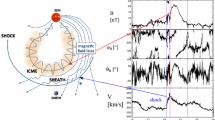
Abstract
ICMEs (interplanetary coronal mass ejections), the heliospheric counterparts of what is observed with coronagraphs at the Sun as CMEs, have been the subject of intense interest since their close association with geomagnetic storms was established in the 1980s. These major interplanetary plasma and magnetic field transients, often preceded and accompanied by solar energetic particles (SEPs), interact with planetary magnetospheres, ionospheres, and upper atmospheres in now fairly well-understood ways, although their details and context affect their overall impacts. The term ICME as it is used here refers to the complete solar-wind plasma and field disturbance, including the leading shock (if present), the compressed, deflected solar-wind plasma and the field behind the shock (“sheath”), and the coronal ejecta (the “driver”) – often called a magnetic cloud. Many uncertainties remain in understanding both the relationship to what is observed at the Sun and the variety of local outcomes suggested by in-situ observations. This impacts our abilities to interpret events and to forecast effects based on solar observations. Here, we briefly consider what is known about ICMEs and their evolution en route from the Sun from the combination of available observations and interpretive models that have been developed up to now. The included references are only representative of the large body of work that has been published on this subject. Our aim is to provide the reader with an updated synthesis of research results in this still active area of heliophysics at the dawn of the Parker Solar Probe (PSP) and Solar Orbiter (SO) mission era.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Haddad, N., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Savani, N.P., Möstl, C., Marubashi, K., Hidalgo, M.A., Roussev, I.I., Poedts, S., Farrugia, C.J.: 2013, Magnetic field configuration models and reconstruction methods for interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys.284, 129. DOI . ADS .
Al-Haddad, N., Poedts, S., Roussev, I., Farrugia, C.J., Yu, W., Lugaz, N.: 2019, The magnetic morphology of magnetic clouds: multi-spacecraft investigation of twisted and writhed coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J.870, 100. DOI .
Arge, C.N., Pizzo, V.J.: 2000, Improvement in the prediction of solar wind conditions using near-real time solar magnetic field updates. J. Geophys. Res.105, 10469.
Attrill, G.D.R., Harra, L.K., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Démoulin, P.: 2007, Coronal “wave”: magnetic footprint of a coronal mass ejection? Astrophys. J. Lett.656, L101.
Bain, H.M., Mays, M.L., Luhmann, J.G., Li, Y., Jian, L.K., Odstrcil, D.: 2016, Shock connectivity in the August 2010 and July 2012 solar energetic particle events inferred from observations and ENLIL modeling. Astrophys. J.825, 1. DOI .
Baker, D.N., Poh, G., Odstrcil, D., Arge, C.N., Benna, M., Johnson, C.L., et al.: 2013, Solar wind forcing at Mercury: WSA-ENLIL model results. J. Geophys. Res.118, 45. DOI .
Blanco-Cano, X., Kajdic, P., Aguilar-Rodríguez, E., Russell, C.T., Jian, L.K., Luhmann, J.G.: 2016, Interplanetary shocks and foreshocks observed by STEREO during 2007-2010. J. Geophys. Res.121, 992. DOI .
Borovsky, J.E., Denton, M.H.: 2006, Differences between CME-driven storms and CIR-driven storms. J. Geophys. Res.111, A07S08. DOI .
Borvikov, D., Sokolov, I.V., Manchester, W.B., Jin, M., Gombosi, T.: 2017, Eruptive event generator based on the Gibson-low magnetic configuration. J. Geophys. Res.122, 7974.
Bougeret, J.-L., Kaiser, M.L., Kellogg, P.J., Manning, R., Goetz, K., Monson, S.J., Monge, N., Friel, L., Meetre, C.A., Perche, C., Sitruk, L., Hoang, S.: 1995, WAVES: the radio and plasma wave investigation on the wind spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev.71, 231.
Burlaga, L.F., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock: Voyager, Helios and IMP-8 observations. J. Geophys. Res.86, 6673.
Burns, A.G., Solomon, S.C., Wang, W., Killeen, T.L.: 2007, The ionospheric and thermospheric response to CMEs: challenges and successes. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.69, 77. DOI .
Cane, H.V., Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Howard, R.A.: 1987, Energetic interplanetary shocks, radio emission, and coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res.92, 9869.
Cane, H.V., Stone, R.G.: 1984, Type II solar radio bursts, interplanetary shocks, and energetic particle events. Astrophys. J.282, 339.
Chen, P.F., Fang, C., Shibata, K.: 2005, A full view of EIT waves. Astrophys. J.622, 1202.
Chen, J., Howard, R.A., Brueckner, G.E., Santoro, R., Krall, J., Paswaters, S.E., St. Cyr, O.C., Schwenn, R., Lamy, P., Simnett, G.M.: 1997, Evidence of an erupting magnetic flux rope: LASCO coronal mass ejection of 1997 April 13. Astrophys. J. Lett.490, L191. DOI .
Chi, Y., Shen, C., Wang, Y.: 2016, Statistical study of the interplanetary coronal mass ejections from 1995 to 2015. Solar Phys.291, 2419. DOI . ADS .
Cho, K.-S., Park, S.-H., Marubashi, K., Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Kim, R.-S., Lim, E.-K.: 2013, Comparison of helicity signs in interplanetary CMEs and their solar source regions. Solar Phys.284, 105. DOI . ADS .
Cohen, C.M.S.: 2006, Observations of energetic storm particles: an overview, in solar eruptions and energetic particles. In: Gopalswamy, N., Mewaldt, R., Torsti, J. (eds.) Geophys. Monogr. Ser.165, 275. DOI .
Cohen, O., Attrill, G.D., Manchester, W.B., Wills-Davey, M.J.: 2009, Numerical simulation of an EUV coronal wave based on the 2009 February 13 CME event observed by STEREO. Astrophys. J.705, 587.
Conner, H.K., Zesta, E., Fedrizzi, M., Shi, Y., Raeder, J., Codrescu, M.V., Fuller-Rowell, T.J.: 2016, Modeling the ionosphere-thermosphere response to a geomagnetic storm using physics-based magnetospheric energy input: OpenGGCM-CTIM results. J. Space Weather Space Clim.6, A25. DOI .
Cremades, H.: 2018, Pursuing forecasts of the behavior and arrival of coronal mass ejections through modeling and observations. In: Foullon, C., Malandraki, O. (eds.) Space Weather of the Heliosphere: Processes and Forecasts, Proc. Inter. Astron. Union S33513, 58. DOI .
Cremades, H., Iglesias, F.A., St. Cyr, O.C., Xie, H., Kaiser, M.L., Gopalswamy, N.: 2015, Low-frequency type-II radio detections and coronagraph data employed to describe and forecast the propagation of 71 CMEs/shocks. Solar Phys.290, 2455. DOI . ADS .
Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H., Démoulin, P., Luoni, M.L.: 2006, A new model-independent method to compute magnetic helicity in magnetic clouds. Astron. Astrophys.455, 349. DOI .
Dasso, S., Nakwacki, M.S., Démoulin, P., Mandrini, C.H.: 2007, Progressive transformation of a flux rope to an ICME. Comparative analysis using the direct and fitted expansion methods. Solar Phys.284, 115. DOI .
Delannée, C., Török, T., Aulanier, G., Hochedez, J.F.: 2008, A new model for propagating parts of EIT waves: a current shell in a CME. Solar Phys.247, 123. DOI . ADS .
Ding, L.-G., Wang, Z.-W., Feng, L., Li, G., Jiang, Y.: 2019, Is the enhancement of type II radio bursts during CME interactions related to the associated solar energetic particle event? Res. Astron. Astrophys.19, 5.
