Abstract
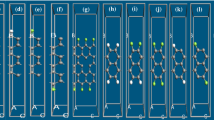
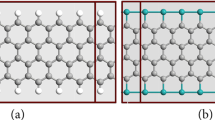
Gold-doped germanene nanoribbons (Au-GeNRs) are investigated for their potential as interconnects, using density functional theory combined with nonequilibrium Green’s function formalism. Various stable doping sites for both zigzag and armchair GeNRs (ZGeNR and AGeNR) are investigated. Based on formation energy (\(E_{{{\mathrm{FE}}}}\)) analysis, all considered Au-GeNRs are revealed to be thermodynamically stable. The analysis also shows that near-edge-doped ZGeNR (with \(E_{{{\mathrm{FE}}}} = -3.46\) eV) is the most stable configuration. It is shown through \(E-k\) structures and density-of-states profiles that Au-doping results in metallic GeNR irrespective of the edge states and ribbon width. To further explore the prospects for the use of Au-doped GeNR for interconnect applications, important small-signal dynamic parameters (including \(R_Q, L_K,\) and \(C_Q\)) for various doped configurations are explored. The present investigations also take into account the effect of bias voltage on \(R_Q, L_K, C_Q\). It is revealed that, with the exception of the edge-doped ZGeNR configuration, bias voltage has a prominent effect on these parameters for every configuration. Thus, edge-doped ZGeNR (with \(L_K = 4.41\) nH/\(\upmu \)m, \(C_Q = 4.21\) pF/cm) represents a potential candidate for nanoscale interconnect applications among the considered configurations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Carballo, W.J. Chan, P.A. Gargini, A.B. Kahng, and S. Nath, IEEE 32nd International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Seoul (2014), p. 139.
M. Chhowalla, D. Jena, and H. Zhang, Nat. Rev. Mat. 1, 16052 (2016).
W. Cao, J. Kang, D. Sarkar, W. Liu, and K. Banerjee, IEEE Trans. Elect. Dev. 62, 3459 (2015).
K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S.V. Dubonos, I.V. Grigorieva, and A.A. Firsov, Science 306, 666 (2004).
A.K. Geim and K.S. Novoselov, Nat. Mater. 6, 183 (2007).
R.R. Nair, P. Blake, A.N. Grigorenko, K.S. Novoselov, T.J. Booth, T. Stauber, N.M.R. Peres, and A.K. Geim, Science 320, 1308 (2008).
Y. Zhang, Y.W. Tan, H.L. Stormer, and P. Kim, Nature 438, 201 (2005).
K.F. Mak, C. Lee, J. Hone, J. Shan, and T.F. Heinz, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 136805 (2010).
D. Pacilé, J.C. Meyer, Ö. Girit, and A. Zettl, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 133107-1-3 (2008).
A. Carvalho, M. Wang, X. Zhu, A.S. Rodin, H. Su, and A.H. Neto, Nat. Rev. Mat. 1, 16061 (2016)
K. Takeda and K. Shiraishi, Phys. Rev. B 50, 14916 (1994).
S. Cahangirov, M. Topsakal, E. Aktürk, H. Şahin, and S. Ciraci, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 236804 (2009)
E. Bianco, S. Butler, S. Jiang, O.D. Restrepo, W. Windl, and J.E. Goldberger, ACS Nano 7, 4414 (2013).
Y. Du, J. Zhuang, J. Wang, Z. Li, H. Liu, J. Zhao, X. Xu, H. Feng, L. Chen, K. Wu, X. Wang, and S.X. Dou, Sci. Adv. 2(7), e1600067 (2016).
J. Zhuang, N. Gao, Z. Li, X. Xu, J. Wang, J. Zhao, S.X. Dou, and Y. Du, ACS Nano 11 (4), 3553 (2017).
J. Zhuang, C. Liu, Z. Zhao, Z. Li, G. Casillas, H. Feng, X. Xu, J. Wang, W. Hao, X. Wang, S.X. Dou, Z. Hu, and Y. Du, Adv. Sci. 5 (7), 1800207 (2018).
