Abstract
Calcium signals play critical functions in regulating diverse arrays of plant growth and development and mediating a variety of biotic and abiotic stress responses as a second messenger. Calcineurin B-like (CBL) proteins were involved with plant-specific Ca2+signaling as calcium sensors. In this work, we retrieved 152 CBL gene members from 15 different grass species, surveyed their phylogenetic relationships and sequence features and also performed expression patterns and functional analyses of rice CBLs. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that grass CBLs fall into four different groups (Group A–D). Sequence analysis showed that CBL proteins harboring four conserved calcium-binding EF-hand have key amino acid residues Asp and Glu which had relatively high proportion in the average abundance. Molecular evolutionary analyses revealed that group A, B and C CBLs in their evolution process suffered the purifying selection, while group D CBLs were subjected to positive selection. Moreover, expression analyses showed significant divergent expression patterns of OsCBLs in various organs and under different hormones and abiotic stresses. Furthermore, tolerance analysis revealed that OsCBL3 and OsCBL8 overexpression transgenic rice seedlings improved salt tolerance and OsCBL5, OsCBL6 and OsCBL7 positively regulated drought stress. In general, the domain and base sequence of the CBL gene family is highly conserved in grasses. OsCBL genes had specific gene expression profiles and function in different stresses.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- CBL:
-
Calcineurin B-like
- [Ca2+]cyt:
-
Cytosolic calcium concentration
- EF-hand:
-
Elongation factor hand
- CaM:
-
Calmodulin
- CMLs:
-
CaM-like proteins
- CDPKs:
-
Ca2+-dependent protein kinases
- CIPKs:
-
CBL-interacting protein kinases
- CNB:
-
Calcineurin B
- AKT1:
-
Arabidopsis K+ transporter 1
- pI:
-
Isoelectric point
- Mw:
-
Molecular weight
- ML:
-
Maximum-likelihood
- JTT:
-
Jones-Taylor-Thornton
- ZH11:
-
Zhonghua 11
- RT-qPCR:
-
Real-time quantitative PCR
- SAM:
-
Shoot apical meristem
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- WT:
-
Wild type
- ώ = dN/dS :
-
Nonsynonymous-to-synonymous rates ratio
References
Albrecht V, Ritz O, Linder S, Harter K, Kudla J (2001) The NAF domain defines a novel protein-protein interaction module conserved in Ca2+-regulated kinases. Embo J 20:1051–1063
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang JH, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Batistic O, Kudla J (2009) Plant calcineurin B-like proteins and their interacting protein kinases. Bba-Mol Cell Res 1793:985–992
Batistic O, Sorek N, Schultke S, Yalovsky S, Kudla J (2008) Dual fatty acyl modification determines the localization and plasma membrane targeting of CBL/CIPK Ca2+ signaling complexes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:1346–1362
Batistic O, Rehers M, Akerman A, Schlucking K, Steinhorst L, Yalovsky S, Kudla J (2012) S-acylation-dependent association of the calcium sensor CBL2 with the vacuolar membrane is essential for proper abscisic acid responses. Cell Res 22:1155–1168
Van Bel M, Diels T, Vancaester E, Kreft L, Botzki A, Van de Peer Y, Coppens F, Vandepoele K (2018) PLAZA 4.0: an integrative resource for functional, evolutionary and comparative plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D1190–D1196
Burstenbinder K, Moller B, Plotner R, Stamm G, Hause G, Mitra D, Abel S (2017) The IQD family of calmodulin-binding proteins links calcium signaling to microtubules, membrane subdomains, and the nucleus. Plant Physiol 173:1692–1708
