Abstract
Purpose
There have been many studies about the effects of long-term fertilizations on crop yields and soil organic carbon. However, little attention has been paid to the response of soil dissolved organic carbon (DOC) to fertilization practices. The aims of this work were to investigate the variations of the content and the chemical composition of soil DOC under long-term different fertilizations and to evaluate their correlations with maize yields.
Materials and methods
A long-term fertilization experiment under a double maize cropping system was established in 1986 in acidic Ultisols of southern China. Soil samples were collected in April 2014 from the following ten treatments: (1) CK (non-fertilization), (2) N (only N fertilization), (3) P (only P fertilization), (4) K (only K fertilization), (5) NP (N and P fertilization), (6) NK (N and K fertilization), (7) NPK (N, P, and K fertilization), (8) HNPK (double doses of NPK fertilization amount), (9) OM (only organic manure), and (10) NPKM (NPK fertilization plus organic manure). The soil basic chemical properties including the content of DOC were determined. Then, the chemical composition of soil DOC was assessed through three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix (3DEEM) and parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC).
Results and discussion
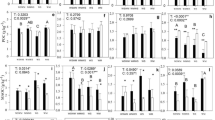
The results showed that long-term application of organic manure significantly increased the content of soil DOC and obviously changed the chemical composition of soil DOC. Based on the 3DEEM and PARAFAC, organic manure treatments (OM, NPKM) had higher proportions of tryptophan-like components and lower proportions of tyrosine-like components as compared with other treatments (CK and inorganic fertilizer treatments). For the fluorescence indices, organic manure treatments showed significantly higher humification index (HIX) and lower biological index (BIX) and McKnight index than other treatments. Aggregated boosted trees analysis revealed that the DOC content explained 24.6% of the total variance in maize yields and ranked first among all tested soil chemical properties. Furthermore, all fluorescence properties of DOC were correlated with maize yields, in which the HIX index was the most important factor.
Conclusions
This research demonstrated that not only the content of DOC but also the chemical composition of DOC in acidic Ultisols were significantly correlated to maize yields. It may be an effective way to improve soil quality and productivity by increasing DOC content and HIX index. From the perspective of soil DOC, our results proved again that application of organic manure could be the most suitable fertilization practice in acidic Ultisols of southern China.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afreh D, Zhang J, Guan DH, Liu KL, Song ZW, Zheng CY, Deng AX, Feng XM, Zhang X, Wu Y, Huang QR, Zhang WJ (2018) Long-term fertilization on nitrogen use efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions in a double maize cropping system in subtropical China. Soil Tillage Res 180:259–267
Bi LD, Zhang B, Liu GR, Li ZZ, Liu YR, Ye C, Yu XC, Lai T, Zhang JG, Yin JM, Liang Y (2009) Long-term effects of organic amendments on the rice yields for double rice cropping systems in subtropical China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 129(4):534–541
Bista P, Machado S, Ghimire R, Del Grosso SJ, Reyes-Fox M (2016) Simulating soil organic carbon in a wheat-fallow system using the Daycent model. Agron J 108(6):2554–2565
Chang DN, Cao WD, Bao XG, Bai JS, Zhang JD, Lu BL, Gao SJ, Zeng NH, Wang XC, Katsuyoshi S (2016) Long-term different fertilizations changed the chemical and spectrum characteristics of DOM of the irrigation-desert soil in north-western China. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 36(1):220–225
Chen ZM, Wang Q, Wang HY, Bao L, Zhou JM (2018) Crop yields and soil organic carbon fractions as influenced by straw incorporation in a rice–wheat cropping system in southeastern China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 112(1):61–73
Coble PG, Del Castillo CE, Avril B (1998) Distribution and optical properties of CDOM in the Arabian Sea during the 1995 southwest monsoon. Deep Sea Res Pt II 45(10–11):2195–2223
De'ath G (2007) Boosted trees for ecological modeling and prediction. Ecology 88(1):243–251
Derrien M, Shin KH, Hur J (2019) Assessment on applicability of common source tracking tools for particulate organic matter in controlled end member mixing experiments. Sci Total Environ 666:187–196
Fan MS, Shen JB, Yuan LX, Jiang RF, Chen XP, Davies WJ, Zhang FS (2012) Improving crop productivity and resource use efficiency to ensure food security and environmental quality in China. J Exp Bot 63(1):13–24
