Abstract
Key message
Overexpression of CpbHLH1 in Arabidopsis and tobacco resulted in a dramatic decrease in anthocyanin accumulation by repressing the expression of late biosynthesis genes in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway.
Abstract
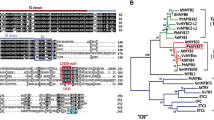
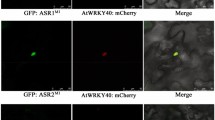
Many basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) transcription factors (TFs) of subgroup IIIf have been characterized as anthocyanin-associated activators in higher plants, but information regarding bHLH TFs that inhibit anthocyanin accumulation remains scarce. In this study, the subgroup IIIf bHLH TF CpbHLH1 from Chimonanthus praecox (L.) was identified as a negative regulator of anthocyanin accumulation. Our results showed that overexpression of CpbHLH1 in model plant species, Arabidopsis and tobacco, resulted in a dramatic decrease in anthocyanin content, whereas the content of proanthocyanidin was little affected. Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) assays of the structural genes in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway revealed that CpbHLH1 inhibits anthocyanin accumulation mainly through repressing the expression of late biosynthesis genes (LBGs). Interactions between CpbHLH1 protein and AtPAP1/NtAN2 protein were detected via yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) and bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays. This is the first bHLH repressor of anthocyanin biosynthesis identified in dicotyledons. These results can help us better understand the anthocyanin regulatory network in plants and may provide insights into the diverse functions of bHLH proteins.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert NW, Davies KM, Lewis DH, Zhang H, Montefiori M, Brendolise C, Boase MR, Ngo H, Jameson PE, Schwinn KE (2014) A conserved network of transcriptional activators and repressors regulates anthocyanin pigmentation in eudicots. Plant Cell 26(3):962–980. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.122069
An XH, Tian Y, Chen KQ, Wang XF, Hao YJ (2012) The apple WD40 protein MdTTG1 interacts with bHLH but not MYB proteins to regulate anthocyanin accumulation. J Plant Physiol 169(7):710–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.01.015
Bai Y, Pattanaik S, Patra B, Werkman JR, Xie CH, Yuan L (2011) Flavonoid-related basic helix-loop-helix regulators, NtAn1a and NtAn1b, of tobacco have originated from two ancestors and are functionally active. Planta 234(2):363–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1407-y
Baudry A, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2006) TT8 controls its own expression in a feedback regulation involving TTG1 and homologous MYB and bHLH factors, allowing a strong and cell-specific accumulation of flavonoids in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 46(5):768–779. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02733.x
Borevitz JO, Xia Y, Blount J, Dixon RA, Lamb C (2000) Activation tagging identifies a conserved MYB regulator of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 12(12):2383–2394. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.12.2383
Burr FA, Burr B, Scheffler BE, Blewitt M, Wienand U, Matz EC (1996) The maize repressor-like gene intensifier1 shares homology with the r1/b1 multigene family of transcription factors and exhibits missplicing. Plant Cell 8(8):1249–1259. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.8.8.1249
Chandler VL, Radicella JP, Robbins TP, Chen J, Turks D (1989) Two regulatory genes of the maize anthocyanin pathway are homologous: isolation of B utilizing R genomic sequences. Plant Cell 1(12):1175–1183. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.1.12.1175
Chen L, Hu B, Qin Y, Hu G, Zhao J (2019) Advance of the negative regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis by MYB transcription factors. Plant Physiol Biochem 136:178–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.01.024
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16(6):735–743. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00343.x
Cone KC, Burr FA, Burr B (1986) Molecular analysis of the maize anthocyanin regulatory locus C1. P Natl Acad Sci USA 83(24):9631–9635. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.83.24.9631
Espley RV, Hellens RP, Putterill J, Stevenson DE, Kutty-Amma S, Allan AC (2007) Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J 49(3):414–427. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02964.x
