Abstract
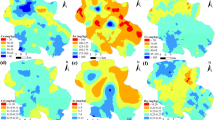
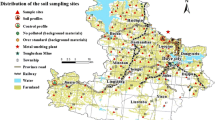
With the purpose of investigate the characteristics and provenances of the hazardous trace elements (HTEs) in a typical agricultural land in the undulating plain area of eastern Anhui province, China, a total of 1170 soil samples were collected. Six HTEs, including Cd, Cr, Hg, Ni, Pb, and As, were determined. Statistical methods including box plot, Pearson correlation analysis, principal component analysis, and cluster analysis, were conducted to illustrate the provenances of HTEs. Results indicate that Cd and Hg were influenced by human activities (such as traffic transportation for Cd and Pb, and chemical pesticides for Hg). Cr, Ni, and As mainly originated from the parent materials (e.g., red detrital rocks, carbonate rocks, and late Pleistocene loess). Pb is of dual provenances of both human activity and parent material. In a word, regarding highly toxic HTEs, the soil in the study area is almost free from pollution, and only a small amount of soil samples contains slightly higher contents of As, Cd and Pb.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bushoven, J.T., Jiang, Z., Ford, H.J., Sawyer, C.D., Hull, R.J., and Amador, J.A. 2000, Stabilization of soil nitrate by reseeding with perennial ryegrass following sudden turf death. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29, 1657–1661.
Chen, X. and Zhou, J. 2012, Features of distribution of trace elements in soils in the Jianghuai area, Anhui and analysis of the cause of formation. Geology of Anhui, 22, 123–129. (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Guan, H., Li, Y., Peng, M., and Liu, D. 2013, The evaluation of heavy metal pollution and its potential ecological risk of urban topsoil in Huangshan City. Geology in China, 40, 1949–1958. (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Guo, G., Wu, F., Xie, F., and Zhang, R. 2012, Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in urban soils from southwest China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24, 410–418.
Hang, X.S., Wang, H.Y., Zhou, J.M., Ma, C.L., Du, X.W., and Chen, X.G. 2009, Risk assessment of potentially toxic element pollution in soils and rice (Oryza Sativa) in a typical area of the Yangtze River Delta. Environmental Pollution, 157, 2542–2549.
Inboonchuay, T., Suddhiprakarn, A., Kheoruenromne, I., Anusontpornperm, S., and Gilkes, R.J. 2016, Amounts and associations of heavy metals in paddy soils of the Khorat Basin, Thailand. Geoderma Regional, 7, 120–131.
Jiang, Y., Chao, S., Liu, J., Yang, Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, A., and Cao, H. 2017, Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere, 168, 1658–1668.
Jia, L., Yang, L., Ouyang, Z., Wang, W., Li, H., Li, Y., and Yu, J. 2009, Assessment of the potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the farmland soils in Yucheng City, Shandong Province. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 28, 2270–2276.
José Marrugo-Negrete, J., José Pinedo-Hernández, J., and Díez, S. 2017, Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinú River Basin, Colombia. Environmental Research, 154, 380–388.
Lee, C.S., Li, X., Shi, W., Cheung, S.C., and Thornton, I. 2006, Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: a study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Science of the Total Environment, 356, 45–61.
Li, R., Pan, C., Chen, J., Jiang, Y., and Ding, G. 2012, Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment for urban topsoil and dust in Tongling City. China Environmental Science, 32, 2261–2270. (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Li, F., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., and Zhou, J. 2017, Analysis and evaluation of the soil and dust contamination by heavy metals in different functional zones on Xiamen. Journal of Safety and Environment, 17, 719–724.
Lu, J., and He, H. 2018, Identifying the origins and spatial distributions of heavy metals in the soils of the Jiangsu coast. Environmental Science, 39, 2853–2864.
Ministry of Ecology and Environment 2018, Soil environmental quality — risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land. National Standards of People’s Republic of China (Standard ID: GB 15618-2018), Beijing, 7 p.
Ministry of Land and Resources 2016, Analysis methods for regional geochemical sample. National Standards of People’s Republic of China (Standard ID: DZ/T0279-2016), Beijing, 12 p.
Nezat, C.A., Hatch, S.A., and Uecker, T. 2017, Heavy metal content in urban residential and park soils: a case study in Spokane, Washington, USA. Applied Geochemistry, 78, 186–193.