Gao JK, Liang CL, Shen GZ, Lv JL, Wu HM (2017) Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter in various agricultural soils throughout China. Chemosphere 176:108–116
Guo XJ, He XS, Zhang H, Deng Y, Chen L, Jiang JY (2012) Characterization of dissolved organic matter extracted from fermentation effluent of swine manure slurry using spectroscopic techniques and parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC). Microchem J 102:115–122
Guo ZB, Liu H, Wan SX, Hua KK, Wang DZ, Guo XS, He CL (2019) Fertilisation practice changes rhizosphere microbial community structure in the agroecosystem. Ann Appl Biol 174(2):123–132
Hammer O, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4(1):1–9
Haynes RJ (2000) Labile organic matter as an indicator of organic matter quality in arable and pastoral soils in New Zealand. Soil Biol Biochem 32(2):211–219
Haynes RJ (2005) Labile organic matter fractions as central components of the quality of agricultural soils: an overview. Adv Agron 85:221–268
He YT, Zhang WJ, Xu MG, Tong XG, Sun FX, Wang JZ, Huang SM, Zhu P, He XH (2015) Long-term combined chemical and manure fertilizations increase soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in aggregate fractions at three typical cropland soils in China. Sci Total Environ 532:635–644
Huang R, Wu YC, Zhang JB, Zhong WH, Jia ZJ, Cai ZC (2012) Nitrification activity and putative ammonia-oxidizing archaea in acidic red soils. J Soils Sediments 12(3):420–428
Huang S, Zhang WJ, Yu XC, Huang QR (2010) Effects of long-term fertilization on corn productivity and its sustainability in an Ultisol of southern China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 138(1–2):44–50
Huguet A, Vacher L, Relexans S, Saubusse S, Froidefond JM, Parlanti E (2009) Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde estuary. Org Geochem 40(6):706–719
Kalbitz K, Schmerwitz J, Schwesig D, Matzner E (2003) Biodegradation of soil-derived dissolved organic matter as related to its properties. Geoderma 113(3–4):273–291
Keeney DR (1982) Nitrogen—availability indices. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological Properties. SSSA Publ. Inc., Madison, pp 711–730
Li J, Wen YC, Li XH, Li YT, Yang XD, Lin ZA, Song ZZ, Cooper JM, Zhao BQ (2018) Soil labile organic carbon fractions and soil organic carbon stocks as affected by long-term organic and mineral fertilization regimes in the North China plain. Soil Tillage Res 175:281–290
Li L, Liu M, Li YL, Ma XY, Tang XX, Li ZP (2016) Changes in dissolved organic matter composition and metabolic diversity of bacterial community during the degradation of organic matter in swine effluent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(13):13498–13507
Li L, Liu M, Wu M, Jiang CY, Chen XF, Ma XY, Liu J, Li WT, Tang XX, Li ZP (2017) Effects of duckweed (Spriodela polyrrhiza) remediation on the composition of dissolved organic matter in effluent of scale pig farms. J Environ Sci 55:247–256
Liu J, Zhang J, Li DM, Xu CX, Xiang XJ (2020) Differential responses of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities to mineral and organic fertilization. Microbiol Open 9(1):e920
Ma L, Feng SY, Reidsma P, Qu FT, Heerink N (2014) Identifying entry points to improve fertilizer use efficiency in Taihu Basin, China. Land Use Policy 37:52–59
Manna MC, Swarup A, Wanjari RH, Mishra B, Shahi DK (2007) Long-term fertilization, manure and liming effects on soil organic matter and crop yields. Soil Tillage Res 94(2):397–409
McKnight DM, Boyer EW, Westerhoff PK, Doran PT, Kulbe T, Andersen DT (2001) Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity. Limnol Oceanogr 46(1):38–48
Mi WH, Wu LH, Brookes PC, Liu YL, Zhang X, Yang X (2016) Changes in soil organic carbon fractions under integrated management systems in a low-productivity paddy soil given different organic amendments and chemical fertilizers. Soil Tillage Res 163:64–70
Mouloubou OR, Prudent P, Mounier S, Boudenne JL, Abaker MG, Théraulaz F (2016) An adapted sequential chemical fractionation coupled with UV and fluorescence spectroscopy for calcareous soil organic matter study after compost amendment. Microchem J 124:139–148
Nguyen HVM, Lee MH, Hur J, Schlautman MA (2013) Variations in spectroscopic characteristics and disinfection byproduct formation potentials of dissolved organic matter for two contrasting storm events. J Hydrol 481:132–142
Ohno T (2002) Fluorescence inner-filtering correction for determining the humification index of dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 36(4):742–746
