Kareem FA, Shariff AM, Ullah S, Dreisbach F, Keong LK, Mellon N, Garg S (2018a) Experimental measurements and modeling of supercritical CO2 adsorption on 13X and 5A zeolites. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 50:115–127
Abdul Kareem FA, Shariff AM, Ullah S, Keong LK, Mellon N (2018b) Total and partial uptakes of multicomponent vapor-gas mixtures on 13X zeolite at 343 K: experimental and modeling study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 258:95–113
Abdul Kareem FA, Shariff AM, Ullah S, Mellon N, Keong LK (2018c) Adsorption of pure and predicted binary (CO2:CH4) mixtures on 13X-Zeolite: Equilibrium and kinetic properties at offshore conditions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 267:221–234
Abdul Kareem FA, Mohd. Shariff A, Ullah S, See TL, Keong LK, Mellon N (2018d) Adsorption performance of 5A molecular sieve zeolite in water vapor–binary gas environment: experimental and modeling evaluation. J Ind Eng Chem 64:173–187
Acharya J, Kumar U, Meikap BC (2019) Thermodynamic spectral and kinetic analysis of the removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution by sodium carbonate treated rice husk. J Environ Sci Health Part A 54:801–809
Adebisi GA, Chowdhury ZZ, Hamid SBA, Ali E (2016) Hydrothermally treated banana empty fruit bunch fiber activated carbon for Pb(II) and Zn (II) removal. BioResources 11:9686–9709
Adenuga AA, Amos OD, Oyekunle JAO, Umukoro EH (2019) Adsorption performance and mechanism of a low-cost biosorbent from spent seedcake of Calophyllum inophyllum in simultaneous cleanup of potentially toxic metals from industrial wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103317
Ahmad JU, Goni MA (2010) Heavy metal contamination in water, soil, and vegetables of the industrial areas in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 166:347–357
Ahmaruzzaman M, Gupta VK (2011) Rice husk and its ash as low-cost adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:13589–13613
Akoteyon I, Mbata U, Olalude G (2011) Investigation of heavy metal contamination in groundwater around landfill site in a typical sub-urban settlement in alimosho, lagos-nigeria. J Appl Sci Environ Sanitation 6(2):155–163
Aksu Z (2001) Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of cadmium (II) biosorption by C. vulgaris in a batch system: effect of temperature. Sep Purif Technol 21:285–294
Ali I, Asim M, Khan TA (2012) Low cost adsorbents for the removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. J Environ Manag 113:170–183
Alkherraz AM, Ali AK, Elsherif KM (2020) Removal of Pb(II), Zn (II), Cu (II) and Cd (II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto olive branches activated carbon: equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Int. 6:11–20
Amuda O, Giwa A, Bello I (2007) Removal of heavy metal from industrial wastewater using modified activated coconut shell carbon. Biochem Eng J 36:174–181
Argun ME, Dursun S (2008) A new approach to modification of natural adsorbent for heavy metal adsorption. Bioresour Technol 99:2516–2527
Ayucitra A, Gunarto C, Kurniawan V, Hartono SB (2017) Preparation and characterisation of biosorbent from local robusta spent coffee grounds for heavy metal adsorption. Chem Eng Trans 56:1441–1446
Bhatnagar A, Minocha AK, Sillanpää M (2010) Adsorptive removal of cobalt from aqueous solution by utilizing lemon peel as biosorbent. Biochem Eng J 48:181–186
Chen JP (2012) Decontamination of heavy metals: processes, mechanisms, and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton ISBN-13: 9781439816677
Chen S, Ma Y, Chen L, Xian K (2010) Adsorption of aqueous Cd2+, Pb2+, Cu2+ ions by nano-hydroxyapatite: single-and multi-metal competitive adsorption study. Geochem J 44:233–239
Demirbas A (2008) Heavy metal adsorption onto agro-based waste materials: a review. J Hazard Mater 157:220–229
Duku MH, Gu S, Hagan EB (2011) Biochar production potential in Ghana—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 15:3539–3551
Feng Q, Lin Q, Gong F, Sugita S, Shoya M (2004) Adsorption of lead and mercury by rice husk ash. J Colloid Interface Sci 278:1–8
Förstner U, Wittmann GT (2012) Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. Springer, Berlin
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag 92:407–418
