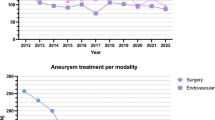
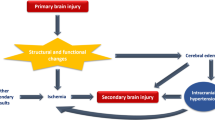
Abstract
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension denotes raised intracranial pressure in the absence of an identifiable cause and presents with symptoms relating to elevated ICP, namely headaches and visual deterioration. Treatment of IIH aims at reducing intracranial pressure, relieving headache and salvaging patients’ vision. Surgical interventions are recommended for medically refractory IIH and include CSF diversion techniques, optic nerve sheath fenestration, bariatric surgery and venous sinus stenting. Prospective studies on the surgical options for IIH are scant and no evidence-based guidelines for the surgical management of medically refractory IIH have been established. A search in Cochrane Library, MEDLINE and EMBASE from 1 January 1985 to 19 April 2019 for controlled or observational studies on the surgical treatment of IIH (defined in accordance with the modified Dandy or the modified Friedman criteria) in adults yielded 109 admissible studies. VSS improved papilledema, visual fields and headaches in 87.1%, 72.7% and 72.1% of the patients respectively, with a 2.3% severe complication rate and 11.3% failure rate. CSF diversion techniques diminished papilledema, visual field deterioration and headaches in 78.9%, 66.8% and 69.8% of the cases and are associated with a 9.4 severe complication rate and a 43.4% failure rate. ONSF ameliorated papilledema, visual field defects and headaches in 90.5, 65.2% and 49.3% of patients. Severe complication rate was 2.2% and failure rate was 9.4%. This is currently the largest systematic review for the available operative modalities for IIH. VSS provided the best results in headache resolution and visual outcomes, with low failure rates and a very favourable complication profile. In light of this, VSS ought to be regarded as the first-line surgical modality for the treatment of medically refractory IIH.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham MG (2017) Unique variant of idiopathic intracranial hypertension dural sinus stenting, 10th annual meeting. 5th Annual Stroke Center Workshop. Society of Vascular and Interventional Neurology November 8–11, 2017, Boston, MA: Abstracts. Interv Neurol 6(suppl 1):1–130. https://doi.org/10.1159/000477925
Abu-Serieh B, Ghassempour K, Duprez T, Raftopoulos C (2007) Stereotactic ventriculoperitoneal shunting for refractory idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurosurgery 60:1039–1043; discussion 1043-1034. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000255456.12978.31
Abubaker K, Ali Z, Raza K, Bolger C, Rawluk D, O’Brien D (2011) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: lumboperitoneal shunts versus ventriculoperitoneal shunts-case series and literature review. Br J Neurosurg 25:94–99. https://doi.org/10.3109/02688697.2010.544781
Acheson JF, Green WT, Sanders MD (1994) Optic nerve sheath decompression for the treatment of visual failure in chronic raised intracranial pressure. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:1426–1429. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.57.11.1426
Aguilar-Pérez M, Martinez-Moreno R, Kurre W, Wendl C, Bäzner H, Ganslandt O, Unsöld R, Henkes H (2017) Endovascular treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension: retrospective analysis of immediate and long-term results in 51 patients. Neuroradiology 59:277–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1783-5
Ahmed RM, Wilkinson M, Parker GD, Thurtell MJ, Macdonald J, McCluskey PJ, Allan R, Dunne V, Hanlon M, Owler BK, Halmagyi GM (2011) Transverse sinus stenting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a review of 52 patients and of model predictions. Am J Neuroradiol 32:1408–1414. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.a2575
Al Abdulsalam H, Ajlan A (2017) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension in males. Neurosciences 22:220–223. https://doi.org/10.17712/nsj.2017.3.20170005
Albuquerque FC, Dashti SR, Hu YC, Newman CB, Teleb M, McDougall CG, Rekate HL (2011) Intracranial venous sinus stenting for benign intracranial hypertension: clinical indications, technique, and preliminary results. World Neurosurg 75:648–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2010.11.012
Alkherayf F, Abou Al-Shaar H, Awad M (2015) Management of idiopathic intracranial hypertension with a programmable lumboperitoneal shunt: early experience. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 136:5–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2015.05.018
Alnemari A, Mansour TR, Gregory S, Miller WK, Buehler M, Gaudin D (2017) Chiari I malformation with underlying pseudotumor cerebri: poor symptom relief following posterior decompression surgery. Int J Surg Case Rep 38:136–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijscr.2017.07.039
