Abstract
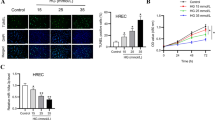
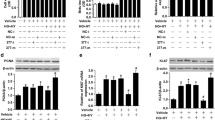
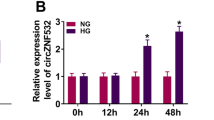
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is the most severe microvascular complication of diabetes and a major cause of visual impairment and blindness. However, the treatment for DR is still limited. Our study aimed to explore the role of circular RNA_0002570 in DR. First, we predicted the potential microRNA and mRNA that could bind to circ_0002570 and identified the miR-1243 and angiomotin gene; then, we used RT-PCR and Western blot to measure their expression. Next, we evaluated the abilities of proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in vitro in human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (hRMECs) by CCK-8, transwell assay, and tube formation assay, respectively. To analyze the relationship among miR-1243, circ_0002570, and angiomotin, RNA pull-down and luciferase assay were performed. Our results showed that, in DR patients and high-glucose–induced hRMECs, miR-1243, circ_0002570, and angiomotin were all abnormally expressed. MiR-1243 could directly and competitively bind to both circ_0002570 and angiomotin mRNA to inhibit their expression. Moreover, circ_0002570 suppressed the abilities of proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in hRMECs induced by high glucose, which was dependent on miR-1243-angiomotin axis. Furthermore, circ_0002570 could upregulate angiomotin by targeting miR-1243 to mediate the dysfunction of hRMECs induced by high glucose. In conclusion, circ_0002570 might serve as a potential target for diagnosis and treatment for DR.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Q et al (2018) Characteristics of retinal structural and microvascular alterations in early type 2 diabetic patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 59:2110–2118. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.17-23193
Cheng Z et al (2019) circTP63 functions as a ceRNA to promote lung squamous cell carcinoma progression by upregulating FOXM1. Nat Commun 10:3200. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11162-4
Cui C, Li Y, Liu Y (2019) Down-regulation of miR-377 suppresses high glucose and hypoxia-induced angiogenesis and inflammation in human retinal endothelial cells by direct up-regulation of target gene SIRT1. Hum Cell 32:260–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-019-00240-w
Erickson KK, Sundstrom JM, Antonetti DA (2007) Vascular permeability in ocular disease and the role of tight junctions. Angiogenesis 10:103–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-007-9067-z
Fu X, Ou B (2020) miR-152/LIN28B axis modulates high-glucose-induced angiogenesis in human retinal endothelial cells via VEGF signaling. J Cell Biochem 121:954–962. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28978
Gao R, Zhu BH, Tang SB, Wang JF, Ren J (2008) Scutellarein inhibits hypoxia- and moderately-high glucose-induced proliferation and VEGF expression in human retinal endothelial cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29:707–712. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00797.x
Gu Y, Ke G, Wang L, Zhou E, Zhu K, Wei Y (2017) Altered Expression Profile of Circular RNAs in the Serum of Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy Revealed by Microarray. Ophthalmic Res 58:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1159/000479156
Han B, Chao J, Yao H (2018) Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: From the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol Ther 187:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.01.010
He M et al (2019) Comparison of expression profiling of circular RNAs in vitreous humour between diabetic retinopathy and non-diabetes mellitus patients. Acta Diabetol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-019-01448-w
Huang Q, Sheibani N (2008) High glucose promotes retinal endothelial cell migration through activation of Src, PI3K/Akt1/eNOS, and ERKs. Am J Phys Cell Phys 295:C1647–C1657. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00322.2008
Huang JK et al (2017) LncRNA-MALAT1 promotes angiogenesis of thyroid cancer by modulating tumor-associated macrophage FGF2 protein secretion. J Cell Biochem 118:4821–4830. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26153
Jourdan T et al (2017) Developmental role of macrophage Cannabinoid-1 receptor signaling in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 66:994–1007. https://doi.org/10.2337/db16-1199
Klaassen I, Van Noorden CJ, Schlingemann RO (2013) Molecular basis of the inner blood-retinal barrier and its breakdown in diabetic macular edema and other pathological conditions. Prog Retin Eye Res 34:19–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2013.02.001
Liu Z et al (2012) Hyperhomocysteinemia exaggerates adventitial inflammation and angiotensin II-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm in mice. Circ Res 111:1261–1273. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.112.270520
Liu P, Jia SB, Shi JM, Li WJ, Tang LS, Zhu XH, Tong P (2019) LncRNA-MALAT1 promotes neovascularization in diabetic retinopathy through regulating miR-125b/VE-cadherin axis. Biosci Rep 39. https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20181469
Mei X, Zhou L, Zhang T, Lu B, Sheng Y, Ji L (2018) Chlorogenic acid attenuates diabetic retinopathy by reducing VEGF expression and inhibiting VEGF-mediated retinal neoangiogenesis. Vasc Pharmacol 101:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2017.11.002
Nicolet BP, Engels S, Aglialoro F, van den Akker E, von Lindern M, Wolkers MC (2018) Circular RNA expression in human hematopoietic cells is widespread and cell-type specific. Nucleic Acids Res 46:8168–8180. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky721
Pascolini D, Mariotti SP (2012) Global estimates of visual impairment: 2010. Br J Ophthalmol 96:614–618. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2011-300539
Salzman J (2016) Circular RNA Expression: Its Potential Regulation and Function. Trends Genet 32:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2016.03.002
Stitt AW et al (2016) The progress in understanding and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res 51:156–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.08.001
Yamamoto K, Ito S, Hanafusa H, Shimizu K, Ouchida M (2015) Uncovering direct targets of MiR-19a involved in lung cancer progression. PLoS One 10:e0137887. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137887
Yang WZ, Yang J, Xue LP, Xiao LB, Li Y (2017) MiR-126 overexpression inhibits high glucose-induced migration and tube formation of rhesus macaque choroid-retinal endothelial cells by obstructing VEGFA and PIK3R2. J Diabetes Complicat 31:653–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.12.004
Yu B et al (2017) CYLD deubiquitinates nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4 contributing to adventitial remodeling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 37:1698–1709. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.117.309859
Zhang SJ, Chen X, Li CP, Li XM, Liu C, Liu BH, Shan K, Jiang Q, Zhao C, Yan B (2017a) Identification and characterization of circular RNAs as a new class of putative biomarkers in diabetes retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 58:6500–6509. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.17-22698
Zhang Y et al (2017b) Nogo-B promotes angiogenesis in proliferative diabetic retinopathy via VEGF/PI3K/Akt pathway in an autocrine manner. Cell Physiol Biochem 43:1742–1754. https://doi.org/10.1159/000484061
Zhang H et al (2019) Apatinib suppresses breast cancer cells proliferation and invasion via angiomotin inhibition. Am J Transl Res 11:4460–4469
Zhu K et al (2019) Downregulation of circRNA DMNT3B contributes to diabetic retinal vascular dysfunction through targeting miR-20b-5p and BAMBI. EBioMedicine 49:341–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.10.004
Funding
This study was supported by the Special Fund of the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University (HYDSYTB201913).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All patients were informed and signed the consent. This study was approved by the Ethical Review Committee of the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Zhou, S., Li, X. et al. Inhibition of hsa_circ_0002570 suppresses high-glucose–induced angiogenesis and inflammation in retinal microvascular endothelial cells through miR-1243/angiomotin axis. Cell Stress and Chaperones 25, 767–777 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-020-01111-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-020-01111-2