Abstract
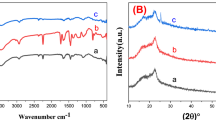
The polyamic acid (PAA) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) blends electrospun fibers were prepared by electrospinning method. PAA with high carbon conversion served as carbon nanofibers; PVP with low carbon conversion served as porogenic sacrificial agent. Then, the PAA-PVP-based carbon nanofibers with well-controlled meso/macro pore structure were obtained via thermally induced phase separation process. The morphology and electrochemical performance of porous carbon nanofibers are investigated by structural analysis and electrochemical measurements. The relationship among pore structure, character of electrolyte and electrochemical performance of porous carbon nanofibers was extensively evaluated. Porous carbon nanofibers derived from PAA-PVP (mass ratio = 5:2) electrospun fibers show adjustable average pore diameter (3.1 nm), high BET specific surface area (743.5 m2 g−1), and average pore volume (0.126 cm3 g−1). The supercapacitor constructed by porous nanofibers as electrode in ionic liquids electrolyte exhibits wide electrochemical stability window (3.4 V), high specific capacity (211.7 F g−1), good power density (2021 W kg−1), and low internal resistance (1.0 Ω). The findings reveal a guideline of the preparation of blending polymer-based porous carbon nanofibers for electrochemical energy conversion and storage.

Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perumal P, Christopher Selvin P, Selvasekarapandian S (2018) Characterization of biopolymer pectin with lithium chloride and its applications to electrochemical devices. Ionics 24:3259–3270
Hemalatha R, Alagar M, Selvasekarapandian S, Sundaresan B, Moniha V, Boopathi G, Christopher Selvin P (2019) Preparation and characterization of proton-conducting polymer electrolyte based on PVA, amino acid proline, and NH4Cl and its applications to electrochemical devices. Ionics 25:141–154
Wang K, Zhang WZ, Lou FP, Wei P, Qian ZM, Guo WH (2018) Preparation of electrospun heterostructured hollow SnO2/CuO nanofibers and their enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance. J Solid State Electrochem 22:2413–2423
Kouchachvili L, Yaïci W, Entchev E (2018) Hybrid battery/supercapacitor energy storage system for the electric vehicles. J Power Sources 374:237–248
Rawool CR, Punde NS, Rajpurohit AS, Karna SP, Srivastava AK (2018) High energy density supercapacitive material based on a ternary hybrid nanocomposite of cobalt hexacyanoferrate/carbon nanofibers/polypyrrole. Electrochim Acta 268:411–423
Li B, Zheng JS, Zhang HY, Jin LM, Yang DJ, Lv H, Shen C, Shellikeri A, Zheng YR, Gong RQ, Zheng JP, Zhang GM (2018) Electrode materials, electrolytes, and challenges in nonaqueous lithium-ion capacitors. Adv Mater 30:1705670
Park J, Yoo YE, Mai LQ, Kim W (2019) Rational design of a redox-active nonaqueous electrolyte for a high-energy-density supercapacitor based on carbon nanotubes. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:7728–7735
He TS, Jia R, Lang XS, Wu X, Wang YB (2017) Preparation and electrochemical performance of PVdF ultrafine porous fiber separator-cum-electrolyte for supercapacitor. J Electrochem Soc 164:E379–E384
Ye YS, Rick J, Hwang BJ (2013) Ionic liquid polymer electrolytes. J Mater Chem A 1:2719–2743
MacFarlane DR, Forsyth M, Howlett PC, Kar M, Passerini S, Pringle JM, Ohno H, Watanabe M, Yan F, Zheng W, Zhang S, Zhang J (2016) Ionic liquids and their solid-state analogues as materials for energy generation and storage. Nat Rev Mater 1:15005
Béguin F, Presser V, Balducci A, Frackowiak E (2015) Carbons and electrolytes for advanced supercapacitors. Adv Mater 26:2219–2251
Zhang C, Zhang P, Zhang H (2019) Electrospun porous Fe2O3 nanotubes as counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Int J Energy Res 43:5355–5366
He TS, Meng XL, Nie JP, Tong Y, Cai KD (2016) Thermally reduced graphene oxide electrochemically activated by bis-spiro quaternary alkyl ammonium for capacitors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:13865–13870
Ding R, Wu H, Thunga M, Bowler N, Kessler MR (2016) Processing and characterization of low-cost electrospun carbon fibers from organosolv lignin/polyacrylonitrile blends. Carbon 100:126–136