Alsuhaibani AH, Carter KD, Nerad JA, Lee AG (2011) Effect of optic nerve sheath fenestration on papilledema of the operated and the contralateral nonoperated eyes in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Ophthalmology 118:412–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2010.06.025
Arac A, Lee M, Steinberg GK, Marcellus M, Marks MP (2009) Efficacy of endovascular stenting in dural venous sinus stenosis for the treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurosurg Focus 27:E14. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.9.focus09165
Asif H, Craven CL, Siddiqui AH, Shah SN, Matloob SA, Thorne L, Robertson F, Watkins LD, Toma AK (2018) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: 120-day clinical, radiological, and manometric outcomes after stent insertion into the dural venous sinus. J Neurosurg 129:723–731. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.4.JNS162871
Banta JT, Farris BK (2000) Pseudotumor cerebri and optic nerve sheath decompression. Ophthalmology 107:1907–1912. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-6420(00)00340-7
Bedford THB (1935) The effect of increased intracranial venous pressure on the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid. Brain 58:427–447. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/58.4.427
Bersani TA, Meeker AR, Sismanis DN, Carruth BP (2016) Pediatric and adult vision restoration after optic nerve sheath decompression for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Orbit 35:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1080/01676830.2016.1176051
Bhandohal JS, Mirza T (2017) BLIND OVERNIGHT: a case of fulminant idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Am J Emerg Med 35:1581.e1581–1581.e1582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2017.07.021
Bjornson A, Tapply I, Nabbanja E, Lalou AD, Czosnyka M, Czosnyka Z, Muthusamy B, Garnett M (2019) Ventriculo-peritoneal shunting is a safe and effective treatment for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Br J Neurosurg 33:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1080/02688697.2018.1538478
Bonfield CM, Weiner GM, Bradley MS, Engh JA (2015) Vaginal extrusion of a ventriculo-peritoneal shunt catheter in an adult. J Neurosci Rural Pract 6:97–99. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-3147.143212
Boulton M, Armstrong D, Flessner M, Hay J, Szalai JP, Johnston M (1998) Raised intracranial pressure increases CSF drainage through arachnoid villi and extracranial lymphatics. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys 275:R889–R896. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1998.275.3.r889
Brourman ND, Spoor TC, Ramocki JM (1988) Optic nerve sheath decompression for pseudotumor cerebri. Arch Ophthalmol 106:1378–1383. https://doi.org/10.1001/archopht.1988.01060140542020
Bruce BB, Kedar S, Van Stavern GP, Monaghan D, Acierno MD, Braswell RA, Preechawat P, Corbett JJ, Newman NJ, Biousse V (2008) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension in men. Neurology 72:304–309. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000333254.84120.f5
Burgett RA, Purvin VA, Kawasaki A (1997) Lumboperitoneal shunting for pseudotumor cerebri. Neurology 49:734–739. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.49.3.734
Bussière M, Falero R, Nicolle D, Proulx A, Patel V, Pelz D (2009) Unilateral transverse sinus stenting of patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Am J Neuroradiol 31:645–650. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.a1890
Bynke G, Zemack G, Bynke H, Romner B (2004) Ventriculoperitoneal shunting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology 63:1314–1316. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000140699.43019.48
Cappuzzo JM, Hess RM, Morrison JF, Davies JM, Snyder KV, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH (2018) Transverse venous stenting for the treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension, or pseudotumor cerebri. Neurosurg Focus 45:E11. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.5.FOCUS18102
Carlow TJ (1974) Pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus. JAMA 228:197–200. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.228.2.197
Cazzo E, Gestic MA, Utrini MP, Mendonca Chaim FD, Mendonca Chaim FH, Candido EC, da Silveira Jarolavsky LB, de Almeida AMN, Pareja JC, Chaim EA (2018) Bariatric surgery as a treatment for pseudotumor cerebri: case study and narrative review of the literature. Sao Paulo medical journal. Rev Paul Med 136:182–187. https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-3180.2016.0305060117
Chandrasekaran S, McCluskey P, Minassian D, Assaad N (2006) Visual outcomes for optic nerve sheath fenestration in pseudotumour cerebri and related conditions. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 34:661–665. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9071.2006.01301.x
