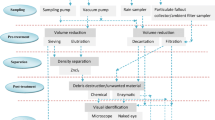
Abstract
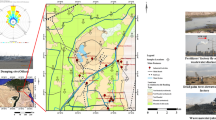
Atmospheric dust originating from the Thar Desert (India) acts as the local source of mineral dust in South Asia, spreading over an area of 0.32 × 106 km2. Regional studies conducted during peak boreal summer are required to characterize this mineral dust that blows in form of episodic dust storms towards Indo-Gangetic Plains (IGP), using a multi-tracer approach. To achieve this goal, atmospheric PM10 particles were collected along with surface dry soils between 3 and 11 June, 2013, from in and around the Jodhpur city (26.2389°N, 73.0243°E) to glean elemental composition, stable isotopic and palynological (pollen types) database. Typical crustal elemental ratios, e.g. Si/Al, Ca/Al, Fe/Al, K/Al, Mg/Al, Ti/Al, varied in narrow ranges 8.1 ± 1.21, 1.02 ± 1.53, 0.50 ± 0.14, 0.34 ± 0.06, 0.19 ± 0.06 and 0.06 ± 0.02, respectively. Average Sr/Al, Rb/Al and Zr/Al ratios were found to be 39.70 ± 12.24, 18.00 ± 2.0 and 70.83 ± 13.11 (μg gm−1/wt%), respectively. Average δ13C, δ15N, δ34S values of surface soils were − 10.5‰ ± 4.0, 11.4‰ ± 1.6 and 3.6‰ ± 2.1, while δ13C and δ15N of atmospheric PM10 particles varied in ranges − 25.6‰ ± 0.67 and 9.9‰ ± 1.7, respectively. Observed palynoassemblage indicated the open nature of vegetation that usually grows under warm-humid conditions with traces of few allergens and pathogens. Generated chemical-isotopic-pollen database could be utilized for deciphering origin of dust storms in IGP. Detailed multi-proxy characterization of mineral dust from the Thar Desert can further help to determine its role in influencing air quality and human health.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Kumar, A.K. Sudheer and M.M. Sarin, Chemical characteristics of aerosols in MABL of Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea during spring inter-monsoon: a comparative study, J. Earth Syst. Sci., 117(1) (2008) 325-332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-008-0035-9.
B. Srinivas, M.M. Sarin and A. Kumar, Impact of anthropogenic sources on aerosol iron solubility over the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea. Biogeochemistry, 110(1-3) (2012) 257-268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-011-9680-1.
P.R. Buseck and M. Pósfai, Airborne minerals and related aerosol particles: effects on climate and the environment. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci., 96(7) (1999) 3372-3379. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.7.3372.
S.K. Mishra, S.N. Tripathi, S.G. Aggarwal and A. Arola, Optical properties of accumulation mode, polluted mineral dust: effects of particle shape, hematite content and semi-external mixing with carbonaceous species, Tellus B:Chem. Phys. Meteorol., 64(1) (2012) 18536.
S.K. Mishra, S. Dey and S.N. Tripathi, Implications of particle composition and shape to dust radiative effect: a case study from the Great Indian Desert. Geophys. Res. Lett., 35(23) (2008). https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL036058.
R. Agnihotri, R. Kumar, M.V.S.N. Prasad, C. Sharma, S.K. Bhatia and B.C. Arya, Experimental setup and standardization of a continuous flow stable isotope mass spectrometer for measuring stable isotopes of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur in environmental samples. MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc India, 29(3) (2014) 195-205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-014-0099-8.
S.K. Mishra, N. Saha, S. Singh, C. Sharma, M.V.S.N. Prasad, S. Gautam, A. Misra, A. Gaur, D. Bhattu, S. Ghosh and A. Dwivedi, Morphology, mineralogy and mixing of individual atmospheric particles over Kanpur (IGP): relevance of homogeneous equivalent sphere approximation in radiative models, MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc India, 32(3) (2017) 229-241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-017-0215-7.
A. Misra, A. Gaur, D. Bhattu, S. Ghosh, A.K. Dwivedi, R. Dalai, D. DebajyotiPaul, T. Gupta, V. Tare, S.K. Mishra, S. Singh and S.N. Tripathi, An overview of the physico-chemical characteristics of dust at Kanpur in the central Indo-Gangetic basin, Atmos. Environ., 97 (2014) 386-396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.08.043.
J. Xu, M.H. Bergin, R. Greenwald, J.J. Schauer, M.M. Shafer, J.L. Jaffrezo and G. Aymoz, Aerosol chemical, physical, and radiative characteristics near a desert source region of northwest China during ACE‐Asia, J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 109(D19) (2004). https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JD004239.
