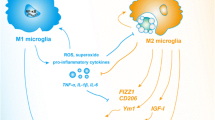
Abstract
Since microglia-associated neuroinflammation plays a pivotal role in the progression of white matter diseases, modulating microglial activation has been suggested as a potential therapeutic strategy. Here, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of fingolimod (FTY720) on microglia and analyzed the crosstalk between microglia autophagy and neuroinflammation. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced primary cultured microglia model was established. Microglial phenotypes were assessed by Western blot, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and flow cytometry. Autophagy was evaluated by immunofluorescence, MDC staining and Western blot. Rapamycin was used to investigate the role of autophagic process in regulating microglial phenotypes. The signaling markers were screened by RT-PCR and Western blot. FTY720 shifted microglial phenotype from pro-inflammatory state to anti-inflammatory state and inhibited microglial autophagy under lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment. Rapamycin reversed the effect of FTY720 on phenotype transformation of microglia. The results of mechanism studies have shown that FTY720 notably repressed LPS-induced STAT1 activity, which was reactivated by rapamycin. Our research suggested that FTY720 could significantly transform pro-inflammatory microglia into anti-inflammatory microglia by suppressing autophagy via STAT1.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araya J et al (2019) PRKN-regulated mitophagy and cellular senescence during COPD pathogenesis. Autophagy 15:510–526. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1532259
Biswas SK, Mantovani A (2010) Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: cancer as a paradigm. Nat Immunol 11:889–896. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1937
Blanc CA, Rosen H, Lane TE (2014) FTY720 (fingolimod) modulates the severity of viral-induced encephalomyelitis and demyelination. J Neuroinflamm 11:138. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-014-0138-y
Boche D, Perry VH, Nicoll JA (2013) Review: activation patterns of microglia and their identification in the human brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 39:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12011
Brinkmann V et al (2010) Fingolimod (FTY720): discovery and development of an oral drug to treat multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:883–897. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3248
Cadwell K (2016) Crosstalk between autophagy and inflammatory signalling pathways: balancing defence and homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol 16:661–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.100
Carta AR, Pisanu A (2013) Modulating microglia activity with PPAR-gamma agonists: a promising therapy for Parkinson's disease? Neurotoxicol Res 23:112–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-012-9342-7
Chang CP, Su YC, Lee PH, Lei HY (2013) Targeting NFKB by autophagy to polarize hepatoma-associated macrophage differentiation. Autophagy 9:619–621. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.23546
Chen ZH et al (2016) Autophagy is essential for ultrafine particle-induced inflammation and mucus hyperproduction in airway epithelium. Autophagy 12:297–311. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1124224
Chhor V et al (2013) Characterization of phenotype markers and neuronotoxic potential of polarised primary microglia in vitro. Brain Behav Immunity 32:70–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2013.02.005
Cipriani R, Chara JC, Rodriguez-Antiguedad A, Matute C (2015) FTY720 attenuates excitotoxicity and neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflamm 12:86. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0308-6
Cui L, Li C, Gao G, Zhuo Y, Yang L, Cui N, Zhang S (2019a) FTY720 inhibits the activation of pancreatic stellate cells by promoting apoptosis and suppressing autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Life Sci 217:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.12.019
Dai J, Zhang X, Li L, Chen H, Chai Y (2017) Autophagy inhibition contributes to ROS-producing NLRP3-dependent inflammasome activation and cytokine secretion in high glucose-induced macrophages. Cell Physiol Biochem 43:247–256. https://doi.org/10.1159/000480367
Das A et al (2016) Transcriptome sequencing reveals that LPS-triggered transcriptional responses in established microglia BV2 cell lines are poorly representative of primary microglia. J Neuroinflamm 13:182. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0644-1
Das A, Arifuzzaman S, Kim SH, Lee YS, Jung KH, Chai YG (2017) FTY720 (fingolimod) regulates key target genes essential for inflammation in microglial cells as defined by high-resolution mRNA sequencing. Neuropharmacology 119:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.03.034
Fu Y et al (2014) Fingolimod for the treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage: a 2-arm proof-of-concept study. JAMA Neurol 71:1092–1101. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.1065
Fu Y, Liu Q, Anrather J, Shi FD (2015) Immune interventions in stroke. Nat Rev Neurol 11:524–535. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2015.144
Hu X et al (2012) Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics reveal novel mechanism of injury expansion after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 43:3063–3070. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.112.659656
Hu X et al (2014) Neurobiology of microglial action in CNS injuries: receptor-mediated signaling mechanisms and functional roles. Prog Neurobiol 119–120:60–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2014.06.002
Hughes R et al (2018) Oral fingolimod for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (FORCIDP trial): a double-blind, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 17:689–698. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(18)30202-3
Jiang P, Mizushima N (2015) LC3- and p62-based biochemical methods for the analysis of autophagy progression in mammalian cells. Methods (San Diego, Calif) 75:13–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.11.021
Kim KH, Lee MS (2014) Autophagy—a key player in cellular and body metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol 10:322–337. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2014.35
Lee JW et al (2019) TLR4 (toll-like receptor 4) activation suppresses autophagy through inhibition of FOXO3 and impairs phagocytic capacity of microglia. Autophagy 15:753–770. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1556946