de Castro E, Sigrist CJA, Gattiker A, Bulliard V, Langendijk-Genevaux PS, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, Hulo N (2006) ScanProsite: detection of PROSITE signature matches and ProRule-associated functional and structural residues in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W362–W365
Chaves-Sanjuan A, Sanchez-Barrena MJ, Gonzalez-Rubio JM, Moreno M, Ragel P, Jimenez M, Pardo JM, Martinez-Ripoll M, Quintero FJ, Albert A (2014) Structural basis of the regulatory mechanism of the plant CIPK family of protein kinases controlling ion homeostasis and abiotic stress. P Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E4532–E4541
Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Grant JJ, Batistic O, Li L, Kim BG, Lee SC, Kudla J, Luan S (2007) Two calcineurin B-like calcium sensors, interacting with protein kinase CIPK23, regulate leaf transpiration and root potassium uptake in Arabidopsis. Plant J 52:223–239
Cheong YH, Sung SJ, Kim BG, Pandey GK, Cho JS, Kim KN, Luan S (2010) Constitutive overexpression of the calcium sensor CBL5 confers osmotic or drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Mol Cells 29:159–165
Cho JH, Choi MN, Yoon KH, Kim KN (2018) Ectopic expression of SjCBL1, Calcineurin B-Like 1 gene from Sedirea japonica, rescues the salt and osmotic stress hypersensitivity in Arabidopsis cbl1 mutant. Front Plant Sci 9:1188
Eckert C, Offenborn JN, Heinz T, Armarego-Marriott T, Schultke S, Zhang CX, Hillmer S, Heilmann M, Schumacher K, Bock R, Heilmann I, Kudla J (2014) The vacuolar calcium sensors CBL2 and CBL3 affect seed size and embryonic development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 78:146–156
Evans NH, McAinsh MR, Hetherington AM (2001) Calcium oscillations in higher plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:415–420
Fotster S, Schmidt LK, Kopic E, Anschutz U, Huang SG, Schlucking K, Koster P, Waadt R, Larrieu A, Batistic O, Rodriguez PL, Grill E, Kudla J, Becker D (2019) Wounding-induced stomatal closure requires jasmonate-mediated activation of GORK K+ channels by a Ca2+ sensor-kinase CBL1-CIPK5 complex. Dev Cell 48:87–89
Gao YL, Zhang GZ (2019) A calcium sensor calcineurin B-like 9 negatively regulates cold tolerance via calcium signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal Behav 14:e1573099
Goodstein DM, Shu SQ, Howson R, Neupane R, Hayes RD, Fazo J, Mitros T, Dirks W, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Rokhsar DS (2012) Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D1178–D1186
Gu ZM, Ma BJ, Jiang Y, Chen ZW, Su X, Zhang HS (2008) Expression analysis of the calcineurin B-like gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under environmental stresses. Gene 415:1–12
Guo Y, Halfter U, Ishitani M, Zhu JK (2001) Molecular characterization of functional domains in the protein kinase SOS2 that is required for plant salt tolerance. Plant Cell 13:1383–1399
Harper JF, Harmon A (2005) Plants, symbiosis and parasites: a calcium signalling connection. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 6:555–566
Huang CL, Ding S, Zhang H, Du H, An LZ (2011) CIPK7 is involved in cold response by interacting with CBL1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci 181:57–64
Ishitani M, Liu JP, Halfter U, Kim CS, Shi WM, Zhu JK (2000) SOS3 function in plant salt tolerance requires N-myristoylation and calcium binding. Plant Cell 12:1667–1677
Jiang M, Chu ZQ (2018) Comparative analysis of plant MKK gene family reveals novel expansion mechanism of the members and sheds new light on functional conservation. BMC Genomics 19:407