Espley RV, Brendolise C, Chagne D, Kutty-Amma S, Green S, Volz R, Putterill J, Schouten HJ, Gardiner SE, Hellens RP, Allan AC (2009) Multiple repeats of a promoter segment causes transcription factor autoregulation in red apples. Plant Cell 21(1):168–183. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.059329
Farcy E, Cornu A (1979) Isolation and characterization of anthocyanin variants originating from the unstable system an2–1 in Petunia hybrida (Hort.). Theor Appl Genet 55(6):273–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265365
Fu CC, Han YC, Kuang JF, Chen JY, Lu WJ (2017) Papaya CpEIN3a and CpNAC2 co-operatively regulate carotenoid biosynthesis-related genes CpPDS2/4, CpLCY-e and CpCHY-b during fruit ripening. Plant Cell Physiol 58(12):2155–2165. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcx149
Garriga-Canut M, Roopra A, Buckley NJ (2001) The basic helix-loop-helix protein, sharp-1, represses transcription by a histone deacetylase-dependent and histone deacetylase-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem 276(18):14821–14828. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M011619200
Gerats AGM, Farcy E, Wallroth M, Groot SPC, Schram A (1984) Control of anthocyanin synthesis in Petunia-hybrida by multiple allelic series of the genes An1 and An2. Genetics 106(3):501–508
Goff SA, Cone KC, Chandler VL (1992) Functional analysis of the transcriptional activator encoded by the maize B gene: evidence for a direct functional interaction between two classes of regulatory proteins. Genes Dev 6(5):864–875. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.6.5.864
Gonzalez A, Zhao M, Leavitt JM, Lloyd AM (2008) Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J 53(5):814–827. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03373.x
Heim MA, Jakoby M, Werber M, Martin C, Weisshaar B, Bailey PC (2003) The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in plants: a genome-wide study of protein structure and functional diversity. Mol Biol Evol 20(5):735–747. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msg088
Holton TA, Cornish EC (1995) Genetics and biochemistry of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7(7):1071–1083. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.7.7.1071
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffmann NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1985) A simple and general-method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227(4691):1229–1231
Ikeda M, Ohme-Takagi M (2009) A novel group of transcriptional repressors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 50(5):970–975. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcp048
Ilk N, Ding J, Ihnatowicz A, Koornneef M, Reymond M (2015) Natural variation for anthocyanin accumulation under high-light and low-temperature stress is attributable to the ENHANCER OF AG-4 2 (HUA2) locus in combination with PRODUCTION OF ANTHOCYANIN PIGMENT1 (PAP1) and PAP2. New Phytol 206(1):422–435. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13177
Li S (2014) Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis: fine-tuning of the MYB-bHLH-WD40 (MBW) complex. Plant Signal Behav 9(1):e27522. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.27522
Ludwig SR, Habera LF, Dellaporta SL, Wessler SR (1989) Lc, a member of the maize R gene family responsible for tissue-specific anthocyanin production, encodes a protein similar to transcriptional activators and contains the myc-homology region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86(18):7092–7096. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.86.18.7092
Luo P, Ning GG, Wang Z, Shen YX, Jin HA, Li PH, Huang SS, Zhao J, Bao MZ (2016) Disequilibrium of flavonol synthase and dihydroflavonol-4-reductase expression associated tightly to white vs red color flower formation in plants. Front Plant Sci 6:1257. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01257
Matsui K, Umemura Y, Ohme-Takagi M (2008) AtMYBL2, a protein with a single MYB domain, acts as a negative regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 55(6):954–967. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03565.x
Mehrtens F, Kranz H, Bednarek P, Weisshaar B (2005) The Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB12 is a flavonol-specific regulator of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 138(2):1083–1096. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.058032
