Abstract
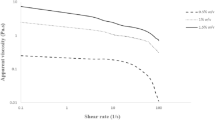
The effect of subsequent use of ultrasound and microwave on the physicochemical and rheological properties of galactomannan extracted from fenugreek seed (locally called as Shanbalileh) was investigated. Maximum yield of 18.54% was gained at optimized conditions: ultrasound power of 150 W, microwave power of 500 W, seed to water ratio of 1:30, and extraction time of 150 min. Chemical composition of the galactomannan was 7.03% (wb) moisture, 5.35% (db) ash, 0.85% (db) protein, 0.59% (db) lipid, and 85.89% (db) carbohydrate, respectively. FT-IR analysis admitted representative peaks of polysaccharide at 3400, 2920, 1620, 1400, and 1050/cm. Thermal analysis results revealed a melting range of 60–135 °C and degradation temperature of 280.54 °C. XRD pattern illustrated a large degree of crystallinity in the galactomannan structure. The results of SEM imaging indicated that the obtained galactomannan had a smooth surface. The steady shear flow experiments showed that the shear stress–shear rate, apparent viscosity–shear rate, and shear stress–time well fitted in Herschel–Bulkley, Carraeu, and Figuni–Shoemaker models. The samples with 0.5 and 1% w/v concentration demonstrated viscous-like and sample with 1.5% w/v indicated gel-like behavior upon strain and frequency sweep tests. Other parameters including bulk and tapped density, powder cohesiveness, powder compressibility index, DPPH-free radical scavenging activity, powder solubility, water holding capacity (WHC), and oil holding capacity (OHC) were also evaluated.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, Z., Wang, Y., Anjum, N., Ahmad, A., & Raza, M. (2013). Characterization of new exopolysaccharides produced by coculturing L. kefiranofaciens with yogurt strains. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 59, 377–383.
Alpizar-Reyes, E., Roman-Guerrero, A., Gallardo-Rivera, R., Varela-Guerrero, V., Cruz-Olivares, J., & Perez-Alonso, C. (2017). Rheological properties of tamarind (Tamarindus indica L.) seed mucilage obtained by spray-drying as a novel source of hydrocolloid. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 107, 817 - 824.
Asha, D., & Shastri, P. N. (2004). Changes in structure, fat binding and water absorption of starch during roasting of wheat and legalactomannane flour. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 41, 681–683.
Belafi-Bako, K., Cserjesi, P., Beszedes, S., Csanadi, Z., & Hodur, C. (2012). Berry pectins: microwave-assisted extraction and rheological properties. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5, 1100–1105.
Bothara, S. B., & Singh, S. (2012). Thermal studies on natural polysaccharides. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 2(2), 1031–1035.
Brummer, Y., Cui, W., & Wang, Q. (2003). Extraction, purification and physicochemical characterization of fenugreek galactomannan. Food Hydrocolloids, 17, 229–236.
Builers, P. F., Mbah, C. C., & Attama, A. A. (2012). Intrinsic and functional properties of a gelling galactomannan from Dioclea reflexa: a potential pharmaceutical excipient. British Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2, 50–68.
Caliskan, G., & Dirim, S. N. (2016). The effect of different drying processes and the amounts of maltodextrin addition on the powder properties of sumac extract powders. Powder Technology, 287, 308–314.
Cano-Chauca, M., Stringheta, P. C., Ramos, A. M., & Cal-Vidal, J. (2005). Effect of the carriers on the microstructure of mango powder obtained by spray drying and its functional characterization. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 6, 420–428.
Cengiz, E., Dogan, M., & Karaman, S. (2013). Characterization of rheological interactions of Gleditsia triacanthos galactomannan with some hydrocolloids: effect of hydration temperature. Food Hydrocolloids, 32, 453–462.
Cerqueira, M. A., Souza, B. W. S., Simoes, J., Teixeira, J. A., Domingues, M. R. M., Coimbra, M. A., & Vicente, A. A. (2011). Structural and thermal characterization of galactomannans from non-conventional sources. Carbohydrate Polymers, 83(1), 179–185.