Downs, C., Roussev, I.I., van der Holst, B., Lugaz, N., Sokolov, I.V., Gombosi, T.I.: 2011, Studying extreme ultraviolet wave transients with a digital laboratory: direct comparison of extreme ultraviolet wave observations to global magnetohydrodynamic simulations. Astrophys. J.728, 2.
Fan, Y., Gibson, S.E.: 2007, Onset of coronal mass ejections due to loss of confinement of coronal flux ropes. Astrophys. J.668, 1232.
Farrugia, C.J., Berdichevsky, D.B., Möstl, C., Galvin, A.B., Leitner, M., Popecki, M.A., Simunac, K.D.C., Opitz, A., Lavraud, B., Ogilvie, K.W., Veronig, A.M., Temmer, M., Luhmann, J.G., Sauvaud, J.A.: 2011, Multiple, distant (40°) in situ observations of a magnetic cloud and a corotating interaction region complex. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.73, 1254. DOI .
Fisher, R.R., Munro, R.H.: 1984, Coronal transient geometry. I. The flare-associated event of 1981 March 25. Astrophys. J.280, 428.
Forbes, T.G.: 2000, A review on the genesis of coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res.105, 23153.
Fox, N.J., Velli, M.C., Bale, S.D., Decker, R., Driesman, A., Howard, R.A., Kasper, J.C., Kinnison, J., Kusterer, M., Lario, D., Lockwood, M.K., McComas, D.J., Raouafi, N.E., Szabo, A.: 2016, The solar probe plus mission: humanity’s first visit to our star. Space Sci. Rev.204, 7. DOI .
Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T.: 1987, Criteria of interplanetary parameters causing intense magnetic storms (Dst < 100 nT). Planet. Space Sci.35, 1101.
Good, S.W., Forsyth, R.J.: 2016, Interplanetary coronal mass ejections observed by MESSENGER and Venus Express. Solar Phys.291, 239. DOI . ADS .
Good, S.W., Forsyth, R.J., Raines, J.M., Gershman, D.J., Slavin, J.A., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2015, Radial evolution of a magnetic cloud: MESSENGER, STEREO, and Venus Express observations. Astrophys. J.807, 177.
Good, S.W., Kilpua, E.K.J., LaMoury, A.T., Forsyth, R.J., Eastwood, J.P., Möstl, C.: 2019, Self-similarity of ICME flux ropes: observations by radially aligned spacecraft in the inner heliosphere. J. Geophys. Res.124, 4960. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N.: 2006a, Properties of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Space Sci. Rev.124, 145.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2006b, Coronal mass ejections and type II radio bursts. In: Gopalswamy, N., Mewaldt, R., Torsti, J. (eds.) Solar Eruptions and Energetic Particles, Geophys. Monogr. Ser.165, Am. Geophys. Union, Washington, 207.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2008, Solar connections of geoeffective magnetic structures. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.70, 2078.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2011, Coronal mass ejections and solar radio emissions. In: Rucker, H.O., Kurth, W.S., Louarn, P., Fischer, G. (eds.) Planetary Radio Emissions VII, Proc. 7th Internat. Workshop on Planetary, Solar Heliospheric Radio Emissions, Austrian Acad. Sci. Press, Vienna, 325.
Gopalswamy, N.: 2016, History and development of coronal mass ejections as a key player in solar terrestrial relationship. Geosci. Lett.3, 8.
Gopalswamy, N., Tsurutani, B., Yan, Y.: 2015, Short-term variability of the Sun-Earth system: an overview of progress made during the CAWSES-II period. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci.2, 13.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S.: 2011, The strength and radial profile of the coronal magnetic field from the standoff distance of a coronal mass ejection-driven shock. Astrophys. J. Lett.736, L17.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2001a, Radio signatures of coronal mass ejection interaction: coronal mass ejection cannibalism? Astrophys. J. Lett.548, L91.
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A.: 2001b, Predicting the 1-AU arrival times of coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res.106, 29207.
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Kaiser, M.L., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2001c, Near-Sun and near-Earth manifestations of solar eruptions. J. Geophys. Res.106, 25261.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Reames, D.V., Leske, R., von Rosenvinge, T.: 2002, Interacting coronal mass ejections and solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. Lett.572, L103.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Krucker, S., Stenborg, G., Howard, R.A.: 2004, Intensity variation of large solar energetic particle events associated with coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res.109, A12105.
Gopalswamy, N., Aguilar-Rodriguez, E., Yashiro, S., Nunes, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A.: 2005, Type II radio bursts and energetic solar eruptions. J. Geophys. Res.110, A12S07.
Gopalswamy, N., Dal Lago, A., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S.: 2009a, The expansion and radial speeds of coronal mass ejections. Cent. Eur. Astrophys. Bull.33, 115.
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S.: 2009b, CME interactions with coronal holes and their interplanetary consequences. J. Geophys. Res.114, 0A22G.
Gopalswamy, N., Thompson, W.T., Davila, J.M., Kaiser, M.L., Yashiro, S., Mäkelä, P., Michalek, G., Bougeret, J.-L., Howard, R.A.: 2009c, Relation between type II bursts and CMEs inferred from STEREO observations. Solar Phys.259, 227. DOI . ADS .
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2010, Interplanetary shocks lacking type II radio bursts. Astrophys. J.710, 1111.
Gopalswamy, N., Nitta, N., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P., Yashiro, S.: 2012a, Coronal magnetic field measurement from EUV images made by the Solar Dynamics Observatory. Astrophys. J.744, 72.
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., MacDowall, R.J., Kaiser, M.L.: 2012b, Radio-loud CMEs from the disk center lacking shocks at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.117, 8106.
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P., Usoskin, I.G.: 2012c, Properties of ground level enhancement events and the associated solar eruptions during solar cycle 23. Space Sci. Rev.171, 23.
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S., Xie, H., Yashiro, S., Reinard, A.A.: 2013a, The solar connection of enhanced heavy ion charge states in the interplanetary medium: implications for the flux-rope structure of CMEs. Solar Phys.284, 17. DOI . ADS .
Gopalswamy, N., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Hidalgo, M., Zhang, J., Riley, P., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Mandrini, C.H.: 2013b, Preface. Solar Phys.284, 1. DOI . ADS .
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Xie, H., Yashiro, S.: 2013c, Testing the empirical shock arrival model using quadrature observations. Space Weather11, 661.
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S., Uddin, W., Srivastava, A.K., Joshi, N.C., Chandra, R., Manoharan, P.K., Mahalakshmi, K., Dwivedi, V.C., Jain, R., Awasthi, A.K., Nitta, N.V., Aschwanden, M.J., Choudhary, D.P.: 2013d, Height of shock formation in the solar corona inferred from observations of type II radio bursts and coronal mass ejections. Adv. Space Res.51, 1981.
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Usoskin, I.G., Davila, J.M.: 2013e, The first ground level enhancement event of solar cycle 24: direct observation of shock formation and particle release heights. Astrophys. J. Lett.765, L30.
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P.A., Yashiro, S.: 2014a, Major solar eruptions and high-energy particle events during solar cycle 24. Earth Planets Space66, 104.
Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Michalek, G.: 2014b, Anomalous expansion of coronal mass ejections during solar cycle 24 and its space weather implications. Geophys. Res. Lett.41, 2673.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P.: 2015a, Properties and geoeffectiveness of magnetic clouds during solar cycles 23 and 24. J. Geophys. Res.120, 9221.
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Thakur, N.: 2015b, CMEs during the two activity peaks in cycle 24 and their space weather consequences. Sun Geosph.10, 111.