Mol J, Grotewold E, Koes R (1998) How genes paint flowers and seeds. Trends Plant Sci 3(6):212–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-1385(98)01242-4
Munis MF, Tu L, Deng F, Tan J, Xu L, Xu S, Long L, Zhang X (2010) A thaumatin-like protein gene involved in cotton fiber secondary cell wall development enhances resistance against Verticillium dahliae and other stresses in transgenic tobacco. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 393(1):38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.01.069
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15(3):473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Nesi N, Debeaujon I, Jond C, Pelletier G, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2000) The TT8 gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix domain protein required for expression of DFR and BAN genes in Arabidopsis siliques. Plant Cell 12(10):1863–1878. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.10.1863
Ohta M, Matsui K, Hiratsu K, Shinshi H, Ohme-Takagi M (2001) Repression domains of class II ERF transcriptional repressors share an essential motif for active repression. Plant Cell 13(8):1959–1968. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.13.8.1959
Pandey A, Misra P, Bhambhani S, Bhatia C, Trivedi PK (2014) Expression of arabidopsis MYB transcription factor, AtMYB111, in tobacco requires light to modulate flavonol content. Sci Rep 4:5018. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05018
Park KI, Ishikawa N, Morita Y, Choi JD, Hoshino A, Iida S (2007) A bHLH regulatory gene in the common morning glory, Ipomoea purpurea, controls anthocyanin biosynthesis in flowers, proanthocyanidin and phytomelanin pigmentation in seeds, and seed trichome formation. Plant J 49(4):641–654. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02988.x
Pattanaik S, Xie CH, Yuan L (2008) The interaction domains of the plant Myc-like bHLH transcription factors can regulate the transactivation strength. Planta 227(3):707–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0676-y
Ramsay NA, Glover BJ (2005) MYB-bHLH-WD40 protein complex and the evolution of cellular diversity. Trends Plant Sci 10(2):63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.12.011
Ramsay NA, Walker AR, Mooney M, Gray JC (2003) Two basic-helix-loop-helix genes (MYC-146 and GL3) from Arabidopsis can activate anthocyanin biosynthesis in a white-flowered Matthiola incana mutant. Plant Mol Biol 52(3):679–688. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024852021124
Schwinn K, Venail J, Shang YJ, Mackay S, Alm V, Butelli E, Oyama R, Bailey P, Davies K, Martin C (2006) A small family of MYB-regulatory genes controls floral pigmentation intensity and patterning in the genus Antirrhinum. Plant Cell 18(4):831–851. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.039255
Spelt C, Quattrocchio F, Mol JN, Koes R (2000) anthocyanin1 of petunia encodes a basic helix-loop-helix protein that directly activates transcription of structural anthocyanin genes. Plant Cell 12(9):1619–1632. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.9.1619
Stracke R, Ishihara H, Huep G, Barsch A, Mehrtens F, Niehaus K, Weisshaar B (2007) Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. Plant J 50(4):660–677. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03078.x
Stracke R, Jahns O, Keck M, Tohge T, Niehaus K, Fernie AR, Weisshaar B (2010) Analysis of PRODUCTION OF FLAVONOL GLYCOSIDES-dependent flavonol glycoside accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana plants reveals MYB11-, MYB12- and MYB111-independent flavonol glycoside accumulation. New Phytol 188(4):985–1000. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03421.x
Sui S, Luo J, Ma J, Zhu Q, Lei X, Li M (2012) Generation and analysis of expressed sequence tags from Chimonanthus praecox (Wintersweet) flowers for discovering stress-responsive and floral development-related genes. Comp Funct Genomics 2012:134596. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/134596
Tian JP, Ma ZY, Zhao KG, Zhang J, Xiang L, Chen LQ (2019) Transcriptomic and proteomic approaches to explore the differences in monoterpene and benzenoid biosynthesis between scented and unscented genotypes of wintersweet. Physiol Plantarum 166(2):478–493. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12828
Tiwari SB, Hagen G, Guilfoyle TJ (2004) Aux/IAA proteins contain a potent transcriptional repression domain. Plant Cell 16(2):533–543. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.017384
