Abstract
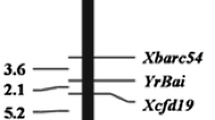
Stripe rust, which is caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. Tritici (Pst), is one of the most destructive wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) diseases worldwide. To control stripe rust, the best strategy is breeding and growing novel resistant cultivars. Qubaichun (QBC), a Tibetan wheat landrace, displays near-immune resistance to wheat stripe rust in western China. Previously, our studies have shown that the stripe rust resistance of QBC is controlled by a dominant gene at the seedling stage and two independent genes at the adult-plant stage. These two genes comprise an all-stage resistance (ASR) gene and a durable adult resistance gene, which was identified as Yr18. The unknown ASR gene is temporarily named Yrqbc. To map this gene, a segregating population of QBC × Chinese Spring (CS) was generated. SSR analysis, BSR-seq and Infinium 660 K iSelect SNP genotyping were successively performed. The results show that Yrqbc finely mapped to a 5.1 cM genetic interval between molecular markers A009200 and A009192, and the genetic distance to the marker A009200 was 0.1 cM. Furthermore, Yrqbc was confirmed to be Yr5 by sequencing. Diagnostic markers are used for detection Yr5 and Yr18 in 323 new cultivars (lines) worldwide. The results show that 27 cultivars (lines) carry the durable adult resistance gene Yr18, and only one material carrying the ASR resistance gene Yr5. In order to analyse the effectiveness and practicality of transferring the pyramided of Yr18 and Yr5, these two stripe rust resistance genes were introduced into elite cultivars which lost resistance. Field test results verified that the combination of Yr5 and Yr18 could provide effective resistance to stripe rust for the whole life of wheat, which provided a genetic foundation for the near immunity of elite cultivars. As a result, this Tibetan landrace could be used for developing high-level, durable resistant wheat cultivars.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bariana HS, Brown GN, Bansal UK, Miah H, Standen GE, Lu M (2007) Breeding triple rust resistant wheat cultivars for Australia using conventional and marker-assisted selection technologies. Aust J Agric Res 58:576–587. https://doi.org/10.1071/AR07124
Chen XM (2005) Epidemiology and control of stripe rust [Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici] on wheat. Can J Plant Path 27:314–337. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060660509507230
Chen X (2013) Review article: high-temperature adult-plant resistance, key for sustainable control of stripe rust. Am J Plant Sci 04:608–627
Chen XM, Tristan C, Xueling H, Meinan W, Andrea D (2013) Understanding molecular mechanisms of durable and non-durable resistance to stripe rust in wheat using a transcriptomics approach. Curr Genom 14:111–126. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389202911314020004
Cheng Z, Wang P, Xu Y (2016) Bulked sample analysis in genetics, genomics and crop improvement. Plant Biotechnol J 14:1941–1955. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12559
Clemence M et al (2018) BED-domain-containing immune receptors confer diverse resistance spectra to yellow rust. Nat Plants 4:662–668
Cox TS, Raupp WJ, Gill BS (1994) Leaf rust-resistance genes Lr41, Lr42, and Lr43 transferred from Triticum tauschii to common wheat. Crop Sci 34:339–343. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1994.0011183X003400020005x
Cui F et al (2017) Utilization of a Wheat660K SNP array-derived high-density genetic map for high-resolution mapping of a major QTL for kernel number. Sci Rep 7:3788
Dong SJ, Xu WG, Hu L et al (2012) Molecular detection of stripe rust resistant genes in 43 wheat varieties planted in Henan Province. Acta Agric Boreal Sin 27:157–162. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-7091.2012.05.030
Elisabeth LM, DePope V-PC, Van der Wanf W (2017) Achieving durable resistance against plant diseases: scenario analyses with a national-ccale spatially explicit model for a wind-dispersed. Plant Pathog Phytopathol 107:580–589. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-05-16-0207-R
Ellis JG, Lagudah ES, Spielmeyer W, Dodds PN (2014) The past, present and future of breeding rust resistant wheat. Front Plant Sci 5:641. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00641
Guo Q, Zhang ZJ, Xu YB, Li GH, Feng J, Zhou Y (2008) Quantitative trait loci for high-temperature adult-plant and slow-rusting resistance to Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in wheat cultivars. Phytopathology 98:803–809. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-98-7-0803
Gupta P et al (2002) Genetic mapping of 66 new microsatellite (SSR) loci in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 105:413–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-0865-9
Hou L, Chen X, Wang M, See DR, Chao S, Bulli P, Jing J (2015) Mapping a large number of QTL for durable resistance to stripe rust in winter wheat druchamp using SSR and SNP markers. PLoS ONE 10:e0126794. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126794
