Abstract
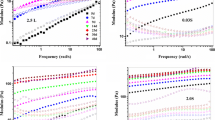
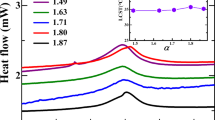
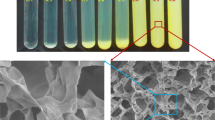
We utilize dynamic light scattering (DLS)-based passive microrheology to probe the dynamics and structural evolution of laponite® and laponite®-polymer glasses and dispersions at the microscale. The results reveal an increase in the dynamic heterogeneity of laponite® dispersions with an increase of laponite® concentration and aging time. In neat laponite® dispersions, the degree of stiffness is enhanced and the dynamics are retarded at higher laponite® concentration due to the formation of a repulsive glass. In the presence of PEO with a moderate molecular weight of 20 kg/mol, the microviscoelastic properties of 2 wt% laponite® dispersions show non-monotonic effects with PEO concentration upon aging, which agrees with the results obtained previously from bulk rheology. However, the magnitudes of the viscoelastic moduli (G’ and G”) of dispersions beyond the gel point obtained from DLS-microrheology is lower than that obtained from conventional rheology. Our results suggest that the DLS-microrheology can be used to qualitatively study dynamic transitions and the microviscoelastic properties of gels and soft solids.

Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin S, Rega CA, Jankevics H (2012) Detection of viscoelasticity in aggregating dilute protein solutions through dynamic light scattering-based optical microrheology. Rheol Acta 51(4):329–342
Amin S, Blake S, Kenyon S, Kennel R, Lewis E (2014) A novel combination of DLS-optical microrheology and low frequency Raman spectroscopy to reveal underlying biopolymer self-assembly and gelation mechanisms. J Chem Phys 141(23):234201
Angelini R, Zaccarelli E, de Melo Marques FA, Sztucki M, Fluerasu A, Ruocco G, Ruzicka B (2014) Glass–glass transition during aging of a colloidal clay. Nat Commun 5:4049
Atmuri AK, Peklaris GA, Kishore S, Bhatia SR (2012) A re-entrant glass transition in colloidal disks with adsorbing polymer. Soft Matter 8(34):8965–8971
Baghdadi HA, Sardinha H, Bhatia SR (2005) Rheology and gelation kinetics in laponite dispersions containing poly (ethylene oxide). J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 43(2):233–240
Baghdadi HA, Parrella J, Bhatia SR (2008) Long-term aging effects on the rheology of neat laponite and laponite–PEO dispersions. Rheol Acta 47(3):349–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-007-0236-1
Bandyopadhyay R, Liang D, Harden JL, Leheny RL (2006) Slow dynamics, aging, and glassy rheology in soft and living matter. Solid State Commun 139(11–12):589–598
Bellour M, Knaebel A, Harden J, Lequeux F, Munch J-P (2003) Aging processes and scale dependence in soft glassy colloidal suspensions. Phys Rev E 67(3):031405
Cardinaux F, Cipelletti L, Scheffold F, Schurtenberger P (2002) Microrheology of giant-micelle solutions. EPL (Europhy Lett) 57(5):738–744
Cipelletti L, Ramos L (2005) Slow dynamics in glassy soft matter. J Phys Condens Matter 17(6):R253–R285
Dávila JL, d’Ávila MA (2017) Laponite as a rheology modifier of alginate solutions: physical gelation and aging evolution. Carbohydr Polym 157:1–8
Elmendorp JJ (1986) A study on polymer blending microrheology. Polym Eng Sci 26(6):418–426
Furst EM, Squires TM (2017) Microrheology. Oxford University Press
Gallegos C, Franco J (1999) Rheology of food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 4(4):288–293
Hassan P, Bhattacharya K, Kulshreshtha S, Raghavan S (2005) Microrheology of wormlike micellar fluids from the diffusion of colloidal probes. J Phys Chem B 109(18):8744–8748
Jabbari-Farouji S, Zargar R, Wegdam G, Bonn D (2012) Dynamical heterogeneity in aging colloidal glasses of Laponite. Soft Matter 8(20):5507–5512
Kishore S, Chen Y, Ravindra P, Bhatia SR (2015) The effect of particle-scale dynamics on the macroscopic properties of disk-shaped colloid–polymer systems. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 482:585–595
Knaebel A, Bellour M, Munch J-P, Viasnoff V, Lequeux F, Harden J (2000) Aging behavior of Laponite clay particle suspensions. EPL (Europhys Lett) 52(1):73–79
Krajina BA, Tropini C, Zhu A, DiGiacomo P, Sonnenburg JL, Heilshorn SC, Spakowitz AJ (2017) Dynamic light scattering microrheology reveals multiscale viscoelasticity of polymer gels and precious biological materials. ACS Cent Sci 3(12):1294–1303