Olk DC, Bloom PR, Perdue EM, McKnight DM, Chen Y, Farenhorst A, Senesi N, Chin YP, Schmitt-Kopplin P, Hertkorn N, Harir M (2019) Environmental and agricultural relevance of humic fractions extracted by alkali from soils and natural waters. J Environ Qual 48(2):217–232
Pansu M, Gautheyrou J (2006) Handbook of soil analysis: mineralogical, organic and inorganic methods. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Richter DD, Hofmockel MS, Callaham MA, Powlson DS, Smith P (2007) Long-term soil experiments: keys to managing Earth’s rapidly changing ecosystems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71(2):266–279
Sanchez NP, Skeriotis AT, Miller CM (2013) Assessment of dissolved organic matter fluorescence PARAFAC components before and after coagulation–filtration in a full scale water treatment plant. Water Res 47(4):1679–1690
Santos CH, Nicolodelli G, Romano RA, Tadini AM, Villas-Boas PR, Montes CR, Mounier S, Milori DMBP (2015) Structure of humic substances from some regions of the amazon assessed coupling 3d fluorescence spectroscopy and cp/parafac. J Brazil Chem Soc 26(6):1136–1142
Shahid M, Nayak AK, Puree C, Tripathi R, Lal B, Gautam P, Bhattacharyya P, Mohanty S, Kumar A, Panda BB, Kumar U, Shukla AK (2017) Carbon and nitrogen fractions and stocks under 41 years of chemical and organic fertilization in a sub-humid tropical rice soil. Soil Tillage Res 170:136–146
Sims JR, Haby VA (1971) Simplified colorimetric determination of soil organic matter. Soil Sci 112(2):137–141
Smith P, Ashmore MR, Black HIJ, Burgess PJ, Evans CD, Quine TA, Thomson AM, Hicks K, Orr HG (2013) The role of ecosystems and their management in regulating climate, and soil, water and air quality. J Appl Ecol 50:812–829
Sun SH, Liu JJ, Li YF, Jiang PK, Chang SX (2013) Similar quality and quantity of dissolved organic carbon under different land use systems in two Canadian and Chinese soils. J Soils Sediments 13(1):34–42
Tong XG, Xu MG, Wang XJ, Bhattacharyya R, Zhang WJ, Cong RH (2014) Long-term fertilization effects on organic carbon fractions in a red soil of China. Catena 113:251–259
Wei WL, Yan Y, Cao J, Christie P, Zhang FS, Fan MS (2016) Effects of combined application of organic amendments and fertilizers on crop yield and soil organic matter: an integrated analysis of long-term experiments. Agric Ecosyst Environ 225:86–92
Wu M, Zhang JW, Bao YY, Liu M, Jiang CY, Feng YZ, Li ZP (2019) Long-term fertilization decreases chemical composition variation of soil humic substance across geographic distances in subtropical China. Soil Tillage Res 186:105–111
Xu MG, Lou YL, Sun XL, Wang W, Baniyamuddin M, Zhao K (2011) Soil organic carbon active fractions as early indicators for total carbon change under straw incorporation. Biol Fertil Soils 47:745–752
Zhang H, Xu M, Zhang F (2009) Long-term effects of manure application on grain yield under different cropping systems and ecological conditions in China. J Agric Sci 147(1):31–42
Zhang J, Liu J, Liu RL (2015) Effects of pyrolysis temperature and heating time on biochar obtained from the pyrolysis of straw and lignosulfonate. Bioresour Technol 176:288–291
Zhang SL, Sadras V, Chen XP, Zhang FS (2014) Water use efficiency of dryland maize in the Loess Plateau of China in response to crop management. Field Crop Res 163:55–63
Zhang YL, Zhang EL, Yin Y, van Dijk MA, Feng LQ, Shi ZQ, Liu ML, Qin BQ (2010) Characteristics and sources of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in lakes of the Yungui Plateau, China, differing in trophic state and altitude. Limnol Oceanogr 55(6):2645–2659
Zhu LQ, Hu NJ, Zhang ZW, Xu JL, Tao BR, Meng YL (2015) Short-term responses of soil organic carbon and carbon pool management index to different annual straw return rates in a rice–wheat cropping system. Catena 135:283–289
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous reviewers and editors for their helpful comments regarding the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported by the Major Research and Development Program for Science and Technology of Jiangxi Province (20182ABC28006) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41661052, 31660599, and 31560582).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human participant and/or animal rights and informed consent
None.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Weixin Ding
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 864 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Chen, X., Li, D. et al. Variation of soil dissolved organic carbon under long-term different fertilizations and its correlation with maize yields. J Soils Sediments 20, 2761–2770 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02631-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02631-1