Chang, Y., Cui, S., Roberts, K., Ng, P., & Wang, Q. (2011). Evaluation of extrusion-modified fenugreek galactomannan. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(5), 1296–1301.
Chemat, S., & Esveld, E. D. C. (2013). Contribution of microwaves or ultrasonics on carvone and limonene recovery from dill fruits (Anethum graveolens L.). Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 17, 114–119.
Chen, Y., Gu, X., Huang, S., Li, J., Wang, X., & Tang, J. (2010). Optimization of ultrasonic/microwave assisted extraction (UMAE) of polysaccharides from Inonotus obliquus and evaluation of its anti-tumor activities. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 46(4), 429–435.
Cheng, H., Feng, S., Jia, X., Li, Q., Zhou, Y., & Ding, C. (2013). Structural characterization and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides extracted from Epimedium acuminatum. Carbohydrate Polymers, 92(1), 63–68.
Cheung, Y., Siu, K., & Wu, J. (2013). Kinetic models for ultrasound-assisted extraction of water-soluble components and polysaccharides from medicinal fungi. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6, 2659–2665.
Clark, A.H., & Ross-Murphy, S.B. (1987). Structural and mechanical properties of biopolymer gels. In Biopolymers (pp. 57–192). Springer.
Dakia, P. A., Blecker, C., Roberta, C., Watheleta, B., & Paquota, M. (2008). Composition and physicochemical properties of locust bean galactomannan extracted from whole seeds by acid or water dehulling pre-treatment. Food Hydrocolloids, 22, 807–818.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P. A., & Smith, F. (1956). Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry, 28(3), 350–356.
Felkai-Haddache, L., Remini, H., Dulong, V., Mamou-Belhabib, K., Picton, L., Madani, K., & Rihouey, C. (2016). Conventional and microwave-assisted extraction of mucilage from Opuntia ficus-indica cladodes: physico-chemical and rheological properties. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 9, 481–492.
Feng, K., Cheng, H., Fu, L., Ding, C., Zhang, L., Yang, R., & Zhou, Y. (2014). Ultrasonic-assisted extraction and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Camellia oleifera leaves. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 68, 7–12.
Figoni, P. I., & Shoemaker, C. F. (1983). Characterization of time dependant flow properties of mayonnaise under steady shear. Journal of Texture Studies, 14, 431–442.
Gorgani, L., Mohammadi, M. D., Najafpour, G., & Nikzad, M. (2017). Sequential microwave-ultrasound-assisted extraction of piperine from black pepper (Piper nigrum L.). Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10, 2199–2207.
Goula, A. M., & Adamopoulos, K. G. (2004). Influence of spray drying conditions on residue accumulation–simulation using CFD. Drying Technology, 22, 1107–1128.
Granizo, D. P., Reuhs, B. L., Stroshine, R., & Mauer, L. J. (2007). Evaluating the solubility of powdered food ingredients using dynamic nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) relaxometry. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 40(1), 36–42.
Gupta, S. K., Kalaiselvan, V., Srivastava, S., Saxena, R., & Agrawal, S. S. (2010). Trigonella foenum-graecum (Fenugreek) protects against selenite-induced oxidative stress in experimental cataractogenesis. Biological Trace Element Research, 136(3), 533–542.
Han, L., Suo, Y., Yang, Y., Meng, J., & Hu, N. (2016). Optimization, characterization and biological activity of polysaccharides from Berberis dasystachya Maxim. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 85, 655–666.
Hu, J., Jia, X., Fang, X., Li, P., He, C., & Chen, M. (2016). Ultrasonic extraction, antioxidant and anticancer activities of novel polysaccharides from Chuanxiong rhizome. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 85, 277–284.
Imeson, A. (2011). Food stabilizers, thickeners and gelling agents. John Wiley and Sons.
Jia, X. J., Ding, C. B., Yuan, S., Zhang, Z. W., Du, L., & Yuan, M. (2014). Extraction, purification and characterization of polysaccharides from hawk tea. Carbohydrate Polymers, 99, 319–324.
Jiang, J., Zhu, L., Zhang, W., & Sun, R. (2007). Characterization of galactomannan gum from fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) seeds and its rheological properties. International Journal of Polymeric Materials, 56(12), 1145–1154.