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Thakur, N., Kahler, S.W.: 2015c, Large solar energetic particle events associated with filament eruptions outside of active regions. Astrophys. J.806, 8.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Thakur, N., Mäkelä, P., Xie, H., Akiyama, S.: 2016, The 2012 July 23 backside eruption: an extreme energetic particle event? Astrophys. J.833, 216.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S., Xie, H.: 2017a, Estimation of reconnection flux using post-eruption arcades and its relevance to magnetic clouds at 1 AU. Solar Phys.292, 65. DOI . ADS .
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Yashiro, S., Thakur, N., Akiyama, S., Xie, H.: 2017b, A hierarchical relationship between the fluence spectra and CME kinematics in large solar energetic particle events: a radio perspective. J. Phys.CS-900, 012009.
Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Xie, H.: 2018a, Coronal flux ropes and their interplanetary counterparts. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.180, 35.
Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Xie, H.: 2018b, A new technique to provide realistic input to CME forecasting models. In: Foullon, C., Malandraki, O. (eds.) Space Weather of the Heliosphere: Processes and Forecasts, Proc. Inter. Astron. Union S33513, 258. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Mäkelä, P., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Monstein, C.: 2018c, Extreme kinematics of the 2017 September 10 solar eruption and the spectral characteristics of the associated energetic particles. Astrophys. J. Lett.863, L39.
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Thakur, N.: 2018d, Sun-to-Earth propagation of the 2015 June 21 coronal mass ejection revealed by optical, EUV, and radio observations. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.179, 225.
Gosling, J.T.: 1993, The solar flare myth. J. Geophys. Res.98, 18937.
Green, L.M., Török, T., Vršnak, B., Manchester, W., Veronig, A.: 2018, The origin and early evolution of solar eruptions. Space Sci. Rev.214, 46. DOI .
Gruesbeck, J.R., Lepri, S.T., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2012, Two-plasma model for low charge state interplanetary coronal mass ejection observations. Astrophys. J.760, 141.
Harrison, R.A., Davies, J.A., Möstl, C., Liu, Y., Temmer, M., Bisi, M.M., Eastwood, J.P., de Koning C.A., Nitta, A., Rollett, T.: 2012, An analysis of the origin and propagation of the multiple coronal mass ejections of 2010 August 1. Astrophys. J.750, 45. DOI .
Harrison, R.A., Davies, J.A., Barnes, D., Byrne, J.P., Perry, C.H., Bothmer, V., Eastwood, J.P., Gallagher, P.T., Kilpua, E.K.J., Möstl, C., Rodriguez, L., Rouillard, A.P., Odstrcil, D.: 2018, CMEs in the heliosphere: I. A statistical analysis of the observational properties of CMEs detected in the heliosphere from 2007 to 2017 by STEREO/HI-1. Solar Phys.293, 77. DOI . ADS .
He, W., Liu, Y.D., Hu, H., Wang, R., Zhao, X.: 2018, A stealth CME bracketed between slow and fast wind producing unexpected geoeffectiveness. Astrophys. J.860, 78.
Hess, P., Colaninno, R.C.: 2017, Comparing automatic CME detections in multiple LASCO and SECCHI catalogs. Astrophys. J.836, 134.
Hess, P., Zhang, J.: 2014, Stereoscopic study of the kinematic evolution of a coronal mass ejection and its driven shock from the Sun to the Earth and the prediction of their arrival times. Astrophys. J.792, 49.
Howard, T.A., Simnett, G.: 2008, Interplanetary coronal mass ejections that are undetected by solar coronagraphs. J. Geophys. Res.113, A08102. DOI .
Hu, Q., Qiu, J., Dasgupta, B., Khare, A., Webb, G.M.: 2014, Structures of interplanetary magnetic flux ropes and comparison with their solar sources. Astrophys. J.793, 2014.
Isavnin, A.: 2016, FRiED: a novel three-dimensional model of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J.833, 267.
Isavnin, A., Vourlidas, A., Kilpua, E.K.J.: 2013, Three-dimensional evolution of erupted flux-rope CMEs from the Sun (2–20 R.) to 1 AU. Solar Phys.284, 203. DOI . ADS .
Isavnin, A., Vourlidas, A., Kilpua, E.K.J.: 2014, Three-dimensional evolution of flux-rope CMEs and its relation to the local orientation of the heliospheric current sheet. Solar Phys.289, 2141. DOI . ADS .
Janvier, M., Démoulin, P., Dasso, S.: 2014, Mean shape of interplanetary shocks deduced from in situ observations and its relation with interplanetary CMEs. Astron. Astrophys.565, A99. DOI .
Janvier, M., Winslow, R.M., Good, S., Bonhomme, E., Démoulin, P., Dasso, S., Möstl, C., Lugaz, N., Amerstorfer, T., Soubrié, E., Boakes, P.D.: 2019, Generic magnetic field intensity profiles of interplanetary coronal mass ejecta at Mercury, Venus and Earth from superposed epoch analysis. J. Geophys. Res.124, 812.
Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G.: 2011, Comparing solar minimum 23/24 with historical solar wind records at 1 AU. Solar Phys.274, 321. DOI . ADS .
Jian, L., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M.: 2006, Properties of interplanetary coronal mass ejections at one AU during 1995-2004. Solar Phys.239, 393. DOI . ADS .
Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M., Steinberg, J.T.: 2008a, Stream interactions and interplanetary coronal mass ejections at 0.72 AU. Solar Phys.249, 85. DOI . ADS .
Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M., Steinberg, J.T.: 2008b, Stream interactions and interplanetary coronal mass ejections at 5.3 AU near the solar ecliptic plane. Solar Phys.250, 375. DOI . ADS .
Jian, L., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M.: 2008c, Evolution of solar wind structures from 0.72 to 1 AU. Adv. Space Res.41, 259. DOI .
Jian, L.K., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Galvin, A.B.: 2018d, STEREO observations of interplanetary coronal mass ejections in 2007-2016. Astrophys. J.885, 114.
Jin, M., Manchester, W.B., van der Holst, B., Sokolov, I., Tóth, G., Vourlidas, A.: 2017, Chromosphere to 1 au simulation of the 2011 March 7th event: a comprehensive study of coronal mass ejection propagation. Astrophys. J.834, 172.
Kahler, S.W.: 2001, The correlation between solar energetic particle peak intensities and speeds of coronal mass ejections: effects of ambient particle intensities and energy spectra. J. Geophys. Res.106, 20947.
Kay, C., Opher, M.: 2015, The heliocentric distance where the deflections and rotations of solar coronal mass ejections occur. Astrophys. J. Lett.811, L36.
Kay, C., Opher, M., Evans, R.M.: 2015, Global trends of CME deflections based on CME and solar parameters. Astrophys. J.805, 168. DOI .
Kilpua, E., Koskinen, H.E.J., Pulkkinen, T.I.: 2017, Coronal mass ejections and their sheath regions in interplanetary space. Liv. Rev. Solar Phys.14, 5. DOI .
Kilpua, E.K.J., Lumme, E., Andreeova, K., Isavnin, A., Koskinen, H.E.J.: 2015, Properties and drivers of fast interplanetary shocks near the orbit of the Earth (1995–2013). J. Geophys. Res.120, 4112. DOI .
Kilpua, E.K.J., Lugaz, N., Mays, M.L., Temmer, M.: 2019, Forecasting the structure and orientation of earthbound coronal mass ejections. Space Weather17, 498. DOI .
Kim, R.S., Gopalswamy, N., Cho, K.-S., Moon, Y.J., Yashiro, S.: 2013, Propagation characteristics of CMEs associated with magnetic clouds and ejecta. Solar Phys.284, 77. DOI . ADS .