Chowdhury HR, Rajak S, Heath D, Brittain P (2015) Optical coherence tomography imaging of the optic nerve head pre optic and post optic nerve sheath fenestration. BMJ Case Rep:bcr2014204511. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2014-204511
Corbett JJ (1988) Results of optic nerve sheath fenestration for pseudotumor cerebri. Arch Ophthalmol 106:1391. https://doi.org/10.1001/archopht.1988.01060140555022
Corbett JJ, Thompson HS (1989) The rational management of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Arch Neurol 46:1049–1051. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1989.00520460025008
Crawford A, McGrath NM (2010) Hearing loss after lumbar puncture. J Clin Neurosci 17:149–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2009.04.006
Crosa R, Marabotto O, Meehroff G, Legnani C, Boschi J, Negrotto A, Terbrugge KG, Lasjaunias P (2007) Pseudotumor cerebri: a new door opens for treatment. Interv Neuroradiol 13:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1177/159101990701300204
Dandy WE (1937) Intracranial pressure without brain tumor: diagnosis and treatment. Ann Surg 106:492–513. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-193710000-00002
Ding D, Chen C-J, Starke RM, Liu KC, Crowley RW (2015) Rapid recovery of bilateral abducens nerve palsies after venous sinus stenting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neurol Sci 357:335–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2015.07.047
Dinkin MJ, Patsalides A (2017) Venous sinus stenting in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neuroophthalmol 37:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1097/wno.0000000000000426
Donnet A, Metellus P, Levrier O, Mekkaoui C, Fuentes S, Dufour H, Conrath J, Grisoli F (2008) Endovascular treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension: clinical and radiologic outcome of 10 consecutive patients. Neurology 70:641–647. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000299894.30700.d2
Ducruet AF, Crowley RW, McDougall CG, Albuquerque FC (2013) Long-term patency of venous sinus stents for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neurointerv Surg 6:238–242. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010691
Durcan FJ, Corbett JJ, Wall M (1988) The incidence of pseudotumor cerebri. Arch Neurol 45:875. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1988.00520320065016
Egan RJ, Meredith HE, Coulston JE, Bennetto L, Morgan JDT, Norton SA (2010) The effects of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding on idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Obes Surg 21:161–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-010-0307-8
Eggenberger ER, Miller NR, Vitale S (1996) Lumboperitoneal shunt for the treatment of pseudotumor cerebri. Neurology 46:1524–1530. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.46.6.1524
El-Saadany WF, Farhoud A, Zidan I (2011) Lumboperitoneal shunt for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: patients’ selection and outcome. Neurosurg Rev 35:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-011-0350-5
El Mekabaty A, Obuchowski NA, Luciano MG, John S, Chung CY, Moghekar A, Jones S, Hui FK (2017) Predictors for venous sinus stent retreatment in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neurointerv Surg 9:1228–1232. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012803
Elder BD, Rory Goodwin C, Kosztowski TA, Radvany MG, Gailloud P, Moghekar A, Subramanian PS, Miller NR, Rigamonti D (2015) Venous sinus stenting is a valuable treatment for fulminant idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Clin Neurosci 22:685–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2014.10.012
Elsaadany WF, Farhoud AH, Achmawi GA, Mousa WM, Shahin MS (2015) Clinical spectrum and management of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurosurg Q 25:374–380. https://doi.org/10.1097/wnq.0000000000000064
Esfahani DR, Stevenson M, Moss HE, Amin-Hanjani S, Aletich V, Jain S, Charbel FT, Alaraj A (2015) Quantitative magnetic resonance venography is correlated with intravenous pressures before and after venous sinus stenting. Neurosurgery 77:254–260. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000000771
Fagan LH, Ferguson S, Yassari R, Frim DM (2006) The Chiari pseudotumor cerebri syndrome: symptom recurrence after decompressive surgery for Chiari malformation type I. Pediatr Neurosurg 42:14–19. https://doi.org/10.1159/000089504
Farb RI, Vanek I, Scott JN, Mikulis DJ, Willinsky RA, Tomlinson G, terBrugge KG (2003) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: the prevalence and morphology of sinovenous stenosis. Neurology 60:1418–1424. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000066683.34093.e2