Jin H, Jia Q, Bo Z, Sun Z, Huang M, Jin S (2018) Epidemic forecasting of the new strains G22-9(CYR34) and G22-14 of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in wheat in Gansu Province. J Plant Prot
Johnson R (1981) Durable resistance: definition of, genetic control, and attainment in plant breeding. Phytopathology 71:567–568
Kankwatsa P, Singh D, Thomson PC, Babiker EM, Bonman JM, Newcomb M, Park RF (2017) Characterization and genome-wide association mapping of resistance to leaf rust, stem rust and stripe rust in a geographically diverse collection of spring wheat landraces. Mol Breed 37:113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0707-8
Lagudah ES et al (2009) Gene-specific markers for the wheat gene Lr34/Yr18/Pm38 which confers resistance to multiple fungal pathogens. Theor Appl Genet 119:889–898
Line RF, Qayoum A (1992) Virulence, aggressiveness, evolution and distribution of races of Puccinia striiformis(the cause of stripe rust of wheat) in North America, 1968–8. US Dept Agric Tech Bull 1788:44
Liu TG, Peng YL, Chen WQ, Zhang ZY (2010) First detection of virulence in Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in China to resistance genes Yr24(=Yr26) present in wheat cultivar Chuanmai 42. Plant Dis 94:1163–1163. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-94-9-1163C
Liu L, Wang MN, Feng JY, See DR, Chao SM, Chen XM (2018) Combination of all-stage and high-temperature adult-plant resistance QTL confers high-level, durable resistance to stripe rust in winter wheat cultivar Madsen. Theor Appl Genet 131:1835–1849. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3116-4
Maccaferri M et al (2015) A genome-wide association study of resistance to stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) in a worldwide collection of hexaploid spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). G3 5:449–465. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.114.014563
Mallick N, Vinod SJB, Tomar RS, Sivasamy M, Prabhu KV (2015) Marker-assisted backcross breeding to combine multiple rust resistance in wheat. Plant Breed 134:172–177. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12242
Miaomiao H, Zhenyu S, Shiqin C, Qiuzhen J, Taiguo L, Wanquan C (2018) Evaluation of the resistance of 223 wheat landraces in Gansu Province to stripe rust and molecular detection. J Plant Prot
Murphy LR, Santra D, Kidwell K, Yan GP, Chen XM, Campbell KG (2009) Linkage maps of wheat stripe rust resistance genes Yr5 and Yr15 for use in marker-assisted selection. Crop Sci 49:1786–1790. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2008.10.0621
Nobuko Y, Takayuki M, Keiko H, Shinzo K, Yoshikatsu F (2015) Effects of pyramiding quantitative resistance genes Pi21, Pi34, and Pi35 on rice leaf blast disease: an international journal of applied plant pathology. Plant Dis. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-02-14-0214-RE
Qi LL et al (2004) A chromosome bin map of 16,000 expressed sequence tag loci and distribution of genes among the three genomes of polyploid wheat. Genetics 168:701–712. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.104.034868
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier MH, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007
Ramirez-Gonzalez RH et al (2015) RNA-Seq bulked segregant analysis enables the identification of high-resolution genetic markers for breeding in hexaploid wheat. Plant Biotechnol J 13:613–624. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12281
Ren Y, Li SR, Zhou Q, Du XY et al (2014) Evaluation of resistance to stripe rust of 134 wheat cultivars and lines from Sichuan Province. J Triticeae Crops 34:847–853
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1985) Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol 5:69–76
Rosewarne GM et al (2006) Leaf tip necrosis, molecular markers and β1-proteasome subunits associated with the slow rusting resistance genes Lr46/Yr29. Theor Appl Genet 112:500–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0153-6
Schneider A, Walker S, Sagan M, Duc G, Ellis T, Downie J (2002) Mapping of the nodulation loci sym9 and sym10 of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Theor Appl Genet 104:1312–1316
Shi A, Chen P, Li D, Zheng C, Bo Z, Hou A (2009) Pyramiding multiple genes for resistance to soybean mosaic virus in soybean using molecular markers. Mol Breed 23:113
Singh D, Park RF, Mcintosh RA, Bariana HS (2008) Characterisation of stem rust and stripe rust seedling resistance genes in selected wheat cultivars from the United Kingdom. J Plant Pathol 90:553–562
Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, William HM (2005) Genetics and breeding for durable resistance to leaf and stripe rusts in wheat Turkish. J Agric For 29:121–127
Somers DJ, Isaac P, Edwards K (2004) A high-density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat (Triticum asetivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:1105–1114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1740-7