Klein, L.W., Burlaga, L.F.: 1982, Interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.87, 613.
Kozarev, K.A., Korreck, K., Lobzin, V.V., Weber, M.A., Schwadron, N.A.: 2011, Off-limb solar coronal wavefronts from SDO/AIA extreme-ultraviolet observations—implications for particle production. Astrophys. J.733, 25.
Kozarev, K.A., Raymond, J.C., Lobzin, V.V., Hammer, M.: 2015, Properties of a coronal shock wave as a driver of early SEP acceleration. Astrophys. J.799, 167.
Kwon, R.Y., Vourlidas, A.: 2017, Investigating the wave nature of the outer envelope of halo coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J.836, 246.
Kwon, R.Y., Vourlidas, A.: 2018, The density compression ratio of shock fronts associated with coronal mass ejections. J. Space Weather Space Clim.8, A08.
Kwon, R.-Y., Zhang, J., Olmedo, O.: 2014, New insights into the physical nature of coronal mass ejections and associated shock waves within the framework of the three-dimensional structure. Astrophys. J.794, 148. DOI .
Kwon, R.Y., Zhang, J., Vourlidas, A.: 2015, Are halo-like solar coronal mass ejections merely a matter of geometric projection effects? Astrophys. J. Lett.799, L29.
Lai, H.R., Russell, C.T., Jian, L.K., Blanco-Cano, X., Anderson, B.J., Luhmann, J.G., Wennmacher, A.: 2012, The radial evolution of interplanetary shocks in the inner heliosphere: observations by helios, MESSENGER, and STEREO. Solar Phys.278, 421. DOI . ADS .
Lario, D., Aran, A., Gómez-Herrero, R., Dresing, N., Heber, B., Ho, G.C., Decker, R.B., Roelof, E.C.: 2013, Longitudinal and radial dependence of solar energetic particle peak intensities: STEREO, ACE, SOHO, GOES, and MESSENGER observations. Astrophys. J.767, 41. DOI .
Lario, D., Raouafi, N.E., Kwon, R.-Y., Xhang, J., Gómez-Herrero, R., Dresing, N., Riley, P.: 2014, The solar energetic particle event on 2013 April 11: an investigation of its solar origin and longitudinal spread. Astrophys. J.797, 8. DOI .
Lario, D., Kwon, R.-Y., Vourlidas, A., Raouafi, N.E., Haggerty, D.K., Ho, G.C.: 2016, Longitudinal properties of a widespread solar energetic particle event on 2014 February 25: evolution of the associated CME shock. Astrophys. J.819, 72.
Lario, D., Kwon, R.-Y., Richardson, I.G., Raouafi, N.E., Thompson, B.J.: 2017, The solar energetic particle event of 2010 August 14: connectivity with the solar source inferred from multiple spacecraft observations and modeling. Astrophys. J.838, 51.
Lavraud, B., Ruffenach, A., Rouillard, A.P., Kajdic, P., Manchester, W.B., Lugaz, N.: 2014, Geo-effectiveness and radial dependence of magnetic cloud erosion by magnetic reconnection. J. Geophys. Res.119, 26.
Lavraud, B., Liu, Y., Segura, K., He, J., Qin, G., Temmer, M., et al.: 2016, A small mission concept to the Sun–Earth Lagrangian L5 point for innovative solar, heliospheric and space weather science. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.146, 171. DOI .
Leblanc, Y., Dulk, G.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 1998, Tracing the electron density from the corona to 1 au. Solar Phys.183, 165. DOI . ADS .
Lee, C.O., Hara, T., Halekas, J.S., Thiemann, E., Chamberlin, P., Eparvier, F.: 2017, MAVEN observations of the solar cycle 24 space weather conditions at Mars. J. Geophys. Res.122, 2768.
Lepping, R.P., Burlaga, L.F., Jones, J.A.: 1990, Magnetic field structure of interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.95, 11957. DOI .
Lepri, S.T., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2004, Iron charge state distributions as an indicator of hot ICMEs: possible sources and temporal and spatial variations during solar maximum. J. Geophys. Res.109, A01112.
Lepri, S.T., Zurbuchen, T.H., Fisk, L.A., Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V., Gloeckler, G.: 2001, Iron charge distribution as an identifier of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res.106, 29231.
Li, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Lynch, B.J.: 2018, Magnetic clouds: solar cycle dependence, sources, and geomagnetic impacts. Solar Phys.293, 135. DOI . ADS .
Li, G., Moore, R., Mewaldt, R.A., Zhao, L., Labrador, A.W.: 2012, A twin-CME scenario for ground level enhancement events. Space Sci. Rev.171, 141.
Li, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Lynch, B.J., Kilpua, E.: 2014, Magnetic clouds and origins in STEREO era. J. Geophys. Res.119, 3237. DOI .
Liewer, P., Panasenco, O., Vourlidas, A., Colaninno, R.: 2015, Observations and analysis of the non-radial propagation of coronal mass ejections near the Sun. Solar Phys.290, 3343. DOI . ADS .
Lionello, R., Linker, J.A., Mikic, Z.: 2009, Multispectral emission of the Sun during the first whole Sun month: magnetohydrodynamic simulations. Astrophys. J.690, 902.
Lionello, R., Downs, C., Linker, J.A., Török, T., Riley, P., Mikic, Z.: 2013, Magnetohydrodynamic simulations of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J.777, 76.
Liu, Y., Thernisien, A., Luhmann, J.G., Vourlidas, A., Davies, J.A., Lin, R.P., Bale, S.D.: 2010, Reconstructing coronal mass ejections with coordinated imaging and in situ observations: global structure, kinematics, and implications for space weather forecasting. Astrophys. J.722, 1762.
Liu, Y.D., Luhmann, J.G., Lugaz, N., Möstl, C., Davies, J.A., Bale, S.D., Lin, R.P.: 2013, On Sun-to-Earth propagation of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J.769, 45.
Liu, Y.D., Yang, Z., Wang, R., Luhmann, J.G., Richardson, J.D., Lugaz, N.: 2014a, Sun-to-Earth characteristics of two coronal mass ejections interacting near 1 AU: formation of a complex ejecta and generation of a two-step geomagnetic storm. Astrophys. J.793, 41.
Liu, Y.D., Luhmann, J., Kajdič, P., Kilpua, E.K.J., Lugaz, N., Nitta, N.V., et al.: 2014b, Observations of an extreme storm in interplanetary space caused by successive coronal mass ejections. Nat. Comm.5, 3481. DOI .
Liu, Y.D., Hu, H., Wang, R., Yang, Z., Zhu, B., Liu, Y.-A., et al.: 2015, Plasma and magnetic field characteristics of solar coronal mass ejections in relation to geomagnetic storm intensity and variability. Astrophys. J. Lett.809, L34.
Long, D.M., Bloomfield, D.S., Chen, P.F., Downs, C., Gallagher, P.T., Kwon, R.-Y., Vanninathan, K., Veronig, A.M., Vourlidas, A., Vršnak, B., Warmuth, A., Žic, T.: 2017, Understanding the physical nature of coronal “EIT waves”. Solar Phys.292, 7. DOI . ADS .
Lugaz, N., Manchester, W.B., Gombosi, T.I.: 2005, Numerical simulation of the interaction of two coronal mass ejections from Sun to Earth. Astrophys. J.634, 651.
Lugaz, N., Vourlidas, A., Roussev, I.I., Jacobs, C., Manchester, W.B., Cohen, O.: 2008, The brightness of density structures at large solar elongation angles: what is being observed by STEREO SECCHI? Astrophys. J. Lett.684, L111.
