Abstract
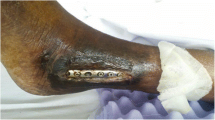
Candida infection is common, while Candida parapsilosis infection in the knee joint is rare. Local symptoms of Candida infections in the knee are atypical, rarely associated with systemic symptoms, and difficult to distinguish from other types of knee arthritis. We here report a special case of C. parapsilosis infections in the knee joint. A patient had previously undergone knee puncture in a private clinic for the treatment of osteoarthritis and developed a left knee joint infection with C. parapsilosis. However, the patient only showed more severe local knee symptoms, and there was no systemic manifestation associated with any Candida infection. Surprisingly, after receiving ozone lavage, the patient showed symptoms of a systemic infection such as fever and chills. There was no positive finding in the blood cultures. Finally, the synovial fluid cultures showed a C. parapsilosis infections. After antifungal treatment and another knee ozone therapy, the patient did not experience recurrence of the infections. It is suggested that in this special case, the strong sterilization with ozone caused the destruction of C. parapsilosis, leading to a transient systemic toxin reaction. In addition, we reviewed the 17 cases of C. parapsilosis infections that have been reported thus far.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fidel PL, Vazquez JA, Sobel JD. Candida glabrata: review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical disease with comparison to C. albicans. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999;12:80–96.
Fang H, Huang L, Zhang R, Xie D, Sun H, Zeng C, Cai D. Recurrent arthritis caused by Candida parapsilosis: a case report and literature review. BMC Infect Dis. 2019;19:631.
Chen S, Chen Y, Zhou YQ, Liu N, Zhou R, Peng JH, Qian QR. Candida glabrata-induced refractory infectious arthritis: a case report and literature review. Mycopathologia. 2019;184:283–93.
Schoch CL, Seifert KA, Huhndorf S, Robert V, Spouge JL, Levesque CA, Chen W. Nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region as a universal DNA barcode marker for fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:6241–6.
Bassetti M, Vena A, Bouza E, Peghin M, Munoz P, Righi E, Pea F, Lackner M, Lass-Florl C. Antifungal susceptibility testing in Candida, Aspergillus and Cryptococcus infections: are the MICs useful for clinicians? Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2020.02.017.
Seki M, Ishikawa T, Terada H, Nashimoto M. Microbicidal effects of stored aqueous ozone solution generated by nano-bubble technology. In Vivo. 2017;31:579–83.
Nagayoshi M, Fukuizumi T, Kitamura C, Yano J, Terashita M, Nishihara T. Efficacy of ozone on survival and permeability of oral microorganisms. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2004;19:240–6.
Bocci VA. Scientific and medical aspects of ozone therapy. State of the art. Arch Med Res. 2006;37:425–35.
Sconza C, Respizzi S, Virelli L, Vandenbulcke F, Iacono F, Kon E, Di Matteo B. Oxygen-ozone therapy for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Arthroscopy. 2020;36:277–86.
Manoto SL, Maepa MJ, Motaung SK. Medical ozone therapy as a potential treatment modality for regeneration of damaged articular cartilage in osteoarthritis. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018;25:672–9.
Seyman D, Ozen NS, Inan D, Ongut G, Ogunc D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa septic arthritis of knee after intra-articular ozone injection. New Microbiol. 2012;35:345–8.
White A, Goetz MB. Candida parapsilosis prosthetic joint infection unresponsive to treatment with fluconazole. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:1068–9.
Tunkel AR, Thomas CY, Wispelwey B. Candida prosthetic arthritis: report of a case treated with fluconazole and review of the literature. Am J Med. 1993;94:100–3.
Vasquez JC, Hart M, Denney CF, Pedowitz R, Ziegler EJ. Fungal arthritis of the knee caused by Candida parapsilosis in a kidney transplant recipient. J Clin Rheumatol. 2002;8:147–50.