Jiao YN, Wickett NJ, Ayyampalayam S, Chanderbali AS, Landherr L, Ralph PE, Tomsho LP, Hu Y, Liang HY, Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Clifton SW, Schlarbaum SE, Schuster SC, Ma H, Leebens-Mack J, dePamphilis CW (2011) Ancestral polyploidy in seed plants and angiosperms. Nature 473:97–U113
Kim BG, Waadt R, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Dominguez-Solis JR, Schultke S, Lee SC, Kudla J, Luan S (2007) The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 52:473–484
Kolukisaoglu U, Weinl S, Blazevic D, Batistic O, Kudla J (2004) Calcium sensors and their interacting protein kinases: Genomics of the Arabidopsis and rice CBL–CIPK signaling networks. Plant Physiol 134:43–58
Kudla J, Xu Q, Harter K, Gruissem W, Luan S (1999) Genes for calcineurin B-like proteins in Arabidopsis are differentially regulated by stress signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4718–4723
Li LG, Kim BG, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Luan S (2006) A Ca2+ signaling pathway regulates a K+ channel for low-K response in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12625–12630
Li Q, Zhang N, Zhang LS, Ma H (2015) Differential evolution of members of the rhomboid gene family with conservative and divergent patterns. New Phytol 206:368–380
Li J, Jiang MM, Ren L, Liu Y, Chen HY (2016) Identification and characterization of CBL and CIPK gene families in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Mol Genet Genomics 291:1769–1781
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452
Liu JP, Zhu JK (1998) A calcium sensor homolog required for plant salt tolerance. Science 280:1943–1945
Lu TT, Zhang GF, Sun LR, Wang J, Hao FS (2017) Genome-wide identification of CBL family and expression analysis of CBLs in response to potassium deficiency in cotton. Peer J 5:e3653
Luan S (2009) The CBL–CIPK network in plant calcium signaling. Trends Plant Sci 14:37–42
Luan S, Kudla J, Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Yalovsky S, Gruissem W (2002) Calmodulins and calcineurin B-like proteins: calcium sensors for specific signal response coupling in plants. Plant Cell 14:S389–S400
Ma Q, Tang RJ, Zheng XJ, Wang SM, Luan S (2015) The calcium sensor CBL7 modulates plant responses to low nitrate in Arabidopsis. Biochem Bioph Res Commun 468:59–65
Mahs A, Steinhorst L, Han JP, Shen LK, Wang Y, Kudla J (2013) The calcineurin B-like Ca2+ Sensors CBL1 and CBL9 function in pollen germination and pollen tube growth in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 6:1149–1162
Mayer KFX, Rogers J, Dolezel J, Pozniak C, Eversole K, Feuillet C, Gill B, Friebe B, Lukaszewski AJ, Sourdille P, Endo TR, Dolezel J, Kubalakova M, Cihalikova J, Dubska Z, Vrana J, Sperkova R, Simkova H, Rogers J, Febrer M, Clissold L, McLay K, Singh K, Chhuneja P, Singh NK, Khurana J, Akhunov E, Choulet F, Sourdille P, Feuillet C, Alberti A, Barbe V, Wincker P, Kanamori H, Kobayashi F, Itoh T, Matsumoto T, Sakai H, Tanaka T, Wu JZ, Ogihara Y, Handa H, Pozniak C, Maclachlan PR, Sharpe A, Klassen D, Edwards D, Batley J, Olsen OA, Sandve SR, Lien S, Steuernagel B, Wulff B, Caccamo M, Ayling S, Ramirez-Gonzalez RH, Clavijo BJ, Steuernagel B, Wright J, Pfeifer M, Spannagl M, Mayer KFX, Martis MM, Akhunov E, Choulet F, Mayer KFX, Mascher M, Chapman J, Poland JA, Scholz U, Barry K, Waugh R, Rokhsar DS, Muehlbauer GJ, Stein N, Gundlach H, Zytnicki M, Jamilloux V, Quesneville H, Wicker T, Mayer KFX, Faccioli P, Colaiacovo M, Pfeifer M, Stanca