Lugaz, N., Vourlidas, A., Roussev, I.I., Morgan, H.: 2009, Solar-terrestrial simulation in the STEREO era: the 24-25 January 2007 eruptions. Solar Phys.256, 269. DOI . ADS .
Lugaz, N., Hernandez-Charpak, J.N., Roussev, I.I., Davis, C.J., Vourlidas, A., Davies, J.A.: 2010, Determining the azimuthal properties of coronal mass ejections from multi-spacecraft remote-sensing observations with STEREO SECCHI. Astrophys. J.715, 493.
Lugaz, N., Farrugia, C.J., Davies, J.A., Möstl, C., Davis, C.J., Roussev, I.I., Temmer, M.: 2012, The deflection of the two interacting coronal mass ejections of 2010 May 23-24 as revealed by combined in situ measurements and heliospheric imaging. Astrophys. J.759, 68.
Lugaz, N., Farrugia, C.J., Manchester, W.B., Schwadron, N.A.: 2013, The interaction of two coronal mass ejections: influence of relative orientation. Astrophys. J.778, 20.
Lugaz, N., Farrugia, C.J., Winslow, R.M., Al-Haddad, N., Kilpua, E.K.J., Riley, P.: 2016, Factors affecting the geoeffectiveness of shocks and sheaths at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.121, 10861.
Lugaz, N., Temmer, M., Wang, Y., Farrugia, C.J.: 2017a, The interaction of successive coronal mass ejections: a review. Solar Phys.292, 64. DOI . ADS .
Lugaz, N., Farrugia, C.J., Winslow, R.M., Small, C.R., Manion, T., Savani, N.P.: 2017b, Importance of CME radial expansion on the ability of slow CMEs to drive shocks. Astrophys. J.848, 75.
Lugaz, N., Farrugia, C.J., Winslow, R.M., Al-Haddad, N., Galvin, A.B., Nieves-Chinchilla, T.: 2018, On the spatial coherence of magnetic ejecta: measurements of coronal mass ejections by multiple spacecraft longitudinally separated by 0.01 au. Astrophys. J. Lett.864, L7.
Lynch, B.J., Edmonson, J.K.: 2013, Sympathetic magnetic breakout coronal mass ejections from pseudostreamers. Astrophys. J.764, 87.
Lynch, B.J., Li, Y., Thernisien, A.F.R., Robbrecht, E., Fisher, G.H., Luhmann, J.G., Vourlidas, A.: 2010, Sun to 1 AU propagation and evolution of a slow streamer - blowout coronal mass ejection. J. Geophys. Res.115, 7106.
Lynch, B.J., Masson, S., Li, Y., DeVore, C.R., Luhmann, J.G., Antiochos, S.K., Fisher, G.H.: 2016, A model for stealth coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res.121, 10677.
Ma, S., Raymond, J.C., Golub, L., Lin, J., Chen, H., Grigis, P., Testa, P., Long, D.: 2011, Observations and interpretation of a low coronal shock wave observed in the EUV by the SDO/AIA. Astrophys. J.738, 160.
Mäkelä, P., Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Xie, H., Yashiro, S.: 2011, Energetic storm particle events in coronal mass ejection-driven shocks. J. Geophys. Res.116, 1801.
Mäkelä, P., Gopalswamy, X.H., Mohamed, A.A., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S.: 2013, Coronal hole influence on the observed structure of interplanetary CMEs. Solar Phys.284, 59. DOI .
Mäkelä, P., Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Xie, H., Yashiro, S.: 2015, Estimating the height of CMEs associated with a major SEP event at the onset of the metric type ii radio burst during solar cycles 23 and 24. Astrophys. J.806, 13.
Mäkelä, P., Gopalswamy, N., Reiner, M.J., Akiyama, S., Krupar, V.: 2016, Source regions of the Type II radio burst observed during a CME-CME interaction on 2013 May 22. Astrophys. J.827, 141.
Manchester, W.B., van der Holst, B., Lavraud, B.: 2014, Flux rope evolution in interplanetary coronal mass ejections: the 13 May 2005 event. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion56, 064006.
Manchester, W.B., Vourlidas, A., Tóth, G., Lugaz, N., Roussev, I.I., Sokolov, I.V., Gombosi, T.I., De Zeeuw, D.L., Opher, M.: 2008, Three-dimensional MHD simulation of the 2003 October 28 coronal mass ejection: comparison with LASCO coronagraph observations. Astrophys. J.684, 1448.
Manchester, W.B., Kozyra, J., Lepri, S.T., Lavraud, B.: 2014, Simulation of magnetic cloud erosion during propagation. J. Geophys. Res.119, 5449.
Manchester, W., Kilpua, E.K.J., Liu, Y.D., Lugaz, N., Riley, P., Török, T., Vrsnak, B.: 2017, The physical processes of CME/ICME evolution. Space Sci. Rev.212, 1159.
Mann, G., Klassen, A., Aurass, H., Classen, H.-T.: 2003, Formation and development of shock waves in the solar corona and the near-Sun interplanetary space. Astron. Astrophys.400, 329.
Mao, S., He, J., Zhang, L., Yang, L., Wang, L.: 2017, Numerical study of erosion, heating, and acceleration of the magnetic cloud as impacted by fast shock. Astrophys. J.842, 109.
Maricic, D., Vrsnak, B., Dumbovic, M., Zic, T.: 2014, Kinematics of interacting ICMEs and related forbush decrease: case study. Solar Phys.289, 351. DOI . ADS .
Marubashi, K.: 1986, Structure of the interplanetary magnetic clouds and their solar origins. Adv. Space Res.6, 335.
Marubashi, K.: 2000, Physics of interplanetary magnetic flux ropes: toward prediction of geomagnetic storms. Adv. Space Res.26, 55.
Marubashi, K., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Cho, K.-S., Park, Y.-D.: 2015, Geometrical relationship between interplanetary flux ropes and their solar sources. Solar Phys.290, 1371. DOI . ADS .
Mays, M.L., Taktakishvili, A., Pulkkinen, A., MacNeice, P.J., Rastaetter, L., Odstrcil, D., et al.: 2015, Ensemble modeling of CMEs using the WSA-ENLIL+Cone model. Solar Phys.290, 1775. DOI . ADS .
Mewaldt, R.A., Looper, M.D., Cohen, C.M.S., Haggerty, D.K., Labrador, A.W., Leske, R.A., Mason, G.M., Mazur, J.E., von Rosenvinge, T.T.: 2012, Energy spectra, composition, and other properties of ground-level events during Solar Cycle 23. Space Sci. Rev.171, 97.
Mishra, W., Srivastava, N.: 2014, Morphological and kinematic evolution of three interacting coronal mass ejections of 2011 February 13-15. Astrophys. J.794, 64.
Mishra, W., Wang, Y., Srivastava, N.: 2016, On understanding the nature of collisions of coronal mass ejections observed by STEREO. Astrophys. J.831, 99.
Morosan, D.E., Carley, E.P., Hayes, L.A., Murray, S.A., Zucca, P., Fallows, R.A., et al.: 2019, Multiple regions of shock-accelerated particles during a solar coronal mass ejection. Nat. Astron.3, 452. DOI .
Möstl, C., Farrugia, C.J., Kilpua, E.K.J., Jian, L.K., Liu, Y., Eastwood, J.P., et al.: 2012, Multi-point shock and flux rope analysis of multiple interplanetary coronal mass ejections around 2010 August 1 in the inner heliosphere. Astrophys. J.758, 10.