Levine B, Kroemer G (2008) Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell 132:27–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.018
Li J, Kim SG, Blenis J (2014) Rapamycin: one drug, many effects. Cell Metab 19:373–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.01.001
Li X, Wang M-H, Qin C, Fan W-H, Tian D-S, Liu J-L (2017) Fingolimod suppresses neuronal autophagy through the mTOR/p70S6K pathway and alleviates ischemic brain damage in mice. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188748
Mecha M, Feliu A, Carrillo-Salinas FJ, Rueda-Zubiaurre A, Ortega-Gutierrez S, de Sola RG, Guaza C (2015) Endocannabinoids drive the acquisition of an alternative phenotype in microglia. Brain Behav Immun 49:233–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.06.002
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Levine B (2010) Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell 140:313–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.028
Nazio F et al (2013) mTOR inhibits autophagy by controlling ULK1 ubiquitylation, self-association and function through AMBRA1 and TRAF6. Nat Cell Biol 15:406–416. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2708
Neumann H, Kotter MR, Franklin RJ (2009) Debris clearance by microglia: an essential link between degeneration and regeneration. Brain 132:288–295. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awn109
Noda H, Takeuchi H, Mizuno T, Suzumura A (2013) Fingolimod phosphate promotes the neuroprotective effects of microglia. J Neuroimmunol 256:13–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2012.12.005
Patel AR, Ritzel R, McCullough LD, Liu F (2013) Microglia and ischemic stroke: a double-edged sword. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 5:73–90
Pratt J, Annabi B (2014) Induction of autophagy biomarker BNIP3 requires a JAK2/STAT3 and MT1-MMP signaling interplay in Concanavalin-A-activated U87 glioblastoma cells. Cell Signal 26:917–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.012
Qin C et al (2017) Fingolimod protects against ischemic white matter damage by modulating microglia toward M2 polarization via STAT3 pathway. Stroke 48:3336–3346. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.117.018505
Qin C et al (2018) Microglial TLR4-dependent autophagy induces ischemic white matter damage via STAT1/6 pathway. Theranostics 8:5434–5451. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.27882
Rothhammer V et al (2017) Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulation suppresses pathogenic astrocyte activation and chronic progressive CNS inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:2012–2017. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1615413114
Saijo K, Glass CK (2011) Microglial cell origin and phenotypes in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11:775–787. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3086
Shi H, Wang J, Wang J, Huang Z, Yang Z (2018) IL-17A induces autophagy and promotes microglial neuroinflammation through ATG5 and ATG7 in intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neuroimmunol 323:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2017.07.015
Su P, Zhang J, Wang D, Zhao F, Cao Z, Aschner M, Luo W (2016) The role of autophagy in modulation of neuroinflammation in microglia. Neuroscience 319:155–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.01.035
Varnum MM, Ikezu T (2012) The classification of microglial activation phenotypes on neurodegeneration and regeneration in Alzheimer's disease brain. Arch Immunol et Ther Exp 60:251–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-012-0181-2
Wang XL, Qiao CM, Liu JO, Li CY (2017) Inhibition of the SOCS1-JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway confers neuroprotection in rats with ischemic stroke. Cell Physiol Biochem 44:85–98. https://doi.org/10.1159/000484585
Wei Y et al (2011) Fingolimod provides long-term protection in rodent models of cerebral ischemia. Ann Neurol 69:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22186
Yang D et al (2014a) Blocking lymphocyte trafficking with FTY720 prevents inflammation-sensitized hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in newborns. J Neurosci 34:16467–16481. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2582-14.2014
Yang Z, Zhang N, Shen H, Lin C, Lin L, Yuan B (2014b) Microglial activation with reduction in autophagy limits white matter lesions and improves cognitive defects during cerebral hypoperfusion. Curr Neurovasc Res 11:223–229
Yang Z et al (2015a) Toll-like receptor-4-mediated autophagy contributes to microglial activation and inflammatory injury in mouse models of intracerebral haemorrhage. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 41:e95–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12177
Yang Z, Zhong L, Zhong S, Xian R, Yuan B (2015b) Hypoxia induces microglia autophagy and neural inflammation injury in focal cerebral ischemia model. Exp Mol Pathol 98:219–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2015.02.003
Yenari MA, Kauppinen TM, Swanson RA (2010) Microglial activation in stroke: therapeutic targets. Neurotherapeutics 7:378–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2010.07.005
Yorimitsu T, Klionsky DJ (2005) Autophagy: molecular machinery for self-eating. Cell Death Differ 12(Suppl 2):1542–1552. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401765
Yu Z, Sun D (2015) MSX3 switches microglia polarization and protects from inflammation-induced. Demyelination 35:6350–6365. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2468-14.2015
Zhang SQ, Ding FF, Liu Q, Tian YY, Wang W, Qin C (2019) Autophagy inhibition exerts neuroprotection on white matter ischemic damage after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in mice. Brain Res 1721:146337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146337
Zhu Z et al (2015) Combination of the immune modulator fingolimod with alteplase in acute ischemic stroke: a pilot trial. Circulation 132:1104–1112. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.016371
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81571132, 81873743 to D.S., Tian, 81801223 to C. Qin) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2017KFYXJJ107 to D.S. Tian, 2017KFYXJJ124 to C. Qin)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, ZW., Zhou, LQ., Yang, S. et al. FTY720 Modulates Microglia Toward Anti-inflammatory Phenotype by Suppressing Autophagy via STAT1 Pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41, 353–364 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00856-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00856-9