M. Schulz, C. Textor, S. Kinne, Y. Balkanski, S. Bauer, T. Berntsen, T. Berglen, O.F. Boucher, F. Dentener, S. Guibert, I.S.A. Isaksen, T. Iversen, D. Koch, A. Kirkevåg, X. Liu, V. Montanaro, G. Myhre, J.E. Penner, G. Pitari, S. Reddy, Ø. Seland, P. Stier and T. Takemura, Radiative forcing by aerosols as derived from the AeroCom present-day and pre-industrial simulations, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 6(12) (2006) 5225-5246.
K. Reinmuth-Selzle, C.J. Kampf, K. Lucas, N. Lang-Yona, J. Fröhlich-Nowoisky, M. Shiraiwa, S.J. Pascale, P.S.J. Lakey, S. Lai, F. Liu, A.T. Kunert, K. Ziegler, F. Shen, R. Sgarbanti, B. Weber, I. Bellinghausen, J. Saloga, M.G. Weller, A. Duschl, D. Schuppan and U. Pöschl, Air pollution and climate change effects on allergies in the anthropocene: abundance, interaction, and modification of allergens and adjuvants, Environ. Sci. Technol., 51(8) (2017) 4119-4141. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b04908.
H. Behrendt, A. Kasche, C.E. Von Eschenbach, U. Risse, J. Huss-Marp and J. Ring, Secretion of proinflammatory eicosanoid-like substances precedes allergen release from pollen grains in the initiation of allergic sensitization, Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol., 124(1–3) (2001) 121-125. https://doi.org/10.1159/000053688.
M.M. Azam and J.K. Tripathi, Recent contributions in the field of sediment geochemistry, Proc. Indian Nat. Sci. Acad., 82(3) (2016) 805–815. https://doi.org/10.16943/ptinsa/2016/48486.
G. Erdtman, An introduction to pollen analysis, ChronicaBotanicaCo, Waltham Mass, (1943).
M.S. Chauhan and S.K. Bera, Pollen morphology of some important plants of tropical deciduous sal (Shorearobusta) forests, District Sidhi, Madhya Pradesh, Geophytology, 20(1) (1990) 30-36.
C.M. Fedo, H. Wayne Nesbitt and G.M. Young, Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance, Geology, 23(10) (1995) 921-924. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023%3c0921:UTEOPM%3e2.3.CO;2.
H.W. Nesbitt and G.M. Young, Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations, GeochimicaetCosmochimicaActa, 48(7) (1984) 1523-1534.
S.G. Aggarwal, K. Kawamura, G.S. Umarji, E. Tachibana, R.S. Patil and P.K. Gupta, Organic and inorganic markers and stable C-, N-isotopic compositions of tropical coastal aerosols from megacity Mumbai: sources of organic aerosols and atmospheric processing, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13(9) (2013), 4667-4680. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-4667-2013.
R. Agnihotri, T.K. Mandal, S.G. Karapurkar, M. Naja, R. Gadi, Y.N. Ahammmed, A. Kumar, T. Saud and M. Saxena, Stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic composition of bulk aerosols over India and Northern Indian Ocean, Atmos. Environ., 45(17) (2011) 2828-2835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.03.003.
C.M. Pavuluri, K. Kawamura, E. Tachibana and T. Swaminathan, Elevated nitrogen isotope ratios of tropical Indian aerosols from Chennai: implication for the origins of aerosol nitrogen in South and Southeast Asia, Atmos. Environ., 44(29) (2010) 3597-3604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.05.039.
R. Sawlani, R. Agnihotri, C. Sharma, P.K. Patra, A.P. Dimri, K. Ram and R.L. Verma, The severe Delhi SMOG of 2016: a case of delayed crop residue burning, coincident firecracker emissions, and typical meteorology, Atmos. Pollut. Res., 10(3) (2019) 868-879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2018.12.015.
S.K. Sharma, P. Agarwal, T.K. Mandal, S.G. Karapurkar, D.M. Shenoy, S.K. Peshin, A. Gupta, M. Saxena, S. Jain and A. Sharma, Study on ambient air quality of megacity Delhi, India during odd–even strategy, MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc India 32(2) (2017) 155-165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-016-0201-5.
R. Agnihotri, S.K. Mishra, P. Yadav, S. Singh, Rashmi, M.V.S.N. Prasad, B.C. Arya and C. Sharma, Bulk level to individual particle level chemical composition of atmospheric dust aerosols (PM5) over a semi-arid zone of Western India (Rajasthan), Aerosol Air Q. R., 15 (2015) 58-74. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2013.08.0270.