Möstl, C., Amla, K., Hall, J.R., Liewer, P.C., De Jong, E.M., Colaninno, R.C., et al.: 2014, Connecting speeds, directions and arrival times of 22 coronal mass ejections from the Sun to 1 AU. Astrophys. J.787, 119.
Möstl, C., Rollett, T., Frahm, R.A., Liu, Y.D., Long, D.M., Colaninno, R.C., Reiss, M.A., Temmer, M., Farrugia, C.J., Posner, A., Dumbović, M., Janvier, M., Démoulin, P., Boakes, P., Devos, A., Kraaikamp, E., Mays, M.L., Vršnak, B.: 2015, Strong coronal channeling and interplanetary evolution of a solar storm up to Earth and Mars. Nature Comm.6, 7135. DOI .
Möstl, C., Isavnin, A., Boakes, P.D., Kilpua, E.K.J., Davies, J.A., Harrison, R.A., et al.: 2017, Modeling observations of solar coronal mass ejections with heliospheric imagers verified with the Heliophysics System Observatory. Space Weather15, 955. DOI .
Möstl, C., Amerstorfer, T., Palmerio, E., Isavnin, A., Farrugia, C.J., Lowder, C., Winslow, R.M., Donnerer, J.M., Kilpua, E.K.J., Boakes, P.D.: 2018, Forward modeling of coronal mass ejection flux ropes in the inner heliosphere with 3DCORE. Space Weather16, 216.
Mouschovias, T.C., Poland, A.I.: 1978, Expansion and broadening of coronal loop transients - a theoretical explanation. Astrophys. J.220, 675.
Müller, D., Zouganelis, I., St. Cyr, O.C., Gilbert, H.R., Nieves-Chinchilla, T.: 2020, Europe’s next mission to the Sun. Nature Astron.4, 205. DOI .
Mulligan, T., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G.: 1998, Solar cycle evolution of the structure of magnetic clouds in the inner heliosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett.25, 2959.
Nelson, G.J., Melrose, D.B.: 1985, Type II bursts. In: McLean, D.J., Labrum, N.R. (eds.) Solar Radiophysics: Studies of Emission from the Sun at Metre Wavelengths, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 333.
Niembro, T., Canto, J., Lara, A., Gonzalez, R.F.: 2015, An analytical model of interplanetary coronal mass ejection interactions. Astrophys. J.811, 2015.
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Colaninno, R., Vourlidas, A., Szabo, A., Lepping, R.P., Boardsen, S.A., Anderson, B.J., Korth, H.: 2012, Remote and in situ observations of an unusual Earth-directed coronal mass ejection from multiple viewpoints. J. Geophys. Res.117, 6106.
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Vourlidas, A., Stenborg, G., Savani, N.P., Koval, A., Szabo, A., Jian, L.K.: 2013, Inner heliospheric evolution of a “stealth” CME derived from multi-view imaging and multipoint in situ observations. I. Propagation to 1 AU. Astrophys. J.779, 55.
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Vourlidas, A., Raymond, J.C., Linton, M.G., Al-haddad, N., Savani, N.P., Szabo, A., Hidalgo, M.A.: 2018, Understanding the internal magnetic field configurations of ICMEs using more than 20 years of wind observations. Solar Phys.293, 25. DOI . ADS .
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Jian, L.K., Balmaceda, L., Vourlidas, A., dos Santos, L.F.G., Szabo, A.: 2019, Unraveling the internal magnetic field structure of the Earth-directed interplanetary coronal mass ejections during 1995-2015. Solar Phys.294, 89. DOI .
Odstrcil, D.: 2003, Modeling 3-D solar wind structure. Adv. Space Res.32, 497.
Odstrcil, D., Pizzo, V.J.: 2009, Numerical heliospheric simulations as assisting tool for interpretation of observations by STEREO heliospheric imagers. Solar Phys.259, 297. DOI . ADS .
Odstrcil, D., Pizzo, V.J., Arge, C.N.: 2005, Propagation of the 12 May 1997 interplanetary coronal mass ejection in evolving solar wind structures. J. Geophys. Res.110, 2106.
Odstrcil, D., Savani, N.P., Rouillard, A.P.: 2018, Launching hydrodynamic and magnetic CME-like structures into the operational heliospheric space weather models. In: Solar Heliospheric and INterplanetary Environment (SHINE) Conf., 123. ADS .
Olmedo, O., Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Yashiro, S., Makela, P.A., Akiyama, S., St. Cyr, O.C., Vourlidas, A.: 2013, Forward Fitting of a Coronal Shock Front to a Spheroid, Am. Geophys. Union Fall Meet., Abstract id. SH13A-2033.
Owens, M.J., Cargill, P.J., Pagel, C., Siscoe, G.L., Crooker, N.U.: 2005, Characteristic magnetic field and speed properties of interplanetary coronal mass ejections and their sheath regions. J. Geophys. Res.110, 1105.
Palmerio, E., Kilpua, E.K.J., Möstl, C., Bothmer, V., James, A.W., Green, L.M., Isvanin, A., Davies, J.A., Harrison, R.A.: 2018, Coronal magnetic structure of earthbound CMEs and in-situ comparison. Space Weather16, 442.
Patsourakos, S., Vourlidas, A.: 2012, On the nature and genesis of EUV waves: a synthesis of observations from SOHO, STEREO, SDO and Hinode. Solar Phys.281, 187. DOI . ADS .
Poedts, S.: 2019, Forecasting space weather with EUHFORIA in the virtual space weather modeling centre. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion61, 014011.
Poedts, S., Pomoell, J.P., Zuccarello, F.: 2016, Self-consistent evolution models for slow CMEs up to 1 AU. In: Zhelyazkov, I., Mishonov, T. (eds.) Black Sea Biennial School and Workshop on Space Plasma PhysicsCP-1714, AIP, Melville, id. 030002. DOI .
Pomoell, J., Poedts, S.: 2018, EUHFORIA: European heliospheric forecasting information asset. J. Space Weather Space Clim.8, A35.
Poomvises, W., Zhang, J., Olmedo, O.: 2010, Coronal mass ejection propagation and expansion in three-dimensional space in the heliosphere based on stereo/SECCHI observations. Astrophys. J. Lett.717, 159.
Prise, A.J., Harra, L.K., Matthews, S.A., Arridge, C.S., Achilleos, N.: 2015, Analysis of a coronal mass ejection and corotating interaction region as they travel from the Sun passing Venus, Earth, Mars, and Saturn. J. Geophys. Res.120, 1566.
Qiu, J., Yurchyshyn, V.B.: 2005, Magnetic reconnection flux and coronal mass ejection velocity. Astrophys. J. Lett.634, L121.
Qiu, J., Hu, Q., Howard, T.A., Yurchyshyn, V.B.: 2007, On the magnetic flux budget in low-corona magnetic reconnection and interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J.659, 758.
Reames, D.V.: 2009, Solar energetic-particle release times in historic ground-level events. Astrophys. J.706, 844.
Reames, D.V.: 2017, Energetic Particles, Springer, Berlin. DOI .
Reiff, P.H., Daou, A.G., Sazykin, S.Y., Nakamura, R., Hairston, M.R., Coffey, V., et al.: 2016, Multispacecraft observations and modeling of the 22/23 June 2015 geomagnetic storm. Geophys. Res. Lett.43, 7311.
Reinard, A.A.: 2008, Analysis of interplanetary coronal mass ejection parameters as a function of energetics, source location, and magnetic structure. Astrophys. J.682, 1289.
Reinard, A.A., Lynch, B.J., Mulligan, T.: 2012, Composition structure of interplanetary coronal mass ejections from multispacecraft observations, modeling, and comparison with numerical simulations. Astrophys. J.761, 175.