Li L, Harnau L, Rosenfeldt S, Ballauff M (2005) Effective interaction of charged platelets in aqueous solution: investigations of colloid laponite suspensions by static light scattering and small-angle x-ray scattering. Phys Rev E 72(5):051504
Liang W, Guzman-Sepulveda J, He S, Dogariu A, Fang J (2015) Microrheology and release behaviors of self-assembled steroid hydrogels. J Mater Sci Chem Eng 3(08):6–15
Mason TG (2000) Estimating the viscoelastic moduli of complex fluids using the generalized stokes–Einstein equation. Rheol Acta 39(4):371–378
Mason TG, Weitz D (1995) Optical measurements of frequency-dependent linear viscoelastic moduli of complex fluids. Phys Rev Lett 74(7):1250–1253
Mason T, Gang H, Weitz D (1996) Rheology of complex fluids measured by dynamic light scattering. J Mol Struct 383(1–3):81–90
Mongondry P, Nicolai T, Tassin J-F (2004) Influence of pyrophosphate or polyethylene oxide on the aggregation and gelation of aqueous laponite dispersions. J Colloid Interface Sci 275(1):191–196
Mongondry P, Tassin JF, Nicolai T (2005) Revised state diagram of Laponite dispersions. J Colloid Interface Sci 283(2):397–405
Moschakis T (2013) Microrheology and particle tracking in food gels and emulsions. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 18(4):311–323
Moschakis T, Murray BS, Dickinson E (2006) Particle tracking using confocal microscopy to probe the microrheology in a phase-separating emulsion containing nonadsorbing polysaccharide. Langmuir 22(10):4710–4719
Nelson A, Cosgrove T (2004) A small-angle neutron scattering study of adsorbed poly(ethylene oxide) on Laponite. Langmuir 20(6):2298–2304. https://doi.org/10.1021/la035268t
Pozzo DC, Walker LM (2004) Reversible shear gelation of polymer–clay dispersions. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 240(1–3):187–198
Puertas AM, Voigtmann T (2014) Microrheology of colloidal systems. J Phys Condens Matter 26(24):243101
Ruzicka B, Zaccarelli E (2011) A fresh look at the Laponite phase diagram. Soft Matter 7(4):1268–1286. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0SM00590H
Schroer CF, Heuer A (2013) Anomalous diffusion of driven particles in supercooled liquids. Phys Rev Lett 110(6):067801
Sciortino F, Mossa S, Zaccarelli E, Tartaglia P (2004) Equilibrium cluster phases and low-density arrested disordered states: the role of short-range attraction and long-range repulsion. Phys Rev Lett 93(5):055701
Shahin A, Joshi YM (2012) Physicochemical effects in aging aqueous Laponite suspensions. Langmuir 28(44):15674–15686
Sohn I, Rajagopalan R (2004) Microrheology of model quasi-hard-sphere dispersions. J Rheol 48(1):117–142
Suman K, Joshi YM (2018) Microstructure and soft glassy dynamics of an aqueous laponite dispersion. Langmuir 34(44):13079–13103
Thompson DW, Butterworth JT (1992) The nature of laponite and its aqueous dispersions. J Colloid Interface Sci 151(1):236–243
Winter HH, Chambon F (1986) Analysis of linear viscoelasticity of a crosslinking polymer at the gel point. J Rheol 30(2):367–382
Xia Z, Woo L, Van de Ven T (1989) Microrheological aspects of adhesion of Escherichia coli on glass. Biorheology 26(2):359–375
Xu J, Tseng Y, Carriere CJ, Wirtz D (2002) Microheterogeneity and microrheology of wheat gliadin suspensions studied by multiple-particle tracking. Biomacromolecules 3(1):92–99
Zheng B, Bhatia SR (2017) Cluster formation during aging of colloid-polymer dispersions. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 520:729–735
Funding
The authors gratefully thank financial support from NSF awards CBET-1335787 and CBET-1903189 and ACS PRF grant 55729-ND9, and a Department of Education Graduate Assistance in Areas of National Need (GAANN) fellowship for B.Z.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Disclosure
The sponsors had no role in the study design; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, B., Breton, J.R., Patel, R.S. et al. Microstructure, microrheology, and dynamics of laponite® and laponite®-poly(ethylene oxide) glasses and dispersions. Rheol Acta 59, 387–397 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-020-01210-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-020-01210-y