D. Widory, S. Roy, Y. Le Moullec, G. Goupil, A. Cocherie and C. Guerrot, The origin of atmospheric particles in Paris: a view through carbon and lead isotopes. Atmos. Environ., 38 (2004) 953e961.
A.L. Norman, L.A. Barrie, D. Toom-Sauntry, A. Sirois, H.R. Krouse, S.M. Li and S. Sharma, Sources of aerosol sulphate at Alert: Apportionment using stable isotopes, J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 104 (1999a) 11619–11631. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999JD900078.
S.M. McLennan, Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust, Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 2(4) (2001). https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GC000109.
S.R. Taylor and S.M. McLennan, The continental crust: its composition and evolution (Oxford: Blackwell), J. Geol., (1985) 312.
G.B. Shimmield and S.R. Mowbray, The inorganic geochemical record of the northwest Arabian Sea: a history of productivity variation over the last 400 ky from Sites 722 and 724. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results (Vol. 117, pp. 409-29) (1991).
S.K. Mishra, R. Agnihotri, P.K. Yadav, S. Singh, M.V.S.N. Prasad, P.S. Praveen, J.S. Jai Shankar Tawale, R. Rashmi, N.D. Mishra, B.C. Arya and C. Sharma, Morphology of atmospheric particles over Semi-Arid region (Jaipur, Rajasthan) of India: implications for optical properties. Aerosol Air Q. Res., 15(3) (2015) 974-984. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2014.10.0244.
Y. Sun, G. Zhuang, Y. Wang, X. Zhao, J. Li, Z. Wang and Z. An, Chemical composition of dust storms in Beijing and implications for the mixing of mineral aerosol with pollution aerosol on the pathway. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 110(D24) (2005). https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD006054.
Y. Wang, G. Zhuang, A. Tang, H. Yuan, Y. Sun, S. Chen and A. Zheng, The ion chemistry and the source of PM2. 5 aerosol in Beijing, Atmos. Environ., 39(21) (2005) 3771-3784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.03.013.
X.Y. Zhang, S.L. Gong, Z.X. Shen, F.M. Mei, X.X. Xi, L.C. Liu, Z.J. Zhou, D. Wang, Y.Q. Wang and Y. Cheng, Characterization of soil dust aerosol in China and its transport and distribution during 2001 ACE‐Asia: 1. Network observations. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 108(D9) (2003). https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002632.
P. Formenti, L. Schütz, Y. Balkanski, K. Desboeufs, M. Ebert, K. Kandler, A. Petzold, D. Scheuvens, S. Weinbruch and D. Zhang, Recent progress in understanding physical and chemical properties of African and Asian mineral dust, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 11(16) (2011) 8231-8256. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-8231-2011.
J. Zhang, A. Ianora, C. Wu, D. Pellegrini, F. Esposito and I. Buttino, How to increase productivity of the copepod Acartiatonsa (D ana): effects of population density and food concentration. Aquacult. Res., 46(12) (2015) 2982-2990.
N.W. Tindale and P.P. Pease, Aerosols over the Arabian Sea: atmospheric transport pathways and concentrations of dust and sea salt, Deep Sea Res. II: Top. Stud. Oceanogr., 46(8) (1999) 1577-1595. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0967-0645(99)00036-3.
Z.X. Shen, J.J. Cao, R. Arimoto, R.J. Zhang, D.M. Jie, S.X. Liu and C.S. Zhu, Chemical composition and source characterization of spring aerosol over Horqin sand land in Northeastern China, J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 112(D14) (2007). https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JD007991
Y. Sun, G. Zhuang, Y. Wang, L. Han, J. Guo, M. Dan, W. Zhang, Z. Wang and Z. Hao, The air-borne particulate pollution in Beijing—concentration, composition, distribution and sources, Atmos. Environ., 38(35) (2004a) 5991-6004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.07.009.
Y. Sun, G. Zhuang, H. Yuan, X. Zhang and J. Guo, Characteristics and sources of 2002 super dust storm in Beijing, Chin. Sci. Bull., 49(7) (2004b) 698-705.
K. Kandler, N. Benker, U. Bundke, E. Cuevas, M. Ebert, P. Knippertz, S. Rodríguez, L. Schütz and S. Weinbruch, Chemical composition and complex refractive index of Saharan Mineral Dust at Izana, Tenerife (Spain) derived by electron microscopy, Atmos. Environ., 41(37) (2007) 8058-8074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.06.047
N. Rastogi and M.M. Sarin, Quantitative chemical composition and characteristics of aerosols over western India: one-year record of temporal variability, Atmos. Environ., 43(22-23) (2009) 3481-3488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.04.030.