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2004, The fraction of interplanetary coronal mass ejections that are magnetic clouds: evidence for a solar cycle variation. Geophys. Res. Lett.31, L18804. DOI .
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Lionello, R., Mikić, Z., Odstrcil, D., Hidalgo, M.A., Cid, C., Hu, Q., Lepping, R.P., Lynch, B.J., Rees, A.: 2004, Fitting flux ropes to a global MHD solution: a comparison of techniques. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.66, 1321. DOI .
Riley, P., Mays, L., Andries, J., Amerstorfer, T., Biesecker, D., Delouille, V., et al.: 2018, Forecasting the arrival time of coronal mass ejections: analysis of the CCMC CME scoreboard. Space Weather16, 1245.
Rouillard, A.P.: 2011, Relating white light and in situ observations of coronal mass ejections: a review. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.73, 1201.
Rouillard, A.P., Odstrcil, D., Sheeley, N.R., Tylka, A., Vourlidas, A., Mason, G., et al.: 2011, Interpreting the properties of solar energetic particle events by using combined imaging and modeling of interplanetary shocks. Astrophys. J.735, 7.
Ruffenach, A., Lavraud, B., Owens, M.J., Sauvaud, J.A., Savani, N.P., Rouillard, A.P., et al.: 2012, Multispacecraft observation of magnetic cloud erosion by magnetic reconnection during propagation. J. Geophys. Res.117, 9101.
Ruffenach, A., Lavraud, B., Farrugia, C.J., Démoulin, P., Dasso, S., Owens, M.J., et al.: 2015, Statistical study of magnetic cloud erosion by magnetic reconnection. J. Geophys. Res.120, 43.
Russell, C.T.: 2000, The solar wind interaction with the Earth’s magnetosphere: a tutorial. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci.28, 1818.
Russell, C.T., Mewaldt, R.A., Luhmann, J.G., Mason, G.M., von Rosenvinge, T.T., Cohen, C.M.S., et al.: 2013, The very unusual interplanetary coronal mass ejection of 2012 July 23: a blast wave mediated by solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J.770, 38.
Savani, N.P., Rouillard, A.P., Davies, J.A., Owens, M.J., Forsyth, R.J., Davis, C.J., Harrison, R.A.: 2009, The radial width of a coronal mass ejection between 0.1 and 0.4 AU estimated from the heliospheric imager on STEREO. Ann. Geophys.27, 4349.
Savani, N.P., Owens, M.J., Rouillard, A.P., Forsyth, R.J., Davies, J.A.: 2010, Observational evidence of a coronal mass ejection distortion directly attributable to a structured solar wind. Astrophys. J. Lett.714, L128.
Savani, N.P., Owens, M.J., Rouillard, A.P., Forsyth, R.J., Kusano, K., Shiota, D., Kataoka, R.: 2011a, Evolution of coronal mass ejection morphology with increasing heliocentric distance. I. Geometrical analysis. Astrophys. J.731, 109.
Savani, N.P., Owens, M.J., Rouillard, A.P., Forsyth, R.J., Kusano, K., Shiota, D., Kataoka, R., Jian, L., Bothmer, V.: 2011b, Evolution of coronal mass ejection morphology with increasing heliocentric distance. II. In situ observations. Astrophys. J.732, 117.
Savani, N.P., Davies, J.A., Davis, C.J., Shiota, D., Rouillard, A.P.: 2012, Observational tracking of the 2D structure of coronal mass ejections between the Sun and 1 AU. Solar Phys.279, 517. DOI . ADS .
Savani, N.P., Vourlidas, A., Shiota, D., Linton, M.G., Kusano, K., Lugaz, N., Rouillard, A.P.: 2013, A plasma ß transition within a propagating flux rope. Astrophys. J.779, 142.
Savani, N.P., Vourlidas, A., Szabo, A., Mays, M.L., Richardson, I.G., Thompson, B.J., Pulkkinen, A., Evans, R., Nieves-Chinchilla, T.: 2015, Predicting the magnetic vectors within coronal mass ejections arriving at Earth: 1. Initial architecture. Space Weather13, 374.
Schmidt, J.M., Cargill, P.J.: 2004, A numerical study of two interacting coronal mass ejections. Ann. Geophys.22, 2245.
Scolini, C., Rodriguez, L., Mierla, M., Pomoell, J., Poedts, S.: 2019, Observation-based modelling of magnetised coronal mass ejections with EUHFORIA. Astron. Astrophys.626, A122. DOI .
Shen, C., Wang, Y., Wang, S., Liu, Y.D., Liu, R., Vourlidas, A., Miao, B., Ye, P., Liu, J., Zhou, Z.: 2012, Super-elastic collision of large-scale magnetized plasmoids in the heliosphere. Nat. Phys.8, 923.
Shen, F., Shen, C., Wang, Y., Feng, X., Xiang, C.: 2013, Could the collision of CMEs in the heliosphere be superelastic? Validation through three-dimensional simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett.40, 1457. DOI .
Shen, C., Wang, Y., Pan, C., Miao, B., Ye, P., Wang, S.: 2014, Full-halo coronal mass ejections: arrival at the Earth. J. Geophys. Res.119, 5107.
Shen, C., Xu, M., Wang, Y., Chi, Y., Luo, B.: 2018, Why the shock-ICME complex structure is important: learning from the early 2017 September CMEs. Astrophys. J.861, 28. DOI .
Shiota, D., Kataoka, R.: 2016, Magnetohydrodynamic simulation of interplanetary propagation of multiple coronal mass ejections with internal magnetic flux rope (SUSANOO-CME). Space Weather14, 56.
Singh, T., Yalim, M.S., Pogorelov, N.V., Gopalswamy, N.: 2019, Simulating solar coronal mass ejections constrained by observations of their speed and poloidal flux. Astrophys. J. Lett.875, L17.
Siscoe, G., Odstrcil, D.: 2008, Ways in which ICME sheaths differ from magnetosheaths. J. Geophys. Res.113, A00B07.
Sterling, A.C.: 2018, Coronal jets and the jet-CME connection. In: Zank, G.P. (ed.) Proc. 17th Ann. Int. Astrophys. Conf., J. Phys.CS-1100, IOP, Bristol, 012024. DOI .
Temmer, M., Nitta, N.: 2015, Interplanetary propagation behavior of the fast coronal mass ejection on 23 July 2012. Solar Phys.290, 919. DOI . ADS .
Temmer, M., Vrsnak, B., Rollett, T., Bein, B., de Koning, C., Liu, Y., Bosman, E., Davies, J.A., Möstl, C., Zic, T.: 2012, Characteristics of kinematics of a coronal mass ejection during the 2010 August 1 CME-CME interaction event. Astrophys. J.749, 57.
Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M., Peinhart, V., Vrsnak, B.: 2014, Asymmetry in the CME-CME interaction process for the events from 2011 February 14-15. Astrophys. J.785, 85.
Thakur, N., Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S., Davila, J.M.: 2014, Ground level enhancement in the 2014 January 6 solar energetic particle event. Astrophys. J. Lett.790, L13.
Thernisien, A.: 2011, Implementation of the graduated cylindrical shell model for the three-dimensional reconstruction of coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. Suppl.194, 33.
Thernisien, A., Vourlidas, A., Howard, R.A.: 2009, Forward modeling of coronal mass ejections using STEREO/SECCHI data. Solar Phys.256, 111. DOI . ADS .
Török, T., Panasenco, O., Titov, V.S., Mikič, Z., Reeves, K.K., Velli, M., Linker, J.A., de Toma, G.: 2011, A model for magnetically coupled sympathetic eruptions. Astrophys. J. Lett.739, L63.