AM, Budak H, Cattivelli L, Glover N, Martis MM, Choulet F, Feuillet C, Mayer KFX, Pfeifer M, Pingault L, Mayer KFX, Paux E, Spannagl M, Sharma S, Mayer KFX, Pozniak C, Appels R, Bellgard M, Chapman B, Pfeifer M, Pfeifer M, Sandve SR, Nussbaumer T, Bader KC, Choulet F, Feuillet C, Mayer KFX, Akhunov E, Paux E, Rimbert H, Wang SC, Poland JA, Knox R, Kilian A, Pozniak C, Alaux M, Alfama F, Couderc L, Jamilloux V, Guilhot N, Viseux C, Loaec M, Quesneville H, Rogers J, Dolezel J, Eversole K, Feuillet C, Keller B, Mayer KFX, Olsen OA, Praud S (2014) A chromosome-based draft sequence of the hexaploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) genome. Science 345:1251788
McCormack E, Tsai YC, Braam J (2005) Handling calcium signaling: Arabidopsis CaMs and CMLs. Trends Plant Sci 10:383–389
Mohanta TK, Mohanta N, Mohanta YK, Parida P, Bae HH (2015) Genome-wide identification of Calcineurin B-Like (CBL) gene family of plants reveals novel conserved motifs and evolutionary aspects in calcium signaling events. BMC Plant Biol 15:189
Nagae M, Nozawa A, Koizumi N, Sano H, Hashimoto H, Sato M, Shimizu T (2003) The crystal structure of the novel calcium-binding protein AtCBL2 from Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 278:42240–42246
Ouyang S, Zhu W, Hamilton J, Lin H, Campbell M, Childs K, Thibaud-Nissen F, Malek RL, Lee Y, Zheng L, Orvis J, Haas B, Wortman J, Buell CR (2007) The TIGR Rice genome annotation resource: improvements and new features. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D883–D887
Pandey GK, Cheong YH, Kim KN, Grant JJ, Li LG, Hung W, D'Angelo C, Weinl S, Kudla J, Luan S (2004) The calcium sensor calcineurin B-Like 9 modulates abscisic acid sensitivity and biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:1912–1924
Ren XL, Qi GN, Feng HQ, Zhao S, Zhao SS, Wang Y, Wu WH (2013) Calcineurin B-like protein CBL10 directly interacts with AKT1 and modulates K+ homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 74:258–266
Sanchez-Barrena MJ, Martinez-Ripoll M, Albert A (2013) Structural biology of a major signaling network that regulates plant abiotic stress: The CBL–CIPK mediated pathway. Int J Mol Sci 14:5734–5749
Sanders D, Pelloux J, Brownlee C, Harper JF (2002) Calcium at the crossroads of signaling. Plant Cell 14:S401–S417
Sanyal SK, Pandey A, Pandey GK (2015) The CBL–CIPK signaling module in plants: a mechanistic perspective. Physiol Plantarum 155:89–108
Schulz P, Herde M, Romeis T (2013) Calcium-dependent protein kinases: hubs in plant stress signaling and development. Plant Physiol 163:523–530
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tang RJ, Liu H, Yang Y, Yang L, Gao XS, Garcia VJ, Luan S, Zhang HX (2012) Tonoplast calcium sensors CBL2 and CBL3 control plant growth and ion homeostasis through regulating V-ATPase activity in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 22:1650–1665
Weinl S, Kudla J (2009) The CBL–CIPK Ca2+-decoding signaling network: function and perspectives. New Phytol 184:517–528
Whittle CA, Krochko JE (2009) Transcript profiling provides evidence of functional divergence and expression networks among ribosomal protein gene Paralogs in Brassica napus. Plant Cell 21:2203–2219
Xi Y, Liu JY, Dong C, Cheng ZM (2017) The CBL and CIPK gene family in grapevine (Vitis vinifera): genome-wide analysis and expression profiles in response to various abiotic stresses. Front Plant Sci 8:978