C-C. Liu, W. Feng, and Y. Yao, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 076802 (2011)
M. Houssa, E. Scalise, K. Sankaran, G. Pourtois, V.V. Afanaśev, and A. Stesmans, Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 223107 (2011).
S. Cahangirov, M. Topsakal, and S. Ciraci, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 195120 (2010).
Y. Ding and Y. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 083102 (2012).
Y.-L. Song, Y. Zhang, Y.-L. Zhang, and D.-B. Lu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 6313 (2010).
W. Xia, W. Hu, Z. Li, and J. Yang, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 22495 (2014).
V. Sharma, P. Srivastava, and N.K. Jaiswal, App. Surf. Sci. 396, 1352 (2017).
Z. Ni, Q. Liu, K. Tang, J. Zheng, J. Zhou, R. Qin, Z. Gao, D. Yu, and J. Lu, Nano Lett. 12 (1), 113 (2011).
Y. Du, J. Zhuang, H. Liu, X. Xu, S. Eilers, K. Wu, P. Cheng, J. Zhao, X. Pi, K. W. See, G. Peleckis, X. Wang, and S.X. Dou, ACS Nano 8 (10), 10019 (2014).
L. Tao, E. Cinquanta, D. Chiappe, C. Grazianetti, M. Fanciulli, M. Dubey, A. Molle, and D. Akinwande, Nat. Nanotechnol. 10, 227 (2015).
R. Vargas-Bernal, The Next generation of nanomaterials for designing analog integrated circuits, in Analog Circuits: Fundamentals, Synthesis and Performance(Nova Science Publishers, USA, Chapter 1, pp. 321, 2nd Quarter, April 2017).
A.H. Bayani, D. Dideban, M. Vali, and N. Moezi, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 31 (4), 045009-1-7 (2016).
A.H. Bayani, D. Dideban, and N. Moezi, J. Comput. Electr. 15 (2), 381 (2016).
A.H. Bayani, D. Dideban, and N. Moezi, Superlattices Microstruct. 100, 198 (2016).
H.F. Nejad, D. Dideban, A. Ketabi, D. Dideban, M. Vali, A.H. Bayani, and H. Heidari, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 80, 18 (2018).
N. Magen, A. Kolodny, U. Weiser, and N. Shamir, Proceedings of the 2004 International Workshop on System Level Interconnect Prediction (SLIP04) 966750, pp. 7–13 (2004).
K. Banerjee and A. Mehrotra, IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 49(11), 2001 (2002).
C. Xu, H. Li, and K. Banerjee, IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 56 (8), 1567 (2009).
H. Li, C. Xu, and K. Banerjee, IEEE Des. Test Comput. 27 (4), 20 (2010).
S. Yamacli, Comp. Mat. Sci. 141, 353 (2018).
V. Sharma, P. Srivastava, and N.K. Jaiswal, IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 65(9), 3893 (2018).
L. Banerjee, A. Sengupta, and H. Rahaman, IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 66(1), 664 (2019).
M. Dávila, L. Xian, S. Cahangirov, A. Rubio, and G.L. Lay, New J. Phys. 16, 095002 (2014).
M. Dávila and G.L. Lay, Sci. Rep. 6, 20714 (2016).
Atomistix ToolKit Virtual NanoLab (ATK-VNL), QuantumWise Simulator [Online]. Available: http://www.quantumwise.com/, version 2014.1.
H.J. Monkhorst and J.D. Pack, Phys. Rev. B 13, 5188 (1976).
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, and M. Ernzerhof, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865-1-4 (1996).
N.K. Jaiswal and P. Srivastava, IEEE. Trans. Nanotechnol. 12, 685 (2013).
Y. Ding, Y. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 143115 (2013).
R. Vargas-Bernal, Performance Analysis of Interconnects based on Carbon Nanotubes for AMS/RF IC Design, (IGI Global, USA, Chapter 14, pp. 336363, 2015)
D. Das and H. Rahaman, Carbon Nanotube and Graphene Nanoribbon Interconnects, 1st edn. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, V., Srivastava, P. Probing Gold-Doped Germanene Nanoribbons for Nanoscale Interconnects Under DFT-NEGF Framework. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 3938–3946 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08104-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08104-y