Jiang, Y., Du, Y., Zhu, X., Xiong, H., Woo, M. W., & Hu, J. (2012). Physicochemical and comparative properties of pectins extracted from Akebia trifoliate var. australis peel. Carbohydrate Polymers, 87(2), 1663–1669.
Jiang, Y., Koteswara Reddy, C., Huang, K., Chen, L., & Xu, B. (2019). Hydrocolloidal properties of flaxseed galactomannan/konjac glucomannan compound gel. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 133, 1156–1163.
Jinapong, N., Suphantharika, M., & Jamnong, P. (2003). Production of instant soymilk powders by ultrafiltration, spray drying and fluidized bed agglomeration. Journal of Food Engineering, 84, 194–205.
Jouki, M., Mortazavi, S., Tabatabaei Yazdi, F., & Koocheki, A. (2014). Optimization of extraction, antioxidant activity and functional properties of quince seed mucilage by RSM. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 66, 113–124.
Khounvilay, K., & Sittikijyothin, W. (2012). Rheological behaviour of tamarind seed galactomannan in aqueous solutions. Food Hydrocolloids, 26, 334–338.
Kia, A., Ganjloo, A., & Bimakr, M. (2018). A short extraction time of polysaccharides from fenugreek (Trigonella foencem graceum) seed using continuous ultrasound acoustic cavitation: process optimization, characterization and biological activities. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 11, 2204–2216.
Kong, L., Yu, L., Feng, T., Yin, X., Liu, T., & Dong, L. (2015). Physicochemical characterization of the polysaccharide from Bletilla striata: effect of drying method. Carbohydrate Polymers, 125, 1–8.
Kumar, D., Singhal, A., Bansal, S., & Gupta, S. (2015). Extraction, isolation and evaluation Trigonella foenum-graecum as mucoadhesive agent for nasal gel drug delivery. Journal of Nepal Pharmaceutical Association, 27(1), 40–45.
Kumar Singh, A., Panner Selvam, R., & Sivakumar, T. (2010). Isolation, characterization and formulation properties of a new plant galactomannan obtained from Mangifera indica. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Research, 1, 35–41.
Kurita, O., Fujiwara, T., & Yamazaki, E. (2008). Characterization of pectin extracted from citrus peel in the presence of citric acid. Carbohydrate Polymers, 74(3), 725–730.
Kutz, M. (2013). Handbook of farm, dairy and food machinery engineering. Academic Press.
Li, J., Yuan, W., Deng, C., & Zhu, H. (2017). Porous SiC/SiCN composite ceramics fabricated by foaming and reaction sintering. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 37(3), 1131–1134.
Li, Q., Yu, N., Wang, Y., Sun, Y., Lu, K., & Guan, W. (2013). Extraction optimization of Bruguiera gymnorrhiza polysaccharides with radical scavenging activities. Carbohydrate Polymers, 96(1), 148–155.
Liu, F., Hou, R. H., Liao, S. T., Zou, Y. X., & Xiao, G. S. (2015). Optimization of ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction conditions for polysaccharides from Mulberry (Morus atropurpurea Roxb) leaves and evaluation of antioxidant activities in vitro. Medicinal Chemistry, 5, 90–95.
Lopez-Franco, Y., Cervantes-Montano, C., Martinez-Robinson, K., Lizardi-Mendoza, J., & Robles-Ozuna, L. (2013). Physicochemical characterization and functional properties of galactomannans from mesquite seeds (Prosopis spp.). Food Hydrocolloids, 30(2), 656–660.
Lu, X., Zheng, Z., Li, H., Cao, R., Zheng, Y., Yu, H., Xiao, J., Miao, S., & Zheng, B. (2017). Optimization of ultrasonic–microwave assisted extraction of oligosaccharides from lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seeds. Industrial Crops and Products, 107, 546–557.
Ma, C. W., Feng, M., Zhai, X., Hu, M., You, L., Luo, W., & Zhao, M. (2013). Optimization for the extraction of polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum and their antioxidant and antiproliferative activities. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 44(6), 886–894.
