Abstract
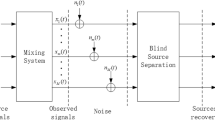
Independent component analysis (ICA), as an important data processing technique, is widely employed in many areas. The objective of the ICA is to recover independent components from observed signals. Several algorithms, such as equivariant adaptive separation via independence algorithm, least-mean-square (LMS)-type algorithms and recursive least-squares (RLS)-type learning rules, are proposed to solve the ICA problem. In the present paper, a modified RLS algorithm for ICA with weighted orthogonal constraint is developed to implement source separation based on the local convergence analysis of the available algorithm. Comparative experiment results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm is better than existing learning rules in the aspect of the accuracy of separation and stability.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.I. Amari, Neural learning in structured parameter spaces natural Riemannian gradient, in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 9, ed. by M.C. Mozer, M.I. Jordan, T. Petsche (The MIT Press, Cambridge, 1997), pp. 127–133
S.I. Amari, J. Cardoso, Blind source separation-semiparametric statistical approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 45(11), 2692–2700 (1997)
A.J. Bell, T.J. Sejnowski, An information-maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Comput. 7(6), 1129–1159 (1995)
J.F. Cardoso, B.H. Laheld, Equivariant adaptive source separation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 44(12), 3017–3030 (1996)
P. Comon, Independent component analysis, a new concept? Signal Process. 36(3), 287–314 (1994)
E. Eleftheriou, D.D. Falconer, Tracking properties and steady-state performance of RLS adaptive filter algorithms. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process 34(5), 1097–1110 (1986)
L.F. Egeren, Multivariate statistical analysis: revised and expanded. Psychophysiology 10(5), 517–532 (1973)
S. Haykin, Simon, Unsupervised Adaptive Filtering (Wiley, New York, 2000)
A. Hyvärinen, E. Oja, A fast fixed-point algorithms for independent component analysis. Neural Comput. 9(7), 1483–1492 (1997)
A. Hyvärinen, J. Karhunen, E. Oja, Independent Component Analysis (Wiley, New York, 2001)
E. Jianwei, Y.L. Bao, J.M. Ye, Crude oil price analysis and forecasting based on variational mode decomposition and independent component analysis. Physica A 484, 412–427 (2017)
H. Jung, J. Kang, T.S. Lee, S. Kim, K. Kim, An iALM-ICA-based anti-jamming DS-CDMA receiver for LMS systems. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 54(5), 2318–2328 (2018)
I. Rejer, P. Gérski, Independent component analysis for EEG data preprocessing-algorithms comparison. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 44(2), 1134–1164 (2017)
M.S. Reza, J. Ma, ICA and PCA integrated feature extraction for classification, in IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing (2017)
A. Singhal, I. Google, Modern information retrieval: a brief overview. Bull. IEEE Comput. Soc. Tech. Comm. Data Eng. 24(24), 35–43 (2001)
Q. Su, Y.M. Wei, Y.H. Shen, C.L. Deng, Underdetermined independent component analysis based on first- and second-order statistics. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 38(7), 3107–3132 (2019)
Y. Tang, Independent component analysis employing exponentials of sparse antisymmetric matrices. Neurocomputing 325, 172–181 (2019)
X.J. Tang, J.M. Ye, X.F. Zhang, On the convergence of ICA algorithms with weighted orthogonal constraint. Digit. Signal Process. 28(1), 39–47 (2014)
X.J. Tang, X.F. Zhang, J.M. Ye, Adaptive step-size natural gradient ICA algorithm with weighted orthogonalization. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(1), 211–221 (2014)
L. Xu, Least mean square error reconstruction principle for self-organizing neural-nets. Neural Netw. 6(5), 627–648 (1993)
B. Yang, Projection approximation subspace tracking. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 43(1), 95–107 (2002)
C.X. Yang, N. Tavassolian, An independent component analysis approach to motion noise cancellation of cardio-mechanical signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 66(3), 784–793 (2019)
J.M. Ye, H.H. Jin, Q.R. Zhang, Adaptive weighted orthogonal constrained algorithm for blind source separation. Digit. Signal Process. 23(2), 514–521 (2013)
X.L. Zhu, X.D. Zhang, Adaptive RLS algorithm for blind source separation using a natural gradient. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 9(12), 432–435 (2002)
X.L. Zhu, X.D. Zhang, J.M. Ye, Natural gradient-based recursive least-squares algorithm for adaptive blind source separation. Sci. China Ser. F: Inf. Sci. 47(1), 55–65 (2004)
X.L. Zhu, X.D. Zhang, Z.Z. Ding, Y. Jia, Adaptive nonlinear PCA algorithms for blind source separation without prewhitening. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 53(3), 745–753 (2006)
H. Zhu, S.N. Zhang, H.C. Zhao, Single-channel source separation of multi-component radar signal with the same generalized period using ICA. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35(1), 353–363 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61573014 and in part by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China under Grant JB180702.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A: Proof of Theorem 1
Appendix A: Proof of Theorem 1
Considering formulation (11), Tang [18] pointed out that the \({\mathbf {B}}_{\mathrm{opt},t}\) at time t is the stable point with the weighted orthogonal constraint (3). When iteration (11) converges, considering the following expression in (10)
applying \(E\{\cdot \}\) operator to (23), we can obtain that
Utilizing the (24) to the \({\mathbf {P}}_{t}\) in (11) yields
Combining result (25) with mathematical expectation on two sides of the final time of (11), we have the following as:
here \(\lambda \) is the forgetting factor \((0\ll \lambda <1)\). It represents that our algorithm is linear convergence. Further, (9) demonstrates that \(E\{{\mathbf {z}}_{t}{\mathbf {z}}^\mathrm{T}_{t}\}=E\{{\mathbf {y}}_{t}{\mathbf {z}}^\mathrm{T}_{t}\}\).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
E, J., Ye, J. A Modified RLS Algorithm for ICA with Weighted Orthogonal Constraint. Circuits Syst Signal Process 39, 3046–3060 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01303-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01303-x