Giri A, Patel R, Mahapatra S (2011) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modelling of arsenic (III) biosorption from aqueous solution by living cells of Bacillus cereus biomass. Chem Eng J 178:15–25
Gode F, Pehlivan E (2006) Removal of chromium (III) from aqueous solutions using Lewatit S 100: the effect of pH, time, metal concentration and temperature. J Hazard Mater 136:330–337
Grassi M, Kaykioglu G, Belgiorno V, Lofrano G (2012) Removal of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater by adsorption process. In: Lofrano G (ed) Emerging compounds removal from wastewater. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 15–37
Gupta VK, Rastogi A, Nayak A (2010) Adsorption studies on the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using a low cost fertilizer industry waste material. J Colloid Interface Sci 342:135–141
Haris MRHM, Wahab NAA, Reng CW, Azahari B, Sathasivam K (2011) The sorption of cadmium (II) ions on mercerized rice husk and activated carbon. Turk J Chem 35:939–950
Hem JD (1972) Chemistry and occurrence of cadmium and zinc in surface water and groundwater. Water Resour Res 8:661–679
Ho Y-S (2006) Second-order kinetic model for the sorption of cadmium onto tree fern: a comparison of linear and non-linear methods. Water Res 40:119–125
Ho Y-S, Mckay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Janyasuthiwong S, Phiri SM, Kijjanapanich P, Rene ER, Esposito G, Lens PNL (2015) Copper, lead and zinc removal from metal-contaminated wastewater by adsorption onto agricultural wastes. Environ Technol 36:3071–3083
Jayawardena R, Ranasinghe P, Galappatthy P, Malkanthi R, Constantine G, Katulanda P (2012) Effects of zinc supplementation on diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol Metab Syndr 4:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-5996-4-13
Jin-Fa C, Yong G, Da-Gang S, Sha Y (2018) Adsorption characteristics of Cr (Vi) on carbonized eupatorium adenophorum spreng. Environ Eng Manag J 17:115–122
Lagergren S (1898) Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. Kungliga svenska vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 24:1–39
Lei Z, Zhai S, Lv J, Fan Y, An Q, Xiao Z (2015) Sodium alginate-based magnetic carbonaceous biosorbents for highly efficient Cr(VI) removal from water. RSC Adv. 5:77932–77941
Liu Y, Luo L, Chen G, Xie M, Yu Z (2010) Adsorption of Lead ions on ground tyre rubber grafted with maleic anhydride via surface-initiated ATRP polymerization. Iran Polym J 19:207–218
Liu H, Feng S, Zhang N, Du X, Liu Y (2014) Removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution by activated carbon impregnated with humic acid. Front Environ Sci Eng 8:329–336
Mahmood-Ul-Hassan M, Suthor V, Rafique E, Yasin M (2015) Removal of Cd, Cr, and Pb from aqueous solution by unmodified and modified agricultural wastes. Environ Monit Assess 187:2–8
Masoumi A, Hemmati K, Ghaemy M (2016) Low-cost nanoparticles sorbent from modified rice husk and a copolymer for efficient removal of Pb(II) and crystal violet from water. Chemosphere 146:253–262
Matilainen A, Gjessing ET, Lahtinen T, Hed L, Bhatnagar A, Sillanpää M (2011) An overview of the methods used in the characterisation of natural organic matter (NOM) in relation to drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 83:1431–1442
Michalak I, Baśladyńska S, Mokrzycki J, Rutkowski P (2019) Biochar from a freshwater macroalga as a potential biosorbent for wastewater treatment. Water 11(1390):1–16
Mohan D, Sarswat A, Ok YS, Pittman CU (2014) Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent–a critical review. Bioresour Technol 160:191–202
Nyamunda BC, Chivhanga T, Guyo U, Chigondo F (2019) Removal of Zn (II) and Cu (II) ions from industrial wastewaters using magnetic biochar derived from water hyacinth. J. Eng. 2019:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5656983
Organization WH (2008) Guidelines for drinking-water quality [electronic resource]: incorporating 1st and 2nd addenda, vol. 1, Recommendations, vol 1. World Health Organization, Geneva
Rafiee E, Shahebrahimi S, Feyzi M, Shaterzadeh M (2012) Optimization of synthesis and characterization of nanosilica produced from rice husk (a common waste material). Int Nano Lett 2(29):1–8