Mirhosseini, H., & Tabatabaee Amid, B. (2013). Effect of different drying techniques on flowability characteristics and chemical properties of natural carbohydrate–protein galactomannan from durian fruit seed. Chemistry Central Journal, 7, 1–8.
Morris, E. R. (1990). Shear-thinning of random coil polysaccharides: characterization by two parameters from a simple linear plot. Carbohydrate Polymers, 13, 85–96.
Naji, S., Razavi, S. M. A., & Karazhiyan, H. (2012). Effect of thermal treatments on functional properties of cress seed (Lepidium sativum) and xanthan galactomannans: a comparative study. Food Hydrocolloids, 28, 75–81.
Naji-Tabasi, S., Razavi, S. M. A., Mohebbi, M., & Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. (2016). New studies on basil (Ocimum bacilicum L.) seed galactomannan: part 1 – fractionation, physicochemical and surface activity characterization. Food Hydrocolloids, 52, 350–358.
Naqavi, S. A., Khan, M., Shahid, M., Jaskani, M., Khan, I. A., & Zuber, M. (2011). Biochemical profiling of mucilage extracted from seeds of different citrus rootstocks. Carbohydrate Polymers, 83(2), 623–628.
Nep, E.l., & Conway, B. R. (2011). Physicochemical characterization of Grewia polysaccharide galactomannan: effect of drying method. Carbohydrate Polymers, 84, 446–453.
Niknam, R., Ghanbarzadeh, B., Ayaseh, A., & Rezagholi, F. (2018). The effects of Plantago major seed gum on steady and dynamic oscillatory shear rheology of sunflower oil-in-water emulsions. Journal of Texture Studies, 49(5), 536–547.
Niknam, R., Ghanbarzadeh, B., Ayaseh, A., & Adun, P. (2019a). Comprehensive study of intrinsic viscosity, steady and oscillatory shear rheology of Barhang seed hydrocolloid in aqueous dispersions. Journal of Food Process Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.13047.
Niknam, R., Ghanbarzadeh, B., Ayaseh, A., & Hamishehkar, H. (2019b). Plantago major seed galactomannan based biodegradable films: effects of various plant oils on microstructure and physicochemical properties of emulsified films. Polymer Testing, 77, 105868.
Niknam, R., Ghanbarzadeh, B., Ayaseh, A., & Rezagholi, F. (2019c). The hydrocolloid extracted from Plantago major seed: effects on emulsifying and foaming properties. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2019.1610426.
Noshad, M., Mohebbi, M., Shahidi, F., & Mortazavi, S. A. (2012). Multi-objective optimization of osmotic-ultrasonic pretreatments and hot air drying of quince using response surface methodology. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5, 2098–2110.
Phimolsiripol, Y., Siripatrawan, U., & Cleland, D. J. (2011). Weight loss of frozen bread dough under isothermal and fluctuating temperature storage conditions. Journal of Food Engineering, 106(2), 134–143.
Rao, M., & Kenny, J. (1975). Flow properties of selected food galactomannans. Canadian Institute of Food Science and Technology Journal, 8, 142–148.
Rashid, F., Hussain, S., & Ahmed, Z. (2018). Extraction purification and characterization of galactomannan from fenugreek for industrial utilization. Carbohydrate Polymers, 180, 88–95.
Razavi, S. M. A., Taheri, H., & Quinchia, L. A. (2011). Steady shear flow properties of wild sage (Salvia macrosiphon) seed galactomannan as a function of concentration and temperature. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(3), 451–458.
Robertson, J. A., de Monredon, F. D., Dysseler, P., Guillon, F., Amado, R., & Thibault, J. F. (2000). Hydration properties of dietary fiber and resistant starch: a European collaborative study. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 33(2), 72–79.
Rostami, H., & Gharibzahedi, S. M. T. (2017). Cellulase-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Malva sylvestris: process optimization and potential functionalities. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 101, 196–206.
Samavati, V., Lorestani, M., & Joolazadeh, S. (2014). Identification and characterization of hydrocolloid from Cordia myxa leaf. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 65, 215–221.
Steffe, J. F. (1996). Rheological methods in food process engineering (2nd ed.). Michigan: Freeman Press.