Pan, J., Wang, J., Wang, C., and Yang, H. 2017, Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment for the main grape base soil heavy metals at the eastern foot of Helan Mountain in Ningxia. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 31, 173–178.
Pan, Y.M. and Dong, P. 1999, The Lower Changjiang (Yangzi/Yangtze River) metallogenic belt, east central China: intrusion and wall rockhosted Cu-Fe-Au, Mo, Zn, Pb, Ag deposits. Ore Geology Reviews, 15, 177–242.
Qin, X., Li, Y., Sun, Y., and Peng, M. 2017, Source apportionment of soil heavy metals in typically agricultural region around Chaohu Lake, China. Earth and Environment, 45, 455–463. (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Qi, W., Liu, J., Zhao, C., Li, F., and Yu, H. 2018, A causation-based method developed for an integrated risk assessment of heavy metals in soil. Science of the Total Environment, 642, 1396–1405.
Ravankhah, N., Mirzaei, R., and Masoum, S. 2017, Determination of heavy metals in surface soils around the brick kilns in an arid region, Iran. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 176, 91–99.
Soil Census Office of Anhui Province, 1996, Anhui soil. Beijing, 84 p.
Tang, Q., Li, L., Zhang, S., Zheng, L., and Miao, C. 2018, Characterization of heavy metals in coal gangue-reclaimed soils from a coal mining area. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 186, 1–11.
Toth, G., Hermann, T., Da Silva, M.R., and Montanarella, L. 2016, Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environment International, 88, 299–309.
Wang, C., Xu, M., Zhang, J., Ding, Q., Ling, R., and Guo, L. 2016, Influence of soils pH and Eh on vertical migration and transformation of Cr(VI). Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 10, 6035–6041. (in Chinese with an English abstract) DOI: https://doi.org/10.12030/j.cjee.201505010; http://www.magsci.cn/magsci/article/article?id=25581347
Webster, R. and Burgess, T.M. 1983, Spatial Variation in soil and the Role of Kriging. Agricultural Water Management, 6, 111–121.
Wei, B. and Yang, L. 2010, A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchemical Journal, 94, 99–107.
Xiao, Y., Wei, L., Wu, X., Xia, Z., Qiu, Z., Tao, H., Wang, S., Wang, W., Wei, J., Zhan, R., and Zhang, Y. 2012, Achievements reports on geochemical survey for land quality (1:50000) in the regions around Chaohu lake (Quanjiao County). Geo-Environment Monitoring Institute of Anhui Province, Hefei, 198 p.
Yang, X., Ren, G., Li, L., and Luo, K. 2017, Effect of pH value on heavy metals form of soil and their relationship. China Mining Magazine, 26, 79–83. (in Chinese with an English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgky201706015
Yi, K., Fan, W., Chen, J., Jiang, S., Huang, S., Peng, L., Zeng, Q., and Luo, S. 2018, Annual input and output fluxes of heavy metals to paddy fields in four types of contaminated areas in Hunan Province, China. Science of the Total Environment, 634, 67–76.
Yin, G., Jiang, H., Wang, Q., Nie, J., Ma, Y., and Hu, H. 2018, Analysis of the sources and characteristics of heavy metals in farmland soil from a typical district in Anhui Province. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37, 96–104. (in Chinese with an English abstract)
Zhang, J., Li, H., Zhou, Y., Dou, L., Cai, L., Mo, L., and You, J. 2018, Bioavailability and soil-to-crop transfer of heavy metals in farmland soils: a case study in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environmental Pollution, 235, 710–719.
Zhang, P., Qin, C., Hong, X., Kang, G., Qin, M., Yang, D., Pang, B., Li, Y., He, J., and Dick, R.P. 2018, Risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution from lower reaches of Yellow River irrigation in China. Science of the Total Environment, 633, 1136–1147.
Zheng, Y., Chen, H., Chen, T., Zheng, G., Wu, H., and Zhou, J. 2003, Spatial distribution patterns of Cr and Ni in soils of Beijing. Quaternary Sciences, 23, 436–445. (in Chinese with an English abstract).
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Geochemical Investigation of Soil Quality in Huaihe River Wanjiang Economic Zone (121201236000160009) and Key R&D Program of Anhui Province, China (1804a0802203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, L., Liu, G. & Wu, D. Characteristics and provenance of hazardous trace elements in soil from a typical agricultural region in eastern Anhui, China. Geosci J 24, 575–584 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-019-0043-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-019-0043-6