Sourdille P et al (2004) Microsatellite-based deletion bin system for the establishment of genetic-physical map relationships in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Funct Integr Genom 4:12–25
Wan AM, Chen XM, He ZH (2007) Wheat stripe rust in China. Aust J Agric Res 58:605–619. https://doi.org/10.1071/AR06142
Wang SH, Gong KY, Chu BY, Sun QY, Luo Y, Zhan-Hong MA (2018) Molecular detection of stripe rust resistance gene(s) in 100 wheat cultivars(lines) from Sichuan Province in China. Acta Phytopathol Sin 164:946–958
Werner K, Friedt W, Ordon F (2005) Strategies for pyramiding resistance genes against the barley yellow mosaic virus complex (BaMMV, BaYMV, BaYMV-2). Mol Breed 16:45–55
Xu LS, Wang MN, Cheng P, Kang ZS, Hulbert SH, Chen XM (2013) Molecular mapping of Yr53, a new gene for stripe rust resistance in durum wheat accession PI 480148 and its transfer to common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 126:523–533
Yan GP, Chen XM, Line RF, Wellings CR (2003) Resistance gene-analog polymorphism markers co-segregating with the Yr5 gene for resistance to wheat stripe rust. Theor Appl Genet 106:636–643
Yan L, Meinan W, Xianming C, Deven S, Shiaoman C, Jinxue J (2014) Mapping of Yr62 and a small-effect QTL for high-temperature adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in spring wheat PI 192252. Theor Appl Genet 127:1449–1459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2312-0
Yanmin Q, Yan L, Meinan W, Xing L, See DR, Diaoguo A, Xianming C (2019) Development, validation, and re-selection of wheat lines with pyramided genes Yr64 and Yr15 linked on the short arm of chromosome 1B for resistance to stripe rust. Plant Dis 103:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-03-18-0470-RE
Zeng SM, Luo Y (2006) Long-distance spread and interregional epidemics of wheat stripe rust in China. Plant Dis 90:980–988. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-90-0980
Zeng QD et al (2014) Stripe rust resistance and genes in Chinese wheat cultivars and breeding lines. Euphytica 196:271–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-1030-z
Zhang ZJ, Yang GH, Li GH, Jin SL, Yang XB (2001) Transgressive segregation, heritability, and number of genes controlling durable resistance to stripe rust in one Chinese and two Italian wheat cultivars. Phytopathology 91:680–686. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO.2001.91.7.680
Zheng S et al (2017) Evaluating the contribution of Yr genes to stripe rust resistance breeding through marker-assisted detection in wheat. Euphytica 213:50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1828-6
Zhou C, Zhibin XU, Feng B, Xiang C, Wang T (2015) Genetic analysis of stripe rust resistance in Tibetan wheat landrace Qubaichun. J Triticeae Crops. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203283
Zhou X et al (2017) Molecular detection of stripe rust resistant genes Yr5 and Yr10 in 38 Wheat Lines Gansu. Agric Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jph.12515
Acknowledgements
We thank Tibet Academy of Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Sciences for providing Qubaichun seeds. The KASP assay was conducted by China Golden Marker (Beijing) Biotech Co., Ltd. Thanks to Professor Zhiyong Liu from Institute of genetics, CAS for BSR-seq data analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31671679) and Youth Innovation Promotion Association, CAS (Grant No. 2018403).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T-W coordinated the project, conceived and designed experiments. B-F conducted the bioinformatics work, generated and analyzed data, and edits the manuscript. Z-B X and F-X L collected the samples; F-W, G-S J and Q-Z performed the laboratory work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10722_2020_938_MOESM1_ESM.pptx
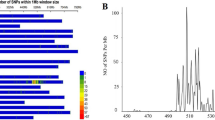
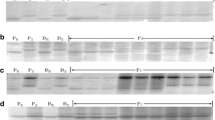
Supplementary file1 (PPTX 506 kb) Supplementary Figure 1 The integrated genetic linkage map of stripe rust resistance gene and its co-segregated markers on 2BL. Supplementary Figure 2 The ASR gene in QBC was identified by Yr5 functional marker. The amplified fragment size of PCR was 1281 bp. Material 1-7 was a randomly selected F2 generation of QBC × CM28 with IT of "0", Material 8 was a cultivar containing Yr5 gene, Material 9 was QBC, Material 10 was CS. The results showed that the ASR gene in QBC was Yr5. Supplementary Figure 3 The analysis results of BSR-seq, SNPs are mainly concentrated in the 633~653 Mb, 673~693 Mb and 723~763 Mb regions of 2BL
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Xu, Z., Fan, X. et al. Genetic mapping and utilization analysis of stripe rust resistance genes in a Tibetan wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) landrace Qubaichun. Genet Resour Crop Evol 67, 1765–1775 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-00938-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-00938-z