Fields JD, Javedani PP, Falardeau J, Nesbit GM, Dogan A, Helseth EK, Liu KC, Barnwell SL, Petersen BD (2011) Dural venous sinus angioplasty and stenting for the treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neurointerv Surg 5:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2011-010156
Friedman DI, Jacobson DM (2002) Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology 59:1492–1495. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000029570.69134.1b
Friedman DI, Liu GT, Digre KB (2013) Revised diagnostic criteria for the pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in adults and children. Neurology 81:1159–1165. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182a55f17
Galvin JA, Van Stavern GP (2004) Clinical characterization of idiopathic intracranial hypertension at the Detroit Medical Center. J Neurol Sci 223:157–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2004.05.009
Gardner K, Cox T, Digre KB (1995) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension associated with tetracycline use in fraternal twins. Neurology 45:6–10. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.45.1.6
Giuseffi V, Wall M, Siegel PZ, Rojas PB (1991) Symptoms and disease associations in idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri): a case-control study. Neurology 41:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.41.2_part_1.239
Goh KY, Schatz NJ, Glaser JS (1997) Optic nerve sheath fenestration for pseudotumor cerebri. J Neuroophthalmol 17:86–91. https://doi.org/10.1097/00041327-199706000-00003
Goodwin CR, Elder BD, Ward A, Orkoulas-Razis D, Kosztowski TA, Hoffberger J, Moghekar A, Radvany M, Rigamonti D (2014) Risk factors for failed transverse sinus stenting in pseudotumor cerebri patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 127:75–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2014.09.015
Gross BA, Albuquerque FC, Moon K, McDougall CG (2016) New frontiers in venous sinus stenting: illustrative cases. J Clin Neurosci 33:241–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2016.05.032
Hammers R, Prabhu VC, Sarker S, Jay WM (2008) Laparoscopic-assisted lumboperitoneal shunt placement for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Semin Ophthalmol 23:151–155. https://doi.org/10.1080/08820530802007333
Hermann EJ, Polemikos M, Heissler HE, Krauss JK (2017) Shunt surgery in idiopathic intracranial hypertension aided by electromagnetic navigation. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 95:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1159/000453277
Hickman SJ, Raoof N, Panesar H, McMullan JM, Pepper IM, Sharrack B (2014) Visual outcomes from shunting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neuro-Ophthalmology 38:310–319. https://doi.org/10.3109/01658107.2014.956183
Higgins JNP (2003) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: 12 cases treated by venous sinus stenting. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:1662–1666. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.74.12.1662
Higgins N, Pickard J, Lever A (2015) Borderline intracranial hypertension manifesting as chronic fatigue syndrome treated by venous sinus stenting. J Neurol Surg Rep 76:e244–e247. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1564060
Hoffmann J, Mollan SP, Paemeleire K, Lampl C, Jensen RH, Sinclair AJ (2018) European headache federation guideline on idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Headache Pain 19:93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10194-018-0919-2
Huang LC, Winter TW, Herro AM, Rosa PR, Schiffman JC, Pasol J, Trombly RS, Tawfik M, Lam BL (2014) Ventriculoperitoneal shunt as a treatment of visual loss in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neuroophthalmol 34:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1097/wno.0000000000000106
Kalyvas A, Vlachos K, Abu-Amara M, Sampalis J, Glantzounis G (2014) Bariatric surgery as metabolic surgery for diabetic patients. Curr Pharm Des 20:3631–3646. https://doi.org/10.2174/13816128113196660672
Kalyvas AV, Liouta E, Komaitis S, Anagnostopoulos C, Stranjalis G (2016a) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical features and contemporary management. Hosp Chron 11(2), 77–84. https://doi.org/10.2015/hc.v11i2.749
Kalyvas AV, Hughes M, Koutsarnakis C, Moris D, Liakos F, Sakas DE, Stranjalis G, Fouyas I (2016b) Efficacy, complications and cost of surgical interventions for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a systematic review of the literature. Acta Neurochir 159:33–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-3010-2
Karahalios DG, Rekate HL, Khayata MH, Apostolides PJ (1996) Elevated intracranial venous pressure as a universal mechanism in pseudotumor cerebri of varying etiologies. Neurology 46:198–202. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.46.1.198