Sun, H., Li, C., Ni, Y., Yao, L., Jiang, H., Ren, X., Fu, Y., & Zhao, C. (2019). Ultrasonic/microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Camptotheca acuminata fruits and its antitumor activity. Carbohydrate Polymers, 206, 557 - 564.
Tabatabaee Amid, B., & Mirhosseini, H. (2012). Optimization of aqueous extraction of galactomannan from durian (Durio zibethinus) seed: a potential, low cost source of hydrocolloid. Food Chemistry, 132(3), 1258–1268.
Thanatcha, R., & Pranee, A. (2011). Extraction and characterization of mucilage in Ziziphus mauritiana Lam. International Food Research Journal, 18, 201–212.
Thirugnanasambandham, K., Sivakumar, V., & Maran, J. P. (2015). Microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from mulberry leaves. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 72, 1–5.
Tiu, C., & Boger, D. V. (1974). Complete rheological characterization of time-dependant food products. Journal of Texture Studies, 5, 329–338.
Torres, M. D., Hallmark, B., & Wilson, D. I. (2014). Effect of concentration on shear and extensional rheology of guar galactomannan solutions. Food Hydrocolloids, 40, 85–95.
Vendruscolo, C. W., Ferrero, C., Pineda, E. A. G., Silveira, J. L. M., Freitas, R. A., Jimenez-Castellanos, M. R., & Bresolin, T. M. B. (2009). Physicochemical and mechanical characterization of galactomannan from Mimosa scabrella: effect of drying method. Carbohydrate Polymers, 76(1), 86–93.
Wang, P., Luo, J., Wang, X. B., Fan, B. Y., & Kong, L. Y. (2015). New indole glucosides as biosynthetic intermediates of camptothecin from the fruits of Camptotheca acuminate. Fitoterapia, 103, 1–8.
Wani, S., & Kumar, P. (2018). Fenugreek: a review on its nutraceutical properties and utilization in various food products. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, 17, 97–106.
Xie, J. H., Shen, M. Y., Xie, M. Y., Nie, S. P., Chen, Y., Li, C., Huang, D. F., & Wang, Y. X. (2012). Ultrasonic-assisted extraction, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja polysaccharides. Carbohydrate Polymers, 89(1), 177–184.
Xiong, Y., Li, Q., Miao, S., Zhang, Y., Zheng, B., & Zhang, L. (2019). Effect of ultrasound on physicochemical properties of emulsion stabilized by fish myofibrillar protein and xanthan galactomannan. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 54, 225–234.
Yadav, M. P., Moreau, R. A., Hotchkiss, A. T., & Hicks, K. B. (2012). A new corn fiber galactomannan polysaccharide isolation process that preserves functional components. Carbohydrate Polymers, 87(2), 1169–1175.
Yamazaki, E., Kurita, O., & Matsumura, Y. (2009). High viscosity of hydrocolloid from leaves of Corchorus olitorius L. Food Hydrocolloids, 23(3), 655–660.
Yang, N., Jin, Y., Jin, Z., & Xu, X. (2016). Electric-field-assisted extraction of garlic polysaccharides via experimental transformer device. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 9, 1612–1622.
Ye, J., Hua, X., Wang, M., Zhang, W., & Yang, R. (2019). Effect of extraction ph on the yield and physicochemical properties of polysaccharides extracts from peanut sediment of aqueous extraction process. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 137–144.
Zheng, Y., Cui, J., Chen, Z., & Wei, X. (2019). Optimization of ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction and hepatoprotective activities of polysaccharides from Trametes orientalis. Molecules, 24(1), 147–154.
Zohuriaan, M., & Shokrolahi, F. (2004). Thermal studies on natural and modified galactomannans. Polymer Testing, 23(5), 575–579.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niknam, R., Mousavi, M. & Kiani, H. New Studies on the Galactomannan Extracted from Trigonella foenum-graecum (Fenugreek) Seed: Effect of Subsequent Use of Ultrasound and Microwave on the Physicochemical and Rheological Properties. Food Bioprocess Technol 13, 882–900 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02437-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02437-6