Wu C, Zhou TZ, Du Y, Dou SX, Zhang H, Jiang L, Cheng Q (2019) Strong bioinspired HPA-rGO nanocomposite films via interfacial interactions for flexible supercapacitors. Nano Energy 58:517–527
Gupta R, Kumar R, Sharma A, Verma N (2015) Novel cu–carbon nanofiber composites for the counter electrodes of dye-sensitized solar cells. Int J Energy Res 39:668–680
Zhao PY, Yu BJ, Sun S, Guo Y, Chang ZZ, Li Q, Wang CY (2017) High-performance anode of sodium ion battery from polyacrylonitrile/humic acid composite electrospun carbon fibers. Electrochim Acta 232:348–356
Chinnappan A, Baskar C, Baskar S, Ratheesh G, Ramakrishna S (2017) An overview of electrospun nanofibers and their application in energy storage, sensors and wearable/flexible electronics. J Mater Chem C 5:12657–12673
Chen LF, Feng Y, Liang HW, Wu ZY, Yu SH (2017) Macroscopic-scale three-dimensional carbon nanofiber architectures for electrochemical energy storage devices. Adv Energy Mater 7:1700826
Frank E, Steudle LM, Ingildeev D, Spoerl JM, Buchmeiser MR (2014) Carbon fibers: precursor systems, processing, structure, and properties. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:5262–5298
Zhao S, Shi ZQ, Wang CY, Chen MM (2008) Structure and surface elemental state analysis of polyimide resin film after carbonization and graphitization. J Appl Polym Sci 108:1852–1856
Le TH, Yang Y, Yu L, Gao T, Huang Z, Kang F (2016) Polyimide-based porous hollow carbon nanofibers for supercapacitor electrode. J Appl Polym Sci 133:43397
Le TH, Yang Y, Yu L, Gao T, Huang Z, Kang F (2016) Polyimide-based porous hollow carbon nanofibers for supercapacitor electrode. J Appl Polym Sci 133(19):43397
Zhou ZP, Liu TY, Khan AU, Liu GL (2019) Block copolymer–based porous carbon fibers. Sci Adv 5:6852
Zhou Z, Liu T, Khan AU, Liu G (2020) Controlling the physical and electrochemical properties of block copolymer-based porous carbon fibers by pyrolysis temperature. Mol Syst Des Eng 5:153–165
Tang CB, Tracz A, Kruk M, Zhang R, Smilgies DM, Matyjaszewski K, Kowalewski T (2005) Long-range ordered thin films of block copolymers prepared by zone-casting and their thermal conversion into ordered nanostructured carbon. J Am Chem Soc 127:6918–6919
Serrano JM, Liu T, Khan AU, Botset B, Stovall BJ, Xu Z, Guo D, Cao K, Hao X, Cheng S (2019) Composition design of block copolymers for porous carbon fibers. Chem Mater 31:8898–8907
Khan WS, Asmatulu R, Rodriguez V, Ceylan M (2014) Enhancing thermal and ionic conductivities of electrospun PAN and PMMA nanofibers by graphene nanoflake additions for battery-separator applications. Int J Energy Res 38:2044–2051
Zhang H, Lin CE, Zhou MY, John AE, Zhu BK (2016) High thermal resistance polyimide separators prepared via soluble precusor and non-solvent induced phase separation process for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 187:125–133
He TS, Su QY, Yildiz Z, Cai KD, Wang YB (2016) Ultrafine carbon fibers with hollow-porous multilayered structure for supercapacitors. Electrochim Acta 222:1120–1127
Xi X, Chung DDL (2019) Colossal electric permittivity discovered in polyacrylonitrile (PAN) based carbon fiber, with comparison of PAN-based and pitch-based carbon fibers. Carbon 145:734–739
He TS, Ren X, Wang YB, Nie JP, Cai KD (2016) Electrochemical performance of reduced graphene oxide in Spiro-(1, 1′)-bipyrrolidinium tetrafluoroborate electrolyte. Int J Energy Res 40:1105–1111
Sharma S, Dhiman N, Pathak D, Kumar R (2016) Effect of nano-size fumed silica on ionic conductivity of PVdF-HFP-based plasticized nano-composite polymer electrolytes. Ionics 22:1865–1872
Funding
This work received financial supports from the Project of Liaoning Province, China (Nos. 0518XN011, 0519BS014), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21671025, 21471021), and Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Project of Liaoning Province, China (Nos. 201910167192, 201910167082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, TS., Yu, XD., Bai, TJ. et al. Porous carbon nanofibers derived from PAA-PVP electrospun fibers for supercapacitor. Ionics 26, 4103–4111 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03529-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03529-1