Kelman SE, Heaps R, Wolf A, Elman MJ (1992) Optic nerve decompression surgery improves visual function in patients with pseudotumor cerebri. Neurosurgery 30:391–395. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199203000-00013
Keltner JL, Johnson CA, Cello KE, Wall M (2014) Baseline visual field findings in the idiopathic intracranial hypertension treatment trial (IIHTT). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 55:3200–3207. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.14-14243
Kesler A, Hadayer A, Goldhammer Y, Almog Y, Korczyn AD (2004) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: risk of recurrences. Neurology 63:1737–1739. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000143067.40281.16
Kessler LA, Novelli PM, Reigel DH (1998) Surgical treatment of benign intracranial hypertension—subtemporal decompression revisited. Surg Neurol 50:73–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0090-3019(97)00359-5
Knapp CM, Sampath R (2005) Optic nerve sheath fenestration: a five year audit. Neuro-Ophthalmology 29:173–177. https://doi.org/10.1080/01658100500481438
Koovor JM, Lopez GV, Riley K, Tejada J (2018) Transverse venous sinus stenting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: safety and feasibility. Neuroradiol J 31:513–517. https://doi.org/10.1177/1971400918782320
Kumpe DA, Bennett JL, Seinfeld J, Pelak VS, Chawla A, Tierney M (2012) Dural sinus stent placement for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neurosurg 116:538–548. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.10.jns101410
Kumpe DA, Seinfeld J, Huang X, Mei Q, Case DE, Roark CD, Subramanian PS, Lind KE, Pelak VS, Bennett JL (2016) Dural sinus stenting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: factors associated with hemodynamic failure and management with extended stenting. J Neurointerv Surg 9:867–874. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012810
Lai LT, Danesh-Meyer HV, Kaye AH (2014) Visual outcomes and headache following interventions for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Clin Neurosci 21:1670–1678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2014.02.025
Lavoie P, Audet M-È, Gariepy J-L, Savard M, Verreault S, Gourdeau A, Milot G, Carrondo Cottin S (2017) Severe cerebellar hemorrhage following transverse sinus stenting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Interv Neuroradiol 24:100–105. https://doi.org/10.1177/1591019917734389
Lazzaro MA, Darkhabani Z, Remler BF, Hong SH, Wolfe TJ, Zaidat OO, Fitzsimmons B-F (2012) Venous sinus pulsatility and the potential role of dural incompetence in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurosurgery 71:877–884. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0b013e318267a8f9
Lenck S, Vallee F, Labeyrie MA, Touitou V, Saint-Maurice JP, Guillonnet A, Tantot A, Crassard I, Bernat AL, Houdart E (2017) Stenting of the lateral sinus in idiopathic intracranial hypertension according to the type of stenosis. Neurosurgery 80:393–400. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000001261
Levin AA, Hess D, Hohler AD (2014) Treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension with gastric bypass surgery. Int J Neurosci 125:78–80. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2014.898144
Levitt MR, Albuquerque FC, Ducruet AF, Kalani MYS, Mulholland CB, McDougall CG (2015) Venous sinus stenting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension is not associated with cortical venous occlusion. J Neurointerv Surg 8:594–595. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2015-011692
Libien J, Blaner WS (2007) Retinol and retinol-binding protein in cerebrospinal fluid: can vitamin a take the “idiopathic” out of idiopathic intracranial hypertension? J Neuroophthalmol 27:253–257. https://doi.org/10.1097/wno.0b013e31815c44bc
Liu KC, Starke RM, Durst CR, Wang TR, Ding D, Crowley RW, Newman SA (2017) Venous sinus stenting for reduction of intracranial pressure in IIH: a prospective pilot study. J Neurosurg 127:1126–1133. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.8.jns16879
Liu X, Di H, Wang J, Cao X, Du Z, Zhang R, Yu S, Li B (2019) Endovascular stenting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension with venous sinus stenosis. Brain Behav 9:e01279. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.1279
Madriz Peralta G, Cestari DM (2018) An update of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 29:495–502. https://doi.org/10.1097/ICU.0000000000000518
Maher CO, Garrity JA, Meyer FB (2001) Refractory idiopathic intracranial hypertension treated with stereotactically planned ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement. Neurosurg Focus 10:1–4. https://doi.org/10.3171/foc.2001.10.2.2