Tsuda T (2012) Dietary anthocyanin-rich plants: biochemical basis and recent progress in health benefits studies. Mol Nutr Food Res 56(1):159–170. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201100526
Xiang L, Zhao K, Chen L (2010) Molecular cloning and expression of Chimonanthus praecox farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene and its possible involvement in the biosynthesis of floral volatile sesquiterpenoids. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(10–11):845–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.015
Xie XB, Li S, Zhang RF, Zhao J, Chen YC, Zhao Q, Yao YX, You CX, Zhang XS, Hao YJ (2012) The bHLH transcription factor MdbHLH3 promotes anthocyanin accumulation and fruit colouration in response to low temperature in apples. Plant Cell Environ 35(11):1884–1897. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02523.x
Xu H, Wang N, Liu J, Qu C, Wang Y, Jiang S, Lu N, Wang D, Zhang Z, Chen X (2017) The molecular mechanism underlying anthocyanin metabolism in apple using the MdMYB16 and MdbHLH33 genes. Plant Mol Biol 94(1–2):149–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-017-0601-0
Yang N, Zhao K, Li X, Zhao R, Aslam MZ, Yu L, Chen L (2018) Comprehensive analysis of wintersweet flower reveals key structural genes involved in flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. Gene 676:279–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.08.050
Zhang W, Ning G, Lv H, Liao L, Bao M (2009) Single MYB-type transcription factor AtCAPRICE: a new efficient tool to engineer the production of anthocyanin in tobacco. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388(4):742–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.092
Zhang LH, Jia BL, Zhuo RY, Liu JL, Pan HY, Baldwin TC, Zhang SH (2012) An acyl-acyl carrier protein thioesterase gene isolated from wintersweet (Chimonanthus praecox), CpFATB, enhances drought tolerance in transgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tobaccum). Plant Mol Biol Rep 30(2):433–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-011-0359-5
Zhang Y, Zhu H, Shao C, Cai F, Zhang J, Bao M (2019) PaMYB82 from Platanus acerifolia regulates trichome development in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 287:110177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110177
Zhao KG, Zhou MQ, Chen LQ, Zhang DL, Robert GW (2007) Genetic diversity and discrimination of Chimonanthus praecox (L.) link germplasm using ISSR and RAPD markers. HortScience 42(5):1144–1148
Zhao PC, Li XX, Jia JT, Yuan GX, Chen SY, Qi DM, Cheng LQ, Liu GS (2019) bHLH92 from sheepgrass acts as a negative regulator of anthocyanin/proanthocyandin accumulation and influences seed dormancy. J Exp Bot 70(1):269–284. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery335
Zhou LL, Shi MZ, Xie DY (2012) Regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis by nitrogen in TTG1-GL3/TT8-PAP1-programmed red cells of Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 236(3):825–837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1674-2
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos: 31272207 and 31972442). We thank Professor Wang-jin Lu (State Key Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of Subtropical Agro-bioresources, College of Horticulture, South China Agricultural University) and Professor Jin-Long Qiu (State Key Laboratory of Plant Genomics, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for the generous gifts of the pBD vectors and the pap1-D mutant of Arabidopsis, respectively. We are also grateful to Professor Guogui Ning (Key Laboratory of Horticultural Plant Biology, College of Horticulture and Forestry Sciences, Huazhong Agricultural University) for helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RZ, XS and KZ: designed the experiments; RZ: performed the majority of experiments; XS, NY, and LC: supplied the materials; RZ, XS, and KZ: analyzed experimental results. RZ: prepared the initial manuscript draft; LX, XL, and KZ: produced the final version of the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Salim Al-Babili.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, R., Song, X., Yang, N. et al. Expression of the subgroup IIIf bHLH transcription factor CpbHLH1 from Chimonanthus praecox (L.) in transgenic model plants inhibits anthocyanin accumulation. Plant Cell Rep 39, 891–907 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-020-02537-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-020-02537-9