Abstract
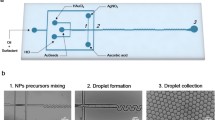
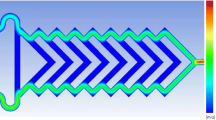
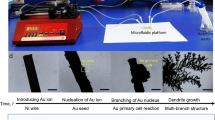
We report a microfluidic chip designed and fabricated for the consecutive synthesis of gold nanobipyramids (Au NBPs) with controllable morphology. The seed-mediated method is employed to synthesize Au NBPs in an S-shaped micromixer. Under sufficient mixing and precise flow rate control of various reactants during microfluidic synthesis, Au NBPs with various aspect ratios can be obtained through this microfluidic platform. The dependence of reactant concentration on the morphology of synthesized Au NBPs is studied by changing the flow rate of silver nitrate (AgNO3), ascorbic acid (AA) and gold seed in microchannel respectively, analytical simulation is performed to validate the control mechanism during Au NBPs synthesis in a microchannel.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boleininger J, Kurz A, Reuss V, Sonnichsen C (2006) Microfluidic continuous flow synthesis of rod-shaped gold and silver nanocrystals. Phys Chem Chem Phys 8:3824–3827
Chen G, Ji B, Gao Y, Wang C, Wu J, Zhou B, Wen W (2019) Towards the rapid and efficient mixing on 'open-surface' droplet-based microfluidics via magnetic actuation. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 286:181–190
Chateau D, Liotta A, Vadcard F, Navarro JRG, Chaput F, Lermé J, Lerouge F, Parola S (2015) From Au NBPs to nanojavelins for a precise tuning of the plasmon resonance to the infrared wavelengths: experimental and theoretical aspects. Nanoscale 7:1934–1943
Cong H, Porco JA Jr (2012) Chemical synthesis of complex molecules using nanoparticle catalysis. ACS Catal 2:65–70
Duraiswamy S, Khan SA (2009) Droplet-based microfluidic synthesis of anisotropic metal nanocrystals. Small 5:2828–2834
Fang C, Zhao G, Xiao Y, Zhao J, Zhang ZJ, Geng BY (2016) Facile growth of high-yield Au NBPs induced by chloroplatinic acid for high refractive index sensing properties. Sci Rep 6:36706
Gelperina S, Kisich K, Iseman MD, Heifets L (2005) The potential advantages of nanoparticle drug delivery systems in chemotherapy of tuberculosis. Am J Resp Crit Care 172:1487–1490
Huang X, Neretina S, El-Sayed MA (2009) Gold nanorods: from synthesis and properties to biological and biomedical applications. Adv Mater 21:4880–4910
Huang XH, Jain PK, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2007) Gold nanoparticles: interesting optical properties and recent applications in cancer diagnostics and therapy. Nanomedicine 2:681–693
Jana NR, Gearheart L, Murphy CJ (2001) Seed-mediated growth approach for shape-controlled synthesis of spheroidal and rod-like gold nanoparticles using a surfactant template. Adv Mater 13:1389–1393
Jana NR, Gearheart L, Obare SO, Murphy CJ (2002) Anisotropic chemical reactivity of gold spheroids and nanorods. Langmuir 18:922–927
Kou XS, Zhang S, Tsung CK, Yeung MH, Shi QH, Stucky GD, Sun LD, Wang JF, Yan CH (2006) Growth of gold nanorods and bipyramids using CTEAB surfactant. J Phys Chem B 110:16377–16383
Kou XS, Ni WH, Tsung CK, Chan K, Lin H-Q, Stucky GD, Wang JF (2007) Growth of gold bipyramids with improved yield and their curvature-directed oxidation. Small 3:2103–2113
Li S, Zeng M, Gaule T, McPherson MJ, Meldrum FC (2017) Passive pico-injection enables controlled crystallization in a droplet microfluidic device. Small 13:1702154
Li Q, Zhuo XL, Li S, Ruan QF, Xu QH, Wang JF (2015) Production of monodisperse Au NBPs with number percentages approaching 100% and evaluation of their plasmonic properties. Adv Optical Mater 3:801–812
Li X, Yang Y, Zhou G, Han S, Wang W, Zhang L, Chen W, Zou C, Huang SM (2013) The unusual effect of AgNO3 on the growth of Au nanostructures and their catalytic performance. Nanoscale 5:4976–4985
Liu MZ, Guyot-Sionnest P (2005) Mechanism of silver (I)-assisted growth of gold nanorods and bipyramids. J Phys Chem B 109:22192–22200
Lohse SE, Eller JR, Sivapalan ST, Plews MR, Murphy CJ (2013) A simple millifluidic benchtop reactor system for the high-throughput synthesis and functionalization of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and shapes. ACS Nano 7:4135–4150
Ma J, Lee SM-Y, Yi C, Li C-W (2019) Controllable synthesis of functional nanoparticles by microfluidic platforms for biomedical applications-a review. Lab Chip 17(2):209–226
Ma J, Li CW (2018) Rapid and continuous parametric screening for the synthesis of gold nanocrystals with different morphologies using a microfluidic device. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 262:236–244
Nath N, Chilkoti A (2002) A colorimetric gold nanoparticle sensor to interrogate biomolecular interactions in real-time on a surface. Anal Chem 74:504–509
Navarro JRG, Manchon D, Lerouge F, Cottancin E, Lerme J, Bonnet C, Chaput F, Mosset A, Pellarin M, Parola S (2012) Synthesis, electron tomography and single-particle optical response of twisted gold nano-bipyramids. Nanotechnology 23:145707
Pappas TC, Wickramanyake WMS, Jan E, Motamedi M, Brodwick M, Kotov NA (2007) Nanoscale engineering of a cellular interface with semiconductor nanoparticle films for photoelectric stimulation of neurons. Nano Lett 7:513–519
Qi Y, Zhu J, Li J, Zhao J (2016) Highly improved synthesis of Au NBPs by tuning the concentration of hydrochloric acid. J Nanopart Res 18:190
Ren K, Zhou J, Wu H (2013) Materials for microfluidic chip fabrication. Accounts Chem Res 46:2396–2406
Sánchez-Iglesias A, Winckelmans N, Altantzis T, Bals S, Grzelczak M, Liz-Marzán LM (2016) High-yield seeded growth of monodisperse pentatwinned gold nanoparticles through thermally induced seed twinning. J Am Chem Soc 139:107–110
Thiele M, Soh JZE, Knauer A, Malsch D, Stranik O, Müller R, Csáki A, Henkel T, Michael Köhler JM, Fritzsche W (2016) Gold nanocubes-direct comparison of synthesis approaches reveals the need for a microfluidic synthesis setup for a high reproducibility. Chem Eng J 288:432–440
Uson L, Sebastian V, Arruebo M, Santamaria J (2016) Continuous microfluidic synthesis and functionalization of gold nanorods. Chem Eng J 285:286–292
Weissleder R, Nahrendorf M, Pittet MJ (2014) Imaging macrophages with nanoparticles. Nat mater 13:125–138
Whitesides GM (2006) The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442:368
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Xiuqing Gong for technical assistance. The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11604295, Grant No. 61705197, Grant No. 21775101) and Shanghai Pujiang Program (17PJ1402800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Z., Wang, K., Lou, M. et al. Consecutive synthesis of gold nanobipyramids with controllable morphologies using a microfluidic platform. Microfluid Nanofluid 24, 38 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-020-02345-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-020-02345-3