Mancera N, Murr MM, Drucker M (2018) Bariatric surgery and its impact on pseudotumor cerebri: a case report. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep 10:68–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajoc.2018.01.047
Markey KA, Mollan SP, Jensen RH, Sinclair AJ (2016) Understanding idiopathic intracranial hypertension: mechanisms, management, and future directions. Lancet Neurol 15:78–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00298-7
Matloob SA, Toma AK, Thompson SD, Gan CL, Robertson F, Thorne L, Watkins LD (2017) Effect of venous stenting on intracranial pressure in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Acta Neurochir 159:1429–1437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3229-6
Matloob SA, Toma AK, Thorne L, Watkins LD (2015) Surgically managed idiopathic intracranial hypertension in adults: a single centre experience. Acta Neurochir 157:2099–2103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2600-8
McGirt MJ, Woodworth G, Thomas G, Miller N, Williams M, Rigamonti D (2004) Cerebrospinal fluid shunt placement for pseudotumor cerebri—associated intractable headache: predictors of treatment response and an analysis of long-term outcomes. J Neurosurg 101:627–632. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2004.101.4.0627
Mei QY, Xiao WZ, Chen HR, Bai RL, Sun KH, Hou LJ (2012) Which is the best peri-operative anti-coagulative therapy of transverse sinus stenting for refractory idiopathic intracranial hypertension? Chin Med J 125:2951–2953
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Moreau A, Lao KC, Farris BK (2014) Optic nerve sheath decompression. J Neuroophthalmol 34:34–38. https://doi.org/10.1097/wno.0000000000000065
Moura FC, Fortini I (2017) Optociliary shunt vessels: role in diagnosis and treatment of atypical pseudotumor cerebri. Neuro-Ophthalmology 41:224–226. https://doi.org/10.1080/01658107.2017.1304967
Nadkarni T, Rekate HL, Wallace D (2004) Resolution of pseudotumor cerebri after bariatric surgery for related obesity. Case report. J Neurosurg 101:878–880. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2004.101.5.0878
Naqvi SMA, Thiagarajah C, Golnik K, Lee A, Kersten R, Nerad J (2013) Optic nerve cyst-like formation presenting as a delayed complication of optic nerve sheath fenestration. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg:1. https://doi.org/10.1097/iop.0b013e31829bb3e8
Noetzel MJ, Rioux SD (1986) Pseudotumor cerebri associated with obstructive nephropathy. Pediatr Neurol 2:238–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/0887-8994(86)90055-x
Obi EE, Lakhani BK, Burns J, Sampath R (2017) Corrigendum to “optic nerve sheath fenestration for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a seven year review of visual outcomes in a tertiary centre” [Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 137 (October) (2015) 94–101]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 159:114–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2017.02.008
Ogungbo B, Roy D, Gholkar A, Mendelow AD (2003) Endovascular stenting of the transverse sinus in a patient presenting with benign intracranial hypertension. Br J Neurosurg 17:565–568. https://doi.org/10.1080/02688690310001627821
Okoroafor F, Karim MA, Ali A (2019) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension and bariatric surgery: a literature review and a presentation of two cases. Br J Neurosurg 33:112–114. https://doi.org/10.1080/02688697.2018.1427211
Owler BK, Parker G, Halmagyi GM, Dunne VG, Grinnell V, McDowell D, Besser M (2003) Pseudotumor cerebri syndrome: venous sinus obstruction and its treatment with stent placement. J Neurosurg 98:1045–1055. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2003.98.5.1045
Paquet C, Poupardin M, Boissonnot M, Neau JP, Drouineau J (2008) Efficacy of unilateral stenting in idiopathic intracranial hypertension with bilateral venous sinus stenosis. Eur Neurol 60:47–48. https://doi.org/10.1159/000131712
Patsalides A, Oliveira C, Wilcox J, Brown K, Grover K, Gobin YP, Dinkin MJ (2019) Venous sinus stenting lowers the intracranial pressure in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neurointerv Surg 11:175–178. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2018-014032
Pineles SL, Volpe NJ (2013) Long-term results of optic nerve sheath fenestration for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: earlier intervention favours improved outcomes. Neuro-Ophthalmology 37:12–19. https://doi.org/10.3109/01658107.2012.757787
Piper RJ, Kalyvas AV, Young AMH, Hughes MA, Jamjoom AAB, Fouyas IP (2015) Interventions for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd003434.pub3
Plotnik JL, Kosmorsky GS (1993) Operative complications of optic nerve sheath decompression. Ophthalmology 100:683–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-6420(93)31588-5