B. Schnetger, H.J. Brumsack, H. Schale, J. Hinrichs and L. Dittert, Geochemical characteristics of deep-sea sediments from the Arabian Sea: a high-resolution study, Deep Sea Res. II: Top. Stud. Oceanog., 47(14) (2000) 2735-2768. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0967-0645(00)00047-3.
J.P. Engelbrecht, H. Moosmüller, S. Pincock, R.K.M. Jayanty, T. Lersch and G. Casuccio, Mineralogical, chemical, morphological, and optical interrelationships of mineral dust re-suspensions, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 16(17) (2016) 10809. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-10809-2016.
R. Arimoto, W. Balsam and C. Schloesslin, Visible spectroscopy of aerosol particles collected on filters: iron-oxide minerals, Atmos. Environ., 36(1) (2002) 89-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00465-4.
R. Arimoto, Y.J. Kim, Y.P. Kim, P.K. Quinn, T.S. Bates, T.L. Anderson, S. Gong, S.I. Uno, M. Chin, B.J. Huebert, A.D. Clarke, Y. Shinozuka, R.J. Weber, J.R. Anderson, S.A. Guazzotti, R.C. Sullivan, D.A. Sodeman, K.A. Prather and I.N. Sokolik, Characterization of Asian dust during ACE-Asia, Glob. Planet. Change, 52(1–4) (2006) 23-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.02.013.
I. Chiapello, G. Bergametti, B. Chatenet, P. Bousquet, F. Dulac and E.S. Soares, Origins of African dust transported over the northeastern tropical Atlantic, J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos., 102(D12) (1997) 13701-13709. https://doi.org/10.1029/97JD00259.
L. Gomes and D.A. Gillette, A comparison of characteristics of aerosol from dust storms in central Asia with soil-derived dust from other regions, Atmos. Environ. A. Gen. Top., 27(16) (1993) 2539-2544. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-1686(93)90027-V.
A. Chehregani and F. Kouhkan, Diesel exhaust particles and allergenicity of pollen grains of Liliummartagon, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 69(3) (2008) 568-573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.05.007.
C.E. Reid and J.L. Gamble, Aeroallergens, allergic disease, and climate change: impacts and adaptation, Ecohealth, 6 (2009) 458-470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-009-0261-x.
C. Rusznak, J.L. Devalia and R.J. Davies, The impact of pollution on allergic disease, Allergy, 49 (1994) 21-27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.1994.tb04234.x.
H. Behrendt and W.M. Becker, Localization, release and bioavailability of pollen allergens: the influence of environmental factors. Curr. Opin. Immunol., 13(6) (2001) 709-715. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0952-7915(01)00283-7.
R.B. Knox, C. Suphioglu, P. Taylor, R. Desai, H.C. Watson, J.L. Peng and L.A. Bursill, Major grass pollen allergen Lol p 1 binds to diesel exhaust particles: implications for asthma and air pollution, Clin. Exp. Allergy, 27(3) (1997) 246-251. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.1997.tb00702.x.
M. Azzazy, Environmental impacts of industrial pollution on pollen morphology of Eucalyptus globulus Labill (Myrtaceae), J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol., 4(05) (2016) 057-062. https://doi.org/10.7324/JABB.2016.40509.
J. Fröhlich-Nowoisky, C.J. Kampf, B. Weber, J.A. Huffman, C. Pöhlker, M.O. Andreae, N. Lang-Yona, S.M. Burrows, S.S. Gunthe, W. Elbert, H. Su, P. Hoor, E. Thines, T. Hoffmann, V.R. Després and U. Pöschl, Bioaerosols in the earth system: climate, health, and ecosystem interactions, Atmos. Res., 182 (2016) 346-376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.07.018.
Acknowledgements
We thank Directors of CSIR—National Physical Laboratory, New Delhi, and Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences, Lucknow, for facilities. This work is a part of project sanctioned by the CSIR under its XII Five Year Plan network project ‘AIM_IGPHim (PSC-0112)’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agnihotri, R., Sawlani, R., Azam, M.M. et al. Geochemical, stable isotopic, palynological characterization of surface dry soils and atmospheric particles over Jodhpur city (Thar Desert, Rajasthan) during peak summer of 2013. MAPAN 35, 53–67 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-019-00337-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-019-00337-5