Ye NH, Wang FZ, Shi L, Chen MX, Cao YY, Zhu FY, Wu YZ, Xie LJ, Liu TY, Su ZZ, Xiao S, Zhang H, Yang JC, Gu HY, Hou XX, Hu QJ, Yi HJ, Zhu CX, Zhang JH, Liu YG (2018) Natural variation in the promoter of rice calcineurin B-like protein10 (OsCBL10) affects flooding tolerance during seed germination among rice subspecies. Plant J 94:612–625
Yin X, Wang QL, Chen Q, Xiang N, Yang YQ, Yang YP (2017) Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the calcineurin B-like protein and calcineurin b-like protein-interacting protein kinase gene families in turnip (Brassica rapa var. rapa). Front Plant Sci 8:1191
Zhang HC, Yin WL, Xia XL (2008) Calcineurin B-Like family in Populus: comparative genome analysis and expression pattern under cold, drought and salt stress treatment. Plant Growth Regul 56:129–140
Zhang HF, Yang B, Liu WZ, Li HW, Wang L, Wang BY, Deng M, Liang WW, Deyholos MK, Jiang YQ (2014) Identification and characterization of CBL and CIPK gene families in canola (Brassica napus L.). BMC Plant Biol 14:8
Zhang CX, Beckmann L, Kudla J, Batistic O (2017) N-terminal S-acylation facilitates tonoplast targeting of the calcium sensor CBL6. Febs Lett 591:3745–3756
Zhou YL, Cheng Y, Yang YQ, Li X, Supriyo B, Sun XD, Yang YP (2016) Overexpression of SpCBL6, a calcineurin B-like protein of Stipa purpurea, enhanced cold tolerance and reduced drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Mol Biol Rep 43:957–966
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81360611) and Shanghai Sailing Program (19YF1414800). The funding bodies had no role in study design, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MJ and GW conceived and designed the project. MJ executed the bioinformatics analysis, conducted the experiments and wrote the manuscript. CZ, MZ, YL and GW retrieved gene sequence data and performed the bioinformatics analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12374_2020_9240_MOESM7_ESM.tif
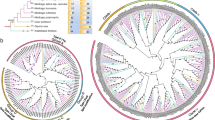
Fig. S1. Maximum Likelihood phylogenetic trees were reconstructed using EF-hand motifs of CBL proteins in 15 grasses. Phylogenetic analysis was carried with EF-hand motifs of protein sequences for 152 CBL proteins from 15 grass species identified in this study Supplementary file7 (TIF 8180 kb)
12374_2020_9240_MOESM8_ESM.tif
Fig. S2. Sequence features shown in the form of web logos representing the conserved EF-hand motif of each group. The red stars indicate residues of functional or structural importance based on phylogenetic conservations. Logos were generated using the Weblogo3 application (http://weblogo.threeplusone.com/) Supplementary file8 (TIF 4225 kb)
12374_2020_9240_MOESM9_ESM.tif
Fig. S3. Sequence features shown in the form of web logos representing the conserved FPSF domain in C-terminal region of each group Supplementary file9 (TIF 1744 kb)
12374_2020_9240_MOESM10_ESM.tif
Fig. S4. Molecular analysis of OsCBLs transgenic rice plants in the level of DNA. 1: OsCBL1,2: OsCBL2,3: OsCBL3,4: OsCBL4,5: OsCBL5,6: OsCBL6,7: OsCBL7,8: OsCBL8,9: OsCBL9,10: OsCBL10, Marker:100 bp plus DNA ladder Supplementary file10 (TIF 2635 kb)
12374_2020_9240_MOESM12_ESM.tif
Fig. S6. Real-time PCR analysis of OsCBLs T3 transgenic rice lines. A: OsCBL1-OE, B:OsCBL2-OE, C:OsCBL3-OE, D: OsCBL4-OE, E: OsCBL5-OE, F: OsCBL6-OE, G: OsCBL7-OE, H:OsCBL8-OE, I: OsCBL9-OE, J:OsCBL10-OE Supplementary file12 (TIF 7048 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, M., Zhao, C., Zhao, M. et al. Phylogeny and Evolution of Calcineurin B-Like (CBL) Gene Family in Grass and Functional Analyses of Rice CBLs. J. Plant Biol. 63, 117–130 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-020-09240-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-020-09240-y