Török, T., Downs, C., Linker, J.A., Lionello, R., Titov, V.S., Mikič, Z., Riley, P., Caplan, R.M., Wijaya, J.: 2018, Sun-to-Earth MHD simulation of the 2000 July 14 “Bastille Day” eruption. Astrophys. J.856, 75.
Vandas, M.S., Fischer, P., Pelant, M., Dryer, M., Smith, Z., Detman, T.: 1997, Propagation of a spheromak: 1. Some comparisons of cylindrical and spherical magnetic clouds. J. Geophys. Res.2012, 24183.
Verbeke, C., Pomoell, J., Poedts, S.: 2019, The evolution of coronal mass ejections in the inner heliosphere: implementing the spheromak model with EUHFORIA. Astron. Astrophys.627, A111. DOI .
Veronig, A.M., Muhr, N., Kienreich, I.W., Temmer, M., Vršnak, B.: 2010, First observations of a dome-shaped large-scale coronal extreme-ultraviolet wave. Astrophys. J. Lett.716, L57.
Vourlidas, A., Webb, D.F.: 2018, Streamer-blowout coronal mass ejections: their properties and relation to the coronal magnetic field structure. Astrophys. J.861, 103.
Vourlidas, A., Lynch, B.J., Howard, R.A., Li, Y.: 2013, How many CMEs have flux ropes? Deciphering the signatures of shocks, flux ropes, and prominences in coronagraph observations of CMEs. Solar Phys.284, 179. DOI . ADS .
Vourlidas, A., Balmaceda, L.A., Stenborg, G., Dal Lago, A.: 2017, Multi-viewpoint coronal mass ejection catalog based on STEREO COR2 observations. Astrophys. J.838, 17. DOI . ADS .
Vršnak, B., Žic, T., Vrbanec, D., Temmer, M., Rollett, T., Möstl, C., et al.: 2013, Propagation of interplanetary coronal mass ejections: the drag-based model. Solar Phys.285, 295. DOI . ADS .
Vršnak, B., Temmer, M., Žic, T., Taktakishvili, A., Dumbovic, M., Möstl, C., Veronig, A.M., Mays, M.L., Odstrcil, D.: 2014, Heliospheric propagation of coronal mass ejections: comparison of numerical WSA-ENLIL+Cone model and analytical drag-based model. Astrophys. J. Suppl.213, 21.
Wang, Y., Wang, B., Shen, C., Shen, F., Lugaz, N.: 2014, Deflected propagation of a coronal mass ejection from the corona to interplanetary space. J. Geophys. Res.119, 5117.
Webb, D.F., Howard, T.A.: 2012, Coronal mass ejections: observations. Liv. Rev. Solar Phys.9, 3.
Webb, D.F., Möstl, C., Jackson, B.V., Bisi, M.M., Howard, T.A., Mulligan, T., et al.: 2013, Heliospheric imaging of 3D density structures during the multiple coronal mass ejections of late July to early August 2010. Solar Phys.285, 317. DOI . ADS .
Wilson, R.M.: 1987, Geomagnetic response to magnetic clouds. Planet. Space Sci.35, 329.
Winslow, R.M., Lugaz, N., Philpott, L.C., Schwadron, N.A., Farrugia, C.J., Anderson, B.J., Smith, C.W.: 2015, Interplanetary coronal mass ejections from MESSENGER orbital observations at Mercury. J. Geophys. Res.120, 6101. DOI .
Winslow, R.M., Lugaz, N., Schwadron, N.A., Farrugia, C.J., Yu, W., Raines, J.M., Mays, M.L., Galvin, A.B., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2016, Longitudinal conjunction between MESSENGER and STEREO a: development of ICME complexity through stream interactions. J. Geophys. Res.121, 6092.
Witasse, O., Sánchez-Cano, B., Mays, M.L., Kajdič, P., Opgenoorth, H., Elliott, H.A., et al.: 2017, Interplanetary coronal mass ejection observed at STEREO-A, Mars, Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, Saturn, and New Horizons en route to Pluto: comparison of its forbush decreases at 1.4, 3.1, and 9.9 AU. J. Geophys. Res.122, 7865.
Wold, A.M., Mays, M.L., Taktakishvili, A., Jian, L.K., Odstrcil, D., MacNeice, P.: 2018, Verification of real-time WSA-ENLIL+Cone simulations of CME arrival-time at the CCMC from 2010 to 2016. J. Space Weather Space Clim.8, A17.
Wood, B.E., Howard, R.: 2009, An empirical reconstruction of the 2008 April 26 coronal mass ejection. Astrophys. J.702, 901.
Wood, B.E., Wu, C.-C., Howard, R.A., Socker, D.G., Rouillard, A.P.: 2011, Empirical reconstruction and numerical modeling of the first geoeffective coronal mass ejection of Solar Cycle 24. Astrophys. J.729, 70.
Wood, B.E., Wu, C.-C., Rouillard, A.P., Howard, R.A., Socker, D.G.: 2012, A coronal hole’s effects on coronal mass ejection shock morphology in the inner heliosphere. Astrophys. J.755, 43.
Wood, B.E., Wu, C.-C., Lepping, R.P., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Howard, R.A., Linton, M.G., Socker, D.G.: 2017, A STEREO survey of magnetic cloud coronal mass ejections observed at Earth in 2008-2012. Astrophys. J.229, 29.
Xie, H., Gopalswamy, N., St. Cyr, O.C.: 2013, Near-sun flux-rope structure of CMEs. Solar Phys.284, 47. DOI . ADS .
Xie, H., Ofman, L., Lawrence, G.: 2004, Cone model for halo CMEs: application to space weather forecasting. J. Geophys. Res.109, 3109.
Xie, H., Gopalswamy, N., Ofman, L., St. Cyr, O.C., Michalek, G., Lara, A., Yashiro, S.: 2006, Improved input to the empirical coronal mass ejection (CME) driven shock arrival model from CME cone models. Space Weather4, S10002.
Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., St. Cyr, O.C., Gopalswamy, N.: 2017, Comparison of the coronal mass ejection shock acceleration of three widespread SEP events during solar cycle 24. J. Geophys. Res.122, 7021.
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Akiyama, S.: 2013, Post eruption arcades and interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys.284, 5. DOI . ADS .
Yurchyshyn, V., Abramenko, V., Tripathi, D.: 2009, Rotation of white-light coronal mass ejection structures as inferred from LASCO coronagraph. Astrophys. J.705, 426.
Zucca, P., Morosan, D.E., Rouillard, A.P., Fallows, R., Gallagher, P.T., Magdalenic, J., et al.: 2018, Shock location and CME 3D reconstruction of a solar type II radio burst with LOFAR. Astron. Astrophys.615, A89. DOI .
Zurbuchen, T.H., Richardson, I.G.: 2006, In-situ solar wind and magnetic field signatures on interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Space Sci. Rev.123, 31. DOI .
Acknowledgements
J.G. Luhmann was supported for her role in this effort by NASA Grant NNX15AG09G to the University of California, Berkeley for the STEREO-IMPACT investigation. L.K. Jian is supported by NASA’s Science Mission Directorate as part of the STEREO project, NASA’s Living with a Star and Heliophysics Supporting Research programs. N. Gopalswamy is supported by NASA’s LWS program. N. Lugaz is supported by NASA grant NNX15AB87G. The authors are also grateful to the reviewer for their careful review and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luhmann, J.G., Gopalswamy, N., Jian, L.K. et al. ICME Evolution in the Inner Heliosphere. Sol Phys 295, 61 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01624-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01624-0