Polemikos M, Heissler HE, Hermann EJ, Krauss JK (2017) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension in monozygotic female twins: intracranial pressure dynamics and treatment outcome. World Neurosurg 101:814.e811–814.e814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.03.004
Prabhakaran V, Selva D (2009) Vertical lid split approach for optic nerve sheath decompression. Indian J Ophthalmol 57:305–306. https://doi.org/10.4103/0301-4738.53057
Radhakrishnan K, Thacker AK, Bohlaga NH, Maloo JC, Gerryo SE (1993) Epidemiology of idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a prospective and case-control study. J Neurol Sci 116:18–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-510x(93)90084-c
Radvany MG, Solomon D, Nijjar S, Subramanian PS, Miller NR, Rigamonti D, Blitz A, Gailloud P, Moghekar A (2013) Visual and neurological outcomes following endovascular stenting for pseudotumor cerebri associated with transverse sinus stenosis. J Neuroophthalmol 33:117–122. https://doi.org/10.1097/wno.0b013e31827f18eb
Raper D, Buell TJ, Ding D, Chen C-J, Starke RM, Liu KC (2017) Pattern of pressure gradient alterations after venous sinus stenting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension predicts stent-adjacent stenosis: a proposed classification system. J Neurointerv Surg 10:391–395. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2017-013135
Rizzo JL, Lam KV, Wall M, Wilson MD, Keltner JL (2015) Perimetry, retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and papilledema grade after cerebrospinal fluid shunting in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neuroophthalmol 35:22–25. https://doi.org/10.1097/wno.0000000000000181
Rosenberg ML, Corbett JJ, Smith C, Goodwin J, Sergott R, Savino P, Schatz N (1993) Cerebrospinal fluid diversion procedures in pseudotumor cerebri. Neurology 43:1071–1072. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.43.6.1071
Roth J, Constantini S, Kesler A (2015) Over-drainage and persistent shunt-dependency in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension treated with shunts and bariatric surgery. Surg Neurol Int 6:S655–S660. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.171230
Satti SR, Leishangthem L, Chaudry MI (2015) Meta-analysis of CSF diversion procedures and dural venous sinus stenting in the setting of medically refractory idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Am J Neuroradiol 36:1899–1904. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.a4377
Satti SR, Leishangthem L, Spiotta A, Chaudry MI (2017) Dural venous sinus stenting for medically and surgically refractory idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Interv Neuroradiol 23:186–193. https://doi.org/10.1177/1591019916680110
Sergott RC, Savino PJ, Bosley TM (1988) Modified optic nerve sheath decompression provides long-term visual improvement for pseudotumor cerebri. Arch Ophthalmol 106:1384–1390. https://doi.org/10.1001/archopht.1988.01060140548021
Shapiro S, Yee R, Brown H (1995) Surgical management of pseudotumor cerebri in pregnancy. Neurosurgery 37:829–831. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199510000-00031
Shields LBE, Shields CB, Yao TL, Plato BM, Zhang YP, Dashti SR (2019) Endovascular treatment for venous sinus stenosis in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: an observational study of clinical indications, surgical technique, and long-term outcomes. World Neurosurg 121:e165–e171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.09.070
Silva J, Conti M, Aguiar G, Jory M, Monzillo P, Veiga J (2017) Endovascular treatment for idiopathic intracranial hypertension improves clinical symptoms and signs. Arquivos Brasileiros de Neurocirurgia: Brazilian Neurosurgery 36:01–06. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1597820
Sinclair AJ, Kuruvath S, Sen D, Nightingale PG, Burdon MA, Flint G (2011) Is cerebrospinal fluid shunting in idiopathic intracranial hypertension worthwhile? A 10-year review. Cephalalgia 31:1627–1633. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102411423305
Smith KA, Peterson JC, Arnold PM, Camarata PJ, Whittaker Thomas J, Abraham MG (2016) A case series of dural venous sinus stenting in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: association of outcomes with optical coherence tomography. Int J Neurosci 127:145–153. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2016.1152967
Smith KH, Wilkinson JT, Brindley GO (1992) Combined third and sixth nerve paresis following optic nerve sheath fenestration. J Clin Neuroophthalmol 12:85–87 discussion 88
Soto FC, Antozzi P, Szomstein S, Cho MY, Zundel N, Locatelli E, Rosenthal RJ (2005) Indication for emergent gastric bypass in a patient with severe idiopathic intracranial hypertension: case report and review of the literature. Surg Obes Relat Dis 1:503–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soard.2005.06.004