Brooks DH, Pupparo F. Successful salvage of a primary total knee arthroplasty infected with Candida parapsilosis. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:707–12.
Fukasawa N, Shirakura K. Candida arthritis after total knee arthroplasty-a case of successful treatment without prosthesis removal. Acta Orthop Scand. 1997;68:306–7.
Paul J, White SH, Nicholls KM, Crook DW. Prosthetic joint infection due to Candida parapsilosis in the UK: case report and literature review. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992;11:847–9.
Wang J, Zhang Z, Zhang M, Yang B, Wang T, Sun X, Chen X, Zhang MY, Guo ZY, Jiang X. A rare primary Candida parapsilosis infection of the knee joint in a patient without predisposing factors: a case report. Medicine. 2019;98:e14327.
Anagnostakos K, Kelm J, Schmitt E, Jung J. Fungal periprosthetic hip and knee joint infections clinical experience with a 2-stage treatment protocol. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27:293–8.
Wada M, Baba H, Imura S. Prosthetic knee Candida parapsilosis infection. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:479–82.
Hennessy MJ. Infection of a total knee arthroplasty by Candida parapsilosis. A case report of successful treatment by joint reimplantation with a literature review. Am J Knee Surg. 1996;9:133–6.
Cushing RD, Fulgenzi WR. Synovial fluid levels of fluconazole in a patient with Candida parapsilosis prosthetic joint infection who had an excellent clinical response. J Arthroplasty. 1997;12:950.
MacGregor RR, Schimmer BM, Steinberg ME. Results of combined amphotericin B-5-fluorcytosine therapy for prosthetic knee joint infected with Candida parapsilosis. J Rheumatol. 1979;6:451–5.
Yang SH, Pao JL, Hang YS. Staged reimplantation of total knee arthroplasty after Candida infection. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16:529–32.
Ueng SW, Lee CY, Hu CC, Hsieh PH, Chang Y. What is the success of treatment of hip and knee candidal periprosthetic joint infection? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471:3002–9.
Lee YR, Kim HJ, Lee EJ, Sohn JW, Kim MJ, Yoon YK. Prosthetic joint infections caused by Candida species: a systematic review and a case series. Mycopathologia. 2019;184:23–33.
Zheng L, Ran X, Dai Y, Ran Y. Elbow malformation with osteoarthritis and bone destruction caused bychromoblastomycosis. Mycopathologia. 2019;184:459–60.
Azzam K, Parvizi J, Jungkind D, Hanssen A, Fehring T, Springer B, Bozic K, Della Valle C, Pulido L. Microbiological, clinical, and surgical features of fungal prosthetic joint infections: a multi-institutional experience. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:142–9.
Ramamohan N, Zeineh N, Grigoris P, Butcher I. Candida glabrata infection after total hip arthroplasty. J Infect. 2001;42:74–6.
Bouchara JP, Chaturvedi V. The curious case of “case report” of infections caused by human and animal fungal pathogens: an educational tool, an online archive, or a format in need of retooling. Mycopathologia. 2018;183:879–91.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the patient we reported for willingness to make his medical records public; in addition, we also thank the Laboratory of Anesthesiology, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University (Luzhou, China) for providing technical support for our DNA sequencing work; thanks to the Department of Laboratory, Southwest Medical University (Luzhou, China) for completing the Antifungal susceptibility testing.
Funding
This study has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was proved by the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University Ethics Committee. This material is original and has not been published in whole or in part elsewhere. All the authors confirm that the checklist for the submission of a case report to Mycopathologia published by Bouchara and Chaturvedi [30] has been completed.
Informed Consent
Informed written consent was obtained from the patient.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Handling Editor: Yuping Ran.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, G., Liu, H., Chen, M. et al. Ozone Treatment Unveils the Veil of Candida parapsilosis Infection in the Knee Joint: A Case Report and Literature Review. Mycopathologia 185, 545–554 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-020-00447-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-020-00447-8