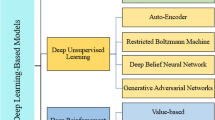
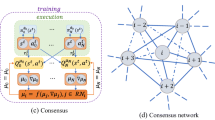
Abstract
In recent years, due to the drastic rise in the number of vehicles and the lack of sufficient infrastructure, traffic jams, air pollution, and fuel consumption have increased in cities. The optimization of timing for traffic lights is one of the solutions for the mentioned problems. Many methods have been introduced to deal with these problems, including reinforcement learning. Although a great number of learning-based methods have been used in traffic signal control, they suffer from poor performance and slow learning convergence. In this paper, a transfer learning-based method for traffic signal control has been proposed. Multi-agent system has also been used for modelling the traffic network and transfer learning has been used to make reinforcement learning agents transfer their experience to each other. Furthermore, a classifier has been utilized to classify the transferred experiences. The results show that using the proposed method leads to a significant improvement on average delay time and convergence time of the learning process.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Abdelghaffar HM, Yang H, Rakha HA (2016) Isolated traffic signal control using a game theoretic framework. In: 2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). IEEE, pp 1496–1501
Abdoos M, Mozayani N, Bazzan AL (2011) Traffic light control in non-stationary environments based on multi agent q-learning. In: 2011 14th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). IEEE, pp 1580–1585
Abdoos M, Mozayani N, Bazzan AL (2013) Holonic multi-agent system for traffic signals control. Eng Appl Artif Intell 26(5–6):1575–1587
Abdoos M, Mozayani N, Bazzan AL (2014) Hierarchical control of traffic signals using q-learning with tile coding. Appl Intell 40(2):201–213
Ammar HB, Eaton E, Taylor ME, Mocanu DC, Driessens K, Weiss G, Tuyls K (2014) An automated measure of MDP similarity for transfer in reinforcement learning. In: Workshops at the Twenty-Eighth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Banerjee B, Taylor ME (2018) Coordination confidence based human-multi-agent transfer learning for collaborative teams. In: AAMAS Adaptive Learning Agents (ALA) Workshop. sn
Brys T, Harutyunyan A, Taylor ME, Nowé A (2015) Policy transfer using reward shaping. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, pp 181–188
Da Silva FL, Costa AHR (2019) A survey on transfer learning for multiagent reinforcement learning systems. J Artif Intell Res 64:645–703
Ding D, Ding Z, Wei G, Han F (2019) An improved reinforcement learning algorithm based on knowledge transfer and applications in autonomous vehicles. Neurocomputing 361:243–255
Fachantidis A, Partalas I, Taylor ME, Vlahavas I (2015) Transfer learning with probabilistic mapping selection. Adapt Behav 23(1):3–19
Hou Y, Ong YS, Feng L, Zurada JM (2017) An evolutionary transfer reinforcement learning framework for multiagent systems. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 21(4):601–615
Li M, Dai Q (2018) A novel knowledge-leverage-based transfer learning algorithm. Appl Intell 48(8):2355–2372
Mannion P, Duggan J, Howley E (2016) An experimental review of reinforcement learning algorithms for adaptive traffic signal control. In: Autonomic road transport support systems. Springer, Birkhäuser, Cham, pp 47–66
Moshkov MJ (2005) Time complexity of decision trees. In: Transactions on rough sets III. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 244–459
Omidshafiei S, Kim DK, Liu M, Tesauro G, Riemer M, Amato C, Campbell M, How JP (2019) Learning to teach in cooperative multiagent reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol 33, pp 6128–6136
Prashanth LA, Bhatnagar S (2011) Reinforcement learning with function approximation for traffic signal control. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 12(2):412–421. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2010.2091408
Prashanth L, Bhatnagar S (2011) Reinforcement learning with average cost for adaptive control of traffic lights at intersections. In: 2011 14th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). IEEE, pp 1640–1645
Rosyadi AR, Wirayuda TAB, Al-Faraby S (2016) Intelligent traffic light control using collaborative q-learning algorithms. In: 2016 4th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology (ICoICT). IEEE, pp 1–6
Shoeleh F, Asadpour M (2017) Graph based skill acquisition and transfer learning for continuous reinforcement learning domains. Pattern Recognit Lett 87:104–116
Shoeleh F, Asadpour M (2019) Skill based transfer learning with domain adaptation for continuous reinforcement learning domains. Appl Intell 50(2):1–17
Taylor ME, Stone P (2007) Cross-domain transfer for reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML ’07. ACM, New York, pp 879–886
Taylor ME, Stone P (2009) Transfer learning for reinforcement learning domains: a survey. J Mach Learn Res 10:1633–1685
Taylor ME, Suay HB, Chernova S (2011) Integrating reinforcement learning with human demonstrations of varying ability. In: The 10th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, vol 2, pp 617–624
Thorpe TL, Anderson CW (1996) Traffic light control using sarsa with three state representations. Technical report, Citeseer
Wang Z, Taylor ME (2016) Effective transfer via demonstrations in reinforcement learning: a preliminary study. In: 2016 AAAI Spring Symposium Series
Zhang S, Taylor ME (2018) Enhanced learning from multiple demonstrations with a two-level structured approach. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS 2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norouzi, M., Abdoos, M. & Bazzan, A.L.C. Experience classification for transfer learning in traffic signal control. J Supercomput 77, 780–795 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03287-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03287-x