Spilberg G, Wajnberg E, Gasparetto E, Magalhªes G (2010) Endovascular treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension: case report and literature review, vol 20
Spoor TC (1993) Long-term effectiveness of optic nerve sheath decompression for pseudotumor cerebri. Arch Ophthalmol 111:632–635. https://doi.org/10.1001/archopht.1993.01090050066030
Starks V, Gilliland G, Vrcek I, Gilliland C (2016) Effect of optic nerve sheath fenestration for idiopathic intracranial hypertension on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Orbit 35:87–90. https://doi.org/10.3109/01676830.2016.1139592
Sugerman HJ, DeMaria EJ, Felton WL, Nakatsuka M, Sismanis A (1997) Increased intra-abdominal pressure and cardiac filling pressures in obesity-associated pseudotumor cerebri. Neurology 49:507–511. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.49.2.507
Sugerman HJ, Felton WL, Salvant JB, Sismanis A, Kellum JM (1995) Effects of surgically induced weight loss on idiopathic intracranial hypertension in morbid obesity. Neurology 45:1655–1659. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.45.9.1655
Sugerman HJ, Felton WL, Sismanis A, Kellum JM, DeMaria EJ, Sugerman EL (1999) Gastric surgery for pseudotumor cerebri associated with severe obesity. Ann Surg 229:634. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-199905000-00005
Tarnaris A, Toma AK, Watkins LD, Kitchen ND (2011) Is there a difference in outcomes of patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension with the choice of cerebrospinal fluid diversion site: a single centre experience. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 113:477–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2011.02.008
Teleb MS, Cziep ME, Issa M, Lazzaro M, Asif K, Hun Hong S, Lynch JR, Fitzsimmons B-FM, Remler BF, Zaidat OO (2013) Stenting and angioplasty for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a case series with clinical, angiographic, ophthalmological, complication, and pressure reporting. J Neuroimaging 25:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/jon.12072
Vaidya NS, Mahmoud AM, Buzzacco D, Katz SE (2016) Visual outcomes following optic nerve sheath fenestration via the medial transconjunctival approach. Orbit 35:271–277. https://doi.org/10.1080/01676830.2016.1193530
Wall M, George D (1991) Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. A prospective study of 50 patients. Brain 114(Pt 1A):155–180
Wall M, Johnson CA, Cello KE, Zamba KD, McDermott MP, Keltner JL (2016) Visual field outcomes for the idiopathic intracranial hypertension treatment trial (IIHTT). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 57:805. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.15-18626
Warden KF, Alizai AM, Trobe JD, Hoff JT (2011) Short-term continuous intraparenchymal intracranial pressure monitoring in presumed idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neuroophthalmol 31:202–205. https://doi.org/10.1097/wno.0b013e3182183c8d
Williams A, Morgan J, Johnson A, Bates S, Pople I, Norton S (2010) Resolution of pseudotumor cerebri following surgery for morbid obesity. J Surg Case Rep 2010:7. https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/2010.6.7
Winters HS, Parker G, Halmagyi GM, Mehta A, Atkins T (2015) Delayed relapse in pseudotumor cerebri due to new stenosis after transverse sinus stenting. BMJ Case Rep:bcr2015011896. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2015-011896
Woodworth GF, McGirt MJ, Elfert P, Sciubba DM, Rigamonti D (2005) Frameless stereotactic ventricular shunt placement for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 83:12–16. https://doi.org/10.1159/000084059
Yadav YR, Parihar V, Agarwal M, Bhatele PR, Saxena N (2011) Lumbar peritoneal shunt in idiopathic intra cranial hypertension. Turk Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.5137/1019-5149.jtn.4307-11.1
Yaqub MM, Mehboob MA, Islam QU (2017) Efficacy and safety of optic nerve sheath fenestration in patients with raised intracranial pressure. Pak J Med Sci 33:471–475
Zheng H, Zhou M, Zhao B, Zhou D, He L (2010) Pseudotumor cerebri syndrome and giant arachnoid granulation: treatment with venous sinus stenting. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21:927–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2010.02.018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Y Pierre Gobin is the CEO and Medical Director of Serenity Medical Inc.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalyvas, A., Neromyliotis, E., Koutsarnakis, C. et al. A systematic review of surgical treatments of idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH). Neurosurg Rev 44, 773–792 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01288-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-020-01288-1