Raju KS, Naidu S (2013) A review on removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by rice husk as an adsorbent. J Chem Biol Phys Sci 3:602
Saeed M, Khan H, Khan MA, Khan F, Khan SA, Muhammad N (2010) Quantification of various metals and cytotoxic profile of aerial parts of Polygonatum verticillatum. Pak J Bot 42:3995–4002
Samadani Langeroodi N, Safaei E (2016) Carbonized medlar-core particles as a new biosorbent for removal of Cu2+ from aqueous solution and study of its surface morphology. Water Sci Technol 74:236–245
Sangodoyin A, Agbawhe O (1992) Environmental study on surface and groundwater pollutants from abattoir effluents. Bioresour Technol 41:193–200
Tofighy MA, Mohammadi T (2011) Adsorption of divalent heavy metal ions from water using carbon nanotube sheets. J Hazard Mater 185:140–147
Turan NG, Mesci B, Ozgonenel O (2011) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modeling Zn (II) adsorption from leachate using a new biosorbent. Chem Eng J 173:98–105
Uchimiya M, Wartelle LH, Klasson KT, Fortier CA, Lima IM (2011) Influence of pyrolysis temperature on biochar property and function as a heavy metal sorbent in soil. J Agric Food Chem 59:2501–2510
Ullah S, Bustam MA, Shariff AM, Elkhalifah AEI, Murshid G, Riaz N (2014a) Synthesis and CO2 adsorption study of modified MOF-5 with multi-wall carbon nanotubes and expandable graphite. AIP Conf Proc 1621:34–39
Ullah S, Shariff AM, Bustam MA, Elkhalifah AE, Murshid G, Riaz N, Shimekit B (2014b) Effect of modified MIL-53 with multi-wall carbon nanotubes and nanofibers on CO2 adsorption. Appl Mech Mater 625:870–873
Ullah S, Shariff AM, Bustam MA, Elkhalifah AEI, Gonfa G, Kareem FAA (2016) The role of multiwall carbon nanotubes in Cu-BTC metal-organic frameworks for CO2 adsorption. J Chin Chem Soc 63:1022–1032
Venkatanarayanan HK, Rangaraju PR (2015) Effect of grinding of low-carbon rice husk ash on the microstructure and performance properties of blended cement concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 55:348–363
Vo AT, Nguyen VP, Ouakouak A, Nieva A, Doma BT, Tran HN, Chao H-P (2019) Efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water by biochar and activated carbon prepared through hydrothermal carbonization and pyrolysis: adsorption-coupled reduction mechanism. Water 11(1164):1–14
Xu X, Gao B-Y, Yue Q-Y, Zhong Q-Q (2010) Preparation and utilization of wheat straw bearing amine groups for the sorption of acid and reactive dyes from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 182:1–9
Xue F, Xia B, Ying R, Shen S, Zhao P (2013) Removal of Zn2+ from aqueous solution by biomass of Agaricus bisporus. Front Environ Sci Eng 7:531–538
Yao S, Zhang J, Shen D, Xiao R, Gu S, Zhao M, Liang J (2016) Removal of Pb(II) from water by the activated carbon modified by nitric acid under microwave heating. J Colloid Interface Sci 463:118–127
Ye J, Cong X, Zhang P, Zeng G, Hoffmann E, Wu Y, Zhang H, Fang W (2016) Operational parameter impact and back propagation artificial neural network modeling for phosphate adsorption onto acid-activated neutralized red mud. J Mol Liq 216:35–41
Yetilmezsoy K, Demirel S (2008) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modeling of Pb(II) adsorption from aqueous solution by Antep pistachio (Pistacia Vera L.) shells. J Hazard Mater 153:1288–1300
Yildiz S (2017) Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modeling Zn (II) adsorption in batch process. Korean J Chem Eng 34:2423–2434
Zhang Z, Li H, Chang H, Pan Z, Luo X (2018) Machine learning predictive framework for CO2 thermodynamic properties in solution. J CO2 Util 26:152–159
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Department of Chemistry and Deanship of Scientific Research King Khalid University, Saudi Arabia, for giving a lot of support in completing this research work through Research Groups Project under the Grant Number (R.G.P.1/163/40).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ullah, S., Assiri, M.A., Bustam, M.A. et al. Equilibrium, kinetics and artificial intelligence characteristic analysis for Zn (II) ion adsorption on rice husks digested with nitric acid. Paddy Water Environ 18, 455–468 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-020-00794-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-020-00794-8